Myanmar | Syria |
|---|---|
Myanmar and Syria established diplomatic relations on 15 June 1972. [1] Myanmar has a non resident ambassador in Cairo.
Myanmar | Syria |
|---|---|
Myanmar and Syria established diplomatic relations on 15 June 1972. [1] Myanmar has a non resident ambassador in Cairo.
The Syrian Arab Republic was a supporter of the Than Shwe government and was among 25 countries to vote against condemning the Burmese government in 2008. [2]
Syria was the only Islamic majority country to vote against condemning Myanmar during the Rohingya crisis. [3]
Myanmar is considered a friendly country to the Syrian Arab Republic. On 76th anniversary of Independence Day of Syria, Assad received a congratulations from Chairman of the State Administration Council of Myanmar Min Aung Hlaing. [4]
Both countries have supported the Russian Invasion of Ukraine. [5] [6] [7]

In November 1975, Comoros became the 143rd member of the United Nations. The new nation was defined as consisting of the entire archipelago, despite the fact that France maintains control over Mayotte.

Kenya maintains relations with various countries around the world. Its closest ties are with its fellow Swahili-speaking neighbors in the African Great Lakes region. Swahili speaking neighbours mainly include countries in the East African Community such as Burundi, the DRC, Rwanda, South Sudan, Tanzania and Uganda.

Morocco is a member of the United Nations and belongs to the African Union, Arab League, Arab Maghreb Union (UMA), Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), the Non-Aligned Movement and the Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD). Morocco's relationships vary greatly between African, Arab, and Western states. Morocco has had strong ties with the West in order to gain economic and political benefits. France and Spain remain the primary trade partners, as well as the primary creditors and foreign investors in Morocco. From the total foreign investments in Morocco, the European Union invests approximately 73.5%, whereas the Arab world invests only 19.3%. As of 2009, many countries from the Persian Gulf and Maghreb regions are also becoming more involved in large-scale development projects in Morocco.

Foreign relations of Qatar is conducted through its Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Arab states were among the first to recognize Qatar, and the country gained admittance to the United Nations and the Arab League after achieving independence in 1971. The country was an early member of OPEC and a founding member of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). Diplomatic missions to Qatar are based in its capital, Doha.

Ensuring national security, increasing influence among its Arab neighbours and securing the return of the Golan Heights, have been the primary goals of the Syrian Arab Republic's foreign policy. At many points in its history, Syria has seen tension with its neighbours, such as Turkey, Israel, Jordan, Iraq, and Lebanon. Syria enjoyed an improvement in relations with several of the states in its region in the 21st century, prior to the Arab Spring and the Syrian Civil War.

Uganda has formal diplomatic relations with many countries, some accredited. Since the colonial era and after independence Uganda has grown to be one of the most important African countries. Uganda has diplomatic relations with many countries throughout Africa, the Americas, Asia, Europe and Oceania. Uganda is a member of the United Nations and the Commonwealth of Nations since 1962.

Since its independence from France in 1962, Algeria has pursued an activist foreign policy. In the 1960s and 1970s, Algeria was noted for its support of Third World policies and independence movements. Since its independence, Algeria has been a member of the Arab League, the African Union and of the United Nations.

Bashar al-Assad is a Syrian politician who is the current and 19th president of Syria since 17 July 2000. In addition, he is the commander-in-chief of the Syrian Armed Forces and the secretary-general of the Central Command of the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party, which nominally espouses a neo-Ba'athist ideology. His father and predecessor was General Hafiz al-Assad, whose presidency between 1971 and 2000 marked the transfiguration of Syria from a republican state into a dynastic dictatorship tightly controlled by an Alawite-dominated elite composed of the armed forces and the Mukhabarat, who are loyal to the al-Assad family.

The foreign relations of the Islamic Republic of Mauritania have, since 1960, been dominated by the issues of the Spanish Sahara and the recognition of its independence by its neighbours, particularly Morocco. Mauritania's foreign relations are handled by the Minister of Foreign Affairs and Cooperation, who is currently Mohamed Salem Ould Merzoug.

Russia–Syria relations are the bilateral relations between Russia and Syria. Russia has an embassy in Damascus and Syria has an embassy in Moscow. Russia enjoys a historically strong, stable, and friendly relationship with Syria, as it did until the Arab Spring with most of the Arab countries. Russia's only Mediterranean naval base for its Black Sea Fleet is located in the Syrian port of Tartus.

Iraq–Syria relations are the bilateral/diplomatic relations between the sovereign states of Iraq and Syria. Both nations are neighbours and they share the Iraq–Syria border. Relations are marked by long-shared cultural and political links, as well as former regional rivalry. The two countries took their present form after the Sykes–Picot Agreement to dismember the Ottoman Empire into British and French spheres of influence after World War I.

From April 2014 until September 2022, the Donetsk People's Republic (DPR) and the Luhansk People's Republic (LPR) were two pro-Russian separatist states established in the Donbas, a historical region in easternmost Ukraine. Escalating tensions between pro-Russian separatists and the Ukrainian government, which regarded the two states' secession as illegal, led to the protracted War in Donbas. While the DPR and the LPR remained unrecognized by the international community, they covertly received a substantial amount of financial and military support from neighbouring Russia.

Palestine–Ukraine relations are bilateral relations between the State of Palestine and Ukraine. The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic recognized Palestinian independence on 19 November 1988. Palestine recognized Ukraine as a sovereign state in February 1992. On 2 November 2001, the two countries established diplomatic relations and the Palestinian embassy opened the same day. Ukraine has supported UN resolutions against Israel's occupation of the Palestinian territories.

Eritrea and Russia relations are diplomatic relations between the State of Eritrea and the Russian Federation. Russia has an embassy in Asmara and Eritrea has its own in Moscow.

Ukrainian–Venezualan relations are bilateral diplomatic relations between Ukraine and Venezuela, which were established on 9 January 1992 with the recognition of Ukraine's independence by Venezuela.
Belarus and Sudan established diplomatic relations on 15 July 1999.
Belarus–Syria relations refer to the relationship between Belarus and the Syrian Arab Republic. Both countries established diplomatic relations in 1992. Belarus has an embassy in Damascus and Syria has an embassy in Minsk.
Cuba–Syria relations are bilateral relations between Cuba and the Syrian Arab Republic. Diplomatic relations were established on 11 August 1965. Syria has an embassy in Havana. Cuba has an embassy in Damascus.
Belarus and Myanmar established diplomatic relations on 22 September 2000.
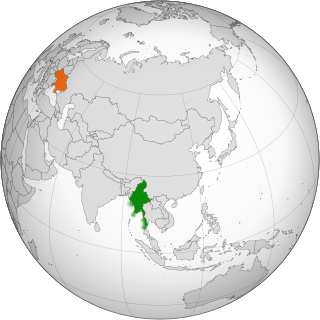
Myanmar and Ukraine established diplomatic relations on 19 January 1999.