Related Research Articles

Kofi Atta Annan was a Ghanaian diplomat who served as the seventh secretary-general of the United Nations from 1997 to 2006. Annan and the UN were the co-recipients of the 2001 Nobel Peace Prize. He was the founder and chairman of the Kofi Annan Foundation, as well as chairman of The Elders, an international organisation founded by Nelson Mandela.

The Somali Armed Forces are the military forces of the Federal Republic of Somalia. Headed by the president as commander-in-chief, they are constitutionally mandated to ensure the nation's sovereignty, independence and territorial integrity.
Foreign relations of Somalia are handled primarily by the President as the head of state, the Prime Minister as the head of government, and the Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Federal Government.

The United Nations (UN) is a diplomatic and political international organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and serve as a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations. It is the world's largest international organization. The UN is headquartered in New York City, and the UN has other offices in Geneva, Nairobi, Vienna, and The Hague, where the International Court of Justice is headquartered at the Peace Palace.

The University for Peace (UPEACE) is an international university and intergovernmental organization established as a treaty organisation by the United Nations General Assembly in 1980. The university offers postgraduate, doctoral, and executive programmes related to the study of peace and conflict, environment and development, and international law.

Somaliland, officially the Republic of Somaliland, is an unrecognised country in the Horn of Africa, recognised internationally as de jure part of Somalia. It is located in the southern coast of the Gulf of Aden and bordered by Djibouti to the northwest, Ethiopia to the south and west, and Somalia to the east. Its claimed territory has an area of 176,120 square kilometres (68,000 sq mi), with approximately 5.7 million residents as of 2021. The capital and largest city is Hargeisa. The Government of Somaliland regards itself as the successor state to British Somaliland, which, as the briefly independent State of Somaliland, united from 1960 to 1991 with the Trust Territory of Somaliland to form the Somali Republic.

The Uganda People's Defence Force (UPDF), previously known as the National Resistance Army, is the armed forces of Uganda. From 2007 to 2011, the International Institute for Strategic Studies estimated the UPDF had a total strength of 40,000–45,000, consisting of land forces and an air wing. Recruitment to the forces is done annually.

Mohammed Siad Barre was a Somali major general, politician and revolutionary who served as the third president of Somalia from 21 October 1969 to 26 January 1991.
The Atlantic Council is an American think tank in the field of international affairs, favoring Atlanticism, founded in 1961. It manages sixteen regional centers and functional programs related to international security and global economic prosperity. It is headquartered in Washington, D.C. It is a member of the Atlantic Treaty Association.

The United Nations Operation in Somalia II was the second phase of the United Nations intervention in Somalia and took place from March 1993 until March 1995, following the outbreak of the Somali Civil War in 1991. UNOSOM II carried on from the transitory United States-controlled (UN-sanctioned) Unified Task Force (UNITAF), which had been preceded by UNOSOM I. Notably, UNOSOM II embarked on a nation-building mission, diverging from its predecessors. As delineated in UNSCR 814, the operation's objectives were to aid in relief provision and economic rehabilitation, foster political reconciliation, and re-establish political and civil administrations across Somalia.

Kismayo is a port city in the southern Lower Juba province of Somalia. It is the commercial capital of the autonomous Jubaland region.

Jendayi Elizabeth Frazer is the former U.S. Assistant Secretary of State for African Affairs, heading the Bureau of African Affairs. She was a Distinguished Service Professor at Carnegie Mellon University's Heinz College and Department of Social and Decision Sciences.

The Somali Civil War is an ongoing civil war that is taking place in Somalia. It grew out of resistance to the military junta which was led by Siad Barre during the 1980s. From 1988 to 1990, the Somali Armed Forces began engaging in combat against various armed rebel groups, including the Somali Salvation Democratic Front in the northeast, the Somali National Movement in the northwest, and the United Somali Congress in the south. The clan-based armed opposition groups overthrew the Barre government in 1991.

The Unified Task Force (UNITAF) was a United States-led, United Nations-sanctioned multinational force which operated in Somalia from 5 December 1992 until 4 May 1993. A United States initiative, UNITAF was charged with carrying out United Nations Security Council Resolution 794 to create a protected environment for conducting humanitarian operations in the southern half of the country.
The Somali National Alliance was a major politico-military faction formed on 16 June 1992 by four different rebel groups that had been in opposition to the regime of former Somali President Mohamed Siad Barre. The SNA was the first major inter-clan and inter-factional political alliance and was considered to be among the most powerful factions of the Somali Civil War. The alliance would most notably face off against the second phase of the United Nations Operation in Somalia in the latter half of 1993.
Maritime security is an umbrella term informed to classify issues in the maritime domain that are often related to national security, marine environment, economic development, and human security. This includes the world's oceans but also regional seas, territorial waters, rivers and ports, where seas act as a “stage for geopolitical power projection, interstate warfare or militarized disputes, as a source of specific threats such as piracy, or as a connector between states that enables various phenomena from colonialism to globalization”. The theoretical concept of maritime security has evolved from a narrow perspective of national naval power projection towards a buzzword that incorporates many interconnected sub-fields. The definition of the term maritime security varies and while no internationally agreed definition exists, the term has often been used to describe both existing, and new regional and international challenges to the maritime domain. The buzzword character enables international actors to discuss these new challenges without the need to define every potentially contested aspect of it. Maritime security is of increasing concern to the global shipping industry, where there are a wide range of security threats and challenges. Some of the practical issues clustered under the term of maritime security include crimes such as piracy, armed robbery at sea, trafficking of people and illicit goods, illegal fishing or marine pollution. War, warlike activity, maritime terrorism and interstate rivalry are also maritime security concerns.

Ahmedou Ould-Abdallah is a Mauritanian diplomat who was a senior United Nations official.
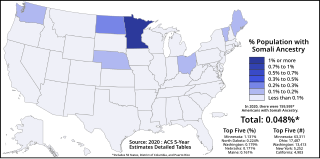
Somali Americans are Americans of Somali ancestry. The first ethnic Somalis to arrive in the U.S. were sailors who came in the 1920s from British Somaliland. They were followed by students pursuing higher studies in the 1960s and 1970s, by the late 1970s through the late 1980s and early 1990s more Somalis arrived. However, it was not until the mid and late 1990s when the civil war in Somalia broke out that the majority of Somalis arrived in the United States. The Somali community in the U.S. is now among the largest in the Somali diaspora.

Baledogle Airfield, also called Wanlaweyn Airstrip, is the largest military air base in Somalia, about 90 kilometers northwest of the capital, Mogadishu. The airfield was constructed in the 1970s for the Somali Air Force with assistance of the Soviet Union. It was later expanded on and modernized by the United States during the 2010s.

Somaliland and the United States do not have official diplomatic relations. While Somaliland operates a representative liaison office in Washington, D.C., it does not have formal diplomatic status under the provisions of the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations. Both countries do maintain contact as delegations from both sides have met in the past.
References
- ↑ Somalia Recent Economic and Political Developments Handbook Volume 1: Strategic Information and Developments. Washington, D.C.: International Business Publications. 2013. p. 60. ISBN 978-1-4330-6256-8.
- ↑ "January 2008". rulers.org. Retrieved 2023-05-12.
- ↑ Report of the Monitoring Group on Somalia pursuant to Security Council resolution 1811 (PDF). United Nations Security Council. 2008. p. 13. Retrieved May 12, 2023.
- ↑ Levy, Hernan; Malone, Patrick O. (1986). Transport Policy Issues in Sub-Saharan Africa (PDF). Washington, D.C.: World Bank. p. 37. Retrieved May 12, 2023.
- ↑ Summary of World Broadcasts: Non-Arab Africa, Issues 7658-7683. BBC. 1984. p. 3.
- ↑ Africa South of the Sahara. Taylor & Francis. 1997. p. 882. ISBN 978-1-85743-029-5.
- ↑ Country of Origin Information Report: Somalia (PDF). London: Home Office. 2006. p. 95. Retrieved May 12, 2023.
- ↑ "MP Osman Atto Detained and Released". Hiiraan Online . May 30, 2008. Retrieved 2023-05-12.