
The Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina is the official military force of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The BiH armed forces were officially unified in 2005 and are composed of two founding armies: the Bosniak-Croat Army of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Bosnian Serbs' Army of Republika Srpska (VRS).

Naser Orić is a former Bosnian military officer who commanded Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) forces in the Srebrenica enclave in eastern Bosnia surrounded by Bosnian Serb forces, during the Bosnian War.
The Army of Republika Srpska, commonly referred to in English as the Bosnian Serb Army, was the military of Republika Srpska (RS), the self-proclaimed Serb secessionist republic, a territory within the newly independent Bosnia and Herzegovina, which it defied. Active during the Bosnian War (1992–95), it continued to exist as the armed forces of RS, one of two entities making up Bosnia and Herzegovina, until 2006 when it was integrated into the Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Forces of the VRS perpetrated the Srebrenica massacre in 1995.
Sefer Halilović is a former general and commanding officer of the Bosnian army during the 1992–95 war in Bosnia and Herzegovina. In 2001, he was indicted for war crimes by the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia and acquitted of all charges in 2005.

The Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, often referred to as Bosnian Army, was the military force of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It was established by the government of Bosnia and Herzegovina in 1992 following the outbreak of the Bosnian War. Following the end of the war, and the signing of the Dayton Peace Agreement in 1995, it was transformed into the Army of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The ARBiH was the only military force on the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina recognised as legal by other governments. Under the State Defense Reform Law the Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina were unified into a single structure, the Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina (OSBiH), making entity armies defunct.
Atif Dudaković is a former general in the Bosnian Army. During the Bosnian War, Dudaković was in command of the Bihać enclave, which was surrounded and besieged from 1991 to 1995, commanding the 5th Corps. After the war he became the general commander of the Army of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. In 2018, he was charged with war crimes.

The Croatian Defence Council was the official military formation of the Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia, an unrecognized entity that existed in Bosnia and Herzegovina between 1991 and 1996. The HVO was the main military force of Croats of Bosnia and Herzegovina.

Operation Sana was the final military offensive of the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina in western Bosnia and Herzegovina and the last major battle of the Bosnian War. It was launched from the area of Bihać on 13 September 1995, against the Army of Republika Srpska, and involved advances towards Bosanski Petrovac, Sanski Most and Bosanska Krupa. At the same time, the Croatian Army and the Croatian Defence Council were engaging the VRS in Operation Maestral 2 further to the southeast. After an initial 70-kilometre (43 mi) advance, VRS reinforcements managed to stop the ARBiH short of Sanski Most and Novi Grad, and reversed some of the ARBiH's territorial gains in a counterattack. After a part of the ARBiH 5th Corps was threatened with defeat around the town of Ključ, the ARBiH requested assistance from the HV.

The Croat–Bosniak War was a conflict between the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the self-proclaimed Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia, supported by Croatia, that lasted from 18 October 1992 to 23 February 1994. It is often referred to as a "war within a war" because it was part of the larger Bosnian War. In the beginning, Bosniaks and Croats fought in an alliance against the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) and the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS). By the end of 1992, however, tensions between Bosniaks and Croats increased. The first armed incidents between them occurred in October 1992 in central Bosnia. Their military alliance held out until early 1993 when their cooperation fell apart and the two former allies engaged in open conflict.

Rasim Delić was the chief of staff of the Bosnian army. He was a career officer in the Yugoslav army but left it during the breakup of Yugoslavia and was convicted of war crimes by the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia, being sentenced to 3 years in prison.
Enver Hadžihasanović is a former Bosnian chief of staff of the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina.

The Supreme Command of the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina was the supreme command of the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina and it was headquartered in the Presidency Building in Sarajevo.

Operation Vrbas '92 was a military offensive undertaken by the Army of Republika Srpska in June–October 1992, during the Bosnian War. The goal of the operation was the destruction of a salient around the central Bosnian town of Jajce, which was held by the Croatian Defence Council and the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The intensity of fighting varied considerably and involved several major VRS offensive efforts interspersed by relative lulls in fighting. Jajce fell to the VRS on 29 October 1992, and the town's capture was followed by the destruction of all its mosques and Roman Catholic churches.
The Leaders of the Yugoslav Wars listed below comprise the important political and military figures of the Yugoslav wars.

The Siege of Mostar was fought during the Bosnian War first in 1992 and then again later in 1993 to 1994. Initially lasting between April 1992 and June 1992, it involved the Croatian Defence Council (HVO) and the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) fighting against the Serb-dominated Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) after Bosnia and Herzegovina declared its independence from Yugoslavia. That phase ended in June 1992 after the success of Operation Jackal, launched by the Croatian Army (HV) and HVO. As a result of the first siege around 90,000 residents of Mostar fled and numerous religious buildings, cultural institutions, and bridges were damaged or destroyed.
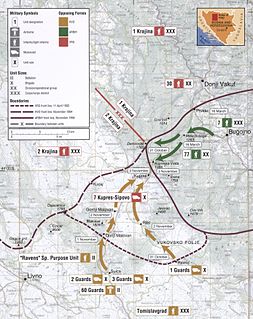
The Battle of Kupres was a battle of the Bosnian War, fought between the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) and the Croatian Defence Council (HVO) on one side and the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS) on the other from 20 October to 3 November 1994. It marks the first tangible evidence of the Bosniak–Croat alliance set out in the Washington Agreement of March 1994, brokered by the United States to end the Croat–Bosniak War fought between the ARBiH and the HVO in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The ARBiH and the HVO were not coordinated at first, rather they launched separate operations aimed at capture of Kupres.

Operation Una was a military offensive conducted by the Croatian Army against the Army of Republika Srpska in western Bosnia and Herzegovina on 18–19 September 1995, during the Bosnian War. The operation entailed a crossing of the Una and Sava rivers to establish bridgeheads at Novi Grad, Bosanska Dubica, Bosanska Kostajnica and opposite Jasenovac to allow for a subsequent advance towards Prijedor and Banja Luka.

Operation Southern Move was the final Croatian Army (HV) and Croatian Defence Council (HVO) offensive of the Bosnian War. It took place in western Bosnia and Herzegovina on 8–11 October 1995. Its goal was to help the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) whose positions around the town of Ključ, captured by them during Operation Sana, were endangered by a counteroffensive by the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS). The objectives of Operation Southern Move included the capture of the town of Mrkonjić Grad and positions on the Manjača Mountain which would allow the HV and the HVO to directly threaten Banja Luka, the largest city controlled by Bosnian Serbs. Finally, the offensive was also aimed at capturing the Bočac Hydroelectric Power Station, the last significant source of electricity under VRS control in western Bosnia and Herzegovina. The combined HV and HVO forces were under the overall command of HV Major General Ante Gotovina.
The Battle of Bugojno was fought between forces of the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) and the Croatian Defence Council (HVO) for control of the town and municipality of Bugojno in central Bosnia, from 18–28 July 1993. The area of Bugojno was under joint control of the ARBiH 307th Brigade and the HVO Eugen Kvaternik Brigade since the start of the Bosnian War. Violent incidents in Bugojno followed the escalation of the Croat-Bosniak War in adjacent municipalities throughout the 1st half of 1993. Bugojno was spared from fighting and the two local brigades were still formally allied by June 1993, at the time of an ARBiH offensive in central Bosnia.
Operation Vlašić was a military offensive undertaken by the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) during the Bosnian War, during which it captured Mount Vlašić in central Bosnia, which had been under the control of the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS) until then. The battle took place from March 20 to 24, 1995. The commander of the forces of the Army of BiH was General Mehmed Alagić. 100 square kilometres (39 sq mi) of territory was liberated in this action, among which was a relay.









