External links
| | This British Columbia politics-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| | This article relating to the Indigenous peoples of North America is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
The Musgamagw Tsawataineuk is a First Nations tribal council based in the Queen Charlotte Strait region around northern Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada.
The headquarters of the Musgamagw Tsawataineuk Tribal Council is in the community of Quinsam, British Columbia in Campbell River, but territories of the three member nations span the Mainland Inlets of the Broughton Archipelago just to the north of the mouth of Knight Inlet.
The Nuxalk Nation is the band government of the Nuxalk people of Bella Coola, British Columbia. It is a member of the Oweekeno-Kitasoo-Nuxalk Tribal Council, and until March 2008 was a member of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization. The population is 1,479.
A Tribal Council is an association of First Nations bands in Canada, generally along regional, ethnic or linguistic lines.
In Canada, an Indian band or band, sometimes referred to as a First Nation band or simply a First Nation, is the basic unit of government for those peoples subject to the Indian Act. Bands are typically small groups of people: the largest in the country, the Six Nations of the Grand River First Nation had 22,294 members in September 2005, and many have a membership below 100 people. Each First Nation is typically represented by a band council chaired by an elected chief, and sometimes also a hereditary chief. As of 2013, there were 614 bands in Canada. Membership in a band is controlled in one of two ways: for most bands, membership is obtained by becoming listed on the Indian Register maintained by the government. As of 2013, there were 253 First Nations which had their own membership criteria, so that not all Status Indians are members of a band.

Tseshaht First Nation is an amalgamation of many tribes up and down Alberni Inlet and in the Alberni Valley of central Vancouver Island in the Canadian province of British Columbia. They are a member of the Nuu-chah-nulth Tribal Council which includes all other Nuu-chah-nulth-aht peoples except the Pacheedaht First Nation.
Ḵwiḵwa̱sut'inux̱w Ha̱xwa'mis, formerly the Kwicksutaineuk-ah-kwa-mish First Nation is a First Nations band government based on northern Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada, in the Queen Charlotte Strait region. It is a member of the Musgamagw Tsawataineuk Tribal Council, along with the ‘Namgis First Nation and the Tsawataineuk First Nation. The Kwikwasut'inuxw and Haxwa'mis are two of the many subgroups of the peoples known as Kwakwaka'wakw, which means "speakers of Kwak'wala", their language, and were combined into one band by the Department of Indian and Northern Affairs.
The Tsawataineuk First Nation is a First Nations band government in the Queen Charlotte Strait region north of northern Vancouver Island in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It is a member of the Musgamagw Tsawataineuk Tribal Council, along with the Gwawaenuk and the Kwicksutaineuk-ah-kwa-mish First Nation.

The Canim Lake Band is a First Nations government of the Secwepemc (Shuswap) Nation, located in the Central Interior region of the Canadian province of British Columbia. Its main Indian reserve is located at Canim Lake, British Columbia, near 100 Mile House. It was created when the government of the then-Colony of British Columbia established an Indian Reserve system in the 1860s. It is a member government of the Northern Shuswap Tribal Council.
The Ktunaxa Nation or Ktunaxa Nation Council is a First Nations tribal council government comprising four Ktunaxa (Kutenai) bands in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It is one of three Kutenai governments, the others being the Kootenai Tribe of Idaho and the Confederated Salish and Kootenai Tribes in the United States.
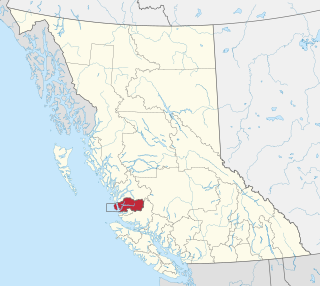
The Wuikinuxv Nation, also known as the Oweekeno Nation, is a First Nations band government whose traditional territory is the shores of Rivers Inlet and Owikeno Lake in the Central Coast region of the Canadian province of British Columbia, in the area south of Bella Bella and north of Queen Charlotte Strait. The Wuikinuxv people a.k.a. the Oweekeno people reside in the area of Rivers Inlet and Owikeno Lake, primarily at a village on the Wannock River. Substantial numbers of Wuikinuxv also reside away from the traditional territory in Port Hardy on Vancouver Island and in larger BC communities such as Campbell River, Vancouver and Victoria. Approximately 80 people reside at the village while overall membership was 283 in 2006, 194 of whom lived off-reserve.
The WuikinuxvIPA: [ʔuwik'inuxʷ],, also rendered Oweekano (Pre-1976); Oowekeeno (1976-2003) (variation: Oweekeno, Owekano, Oweekayno, Wuikenukv, Wikeno, Owikeno, Awikenox, and also known as the Rivers Inlet people, are an Indigenous First Nations people of the Central Coast region of the Canadian province of British Columbia, located around Rivers Inlet and Owikeno Lake, to the north of Queen Charlotte Strait. The Wuikinuxv people and their neighbours the Heiltsuk and Haisla peoples were in the past sometimes known incorrectly as the "Northern Kwakiutl".

The Homalco First Nation is a First Nations government located in Bute Inlet near the upper Sunshine Coast of British Columbia, Canada. The Homalco are also known, with their neighbours the Sliammon and Klahoose and the K'ómoks of nearby parts of Vancouver Island, as the Mainland Comox. Their ancestral tongue is the Comox language.
Malahat Nation is a Coast Salish First Nations community of W̱SÁNEĆ representing approximately 350 members with two reserve lands located on the western shore of Saanich Inlet, Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada.

The Tla'amin First Nation, formerly Sliammon Indian Band or Sliammon First Nation, is a First Nations self governing nation whose lands and traditional territories are located on the upper Sunshine Coast in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. The Tla'amin are closely related to the Klahoose and Homalco peoples and have shared their adjoining territories; formerly all three as well as K'omoks were grouped collectively as the Mainland Comox due to their shared language. They have been part of the Coast Salish indigenous peoples of the western coast of Canada since ancient times.

The ƛoʔos Klahoose are one of the three groups comprising the ʔayʔaǰuθəm Tla'Amin or Mainland Comox. The other two divisions of this once-populous group are the χʷɛmaɬku Homalco and Sliammon. The Klahoose, Homalco and Sliammon are, according to oral tradition, the descendants of the survivors of the Great Flood. The three groups were split by colonialism into different band councils but united historically as the Tla A'min, known as the Mainland Comox, and K’ómoks, the larger grouping of the Comox people, also known as the Island Comox and before the merger with the Laich-kwil-tach culture. Historically both groups are a subgroup of the Coast Salish though the K’ómoks name is from, and their language today, is the Lik'wala dialect of Kwak'wala. The ancestral tongue is the Comox language, though the Sahtloot/Island dialect is extinct.
Kingcome, also known as Okwunalis or Ukwana'lis is an unincorporated settlement in the Kingcome Inlet area of the Central Coast of British Columbia, Canada, located a few miles up the Kingcome River from the head of the inlet. Quaee Indian Reserve No. 7 is the Indian reserve containing the village.
The Kaska Dena Council is a tribal council formed of five band governments of the Kaska Dena people in northern British Columbia, Yukon Territory, and Northwest Territories, Canada.
The Kitasoo/Xaixais First Nation, also known as the Kitasoo/Xaixais Nation, is the band government of the First Nations people of Klemtu, British Columbia, Canada. The band comprises two ethnic groups who share an ancient alliance, the Kitasoo, a Tsimshian group, and the Xai'xais, a Heiltsuk group. The government is a member of the Oweekeno-Kitasoo-Nuxalk Tribal Council and a member of the Tsimshian First Nations treaty council.
The lack of treaties between the First Nations of British Columbia (BC) and the Canadian Crown, is a long-standing problem that has become a major issue in recent years. In 1763, the British Crown declared that only it could acquire land from First Nations through treaties. Historically only two treaties were signed with the First Nations of British Columbia. The first of which was the Douglas Treaties, negotiated by Sir James Douglas with the native people of southern Vancouver Island from 1850-1854. The second treaty, Treaty 8, signed in 1899 was part of the Numbered Treaties that were signed with First Nations across the Prairie regions. British Columbian Treaty 8 signatories are located in the Peace River Country or the far North East of BC. For over nine decades no more treaties were signed with First Nations of BC; many Native people wished to negotiate treaties, but successive BC provincial governments refused until the 1990s. A major development was the 1997 decision of the Supreme Court of Canada in the Delgamuukw v. British Columbia case that Aboriginal title still exists in British Columbia and that when dealing with Crown land, the government must consult with and may have to compensate First Nations whose rights are affected.
Alfred John Scow was the first Aboriginal person to graduate from a BC law school, the first Aboriginal lawyer called to the BC bar and the first Aboriginal legally trained judge appointed to the BC Provincial Court.
Bill Wilson is a hereditary chief, politician, and lawyer. He carries the Kwak’wala name Hemas Kla-Lee-Lee-Kla. Hemas means “the Chief who is always there to help” and Kla-Lee-Lee-Kla means “the first rank among the eagles.” He is a descendant of the Musgamgw Tsawataineuk and Laich-kwil-tach peoples, which are part of the Kwakwaka'wakw, also known as the Kwak’wala-speaking peoples.