
Myringomycosis is a fungal infection of the tympanic membrane. It is caused by the presence of the fungus Aspergillus nigricans or flavescens . [1]

Myringomycosis is a fungal infection of the tympanic membrane. It is caused by the presence of the fungus Aspergillus nigricans or flavescens . [1]
Antisemitism is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. This sentiment is a form of racism, and a person who harbours it is called an antisemite. Though antisemitism is overwhelmingly perpetrated by non-Jews, it may occasionally be perpetrated by Jews in a phenomenon known as auto-antisemitism. Primarily, antisemitic tendencies may be motivated by negative sentiment towards Jews as a people or by negative sentiment towards Jews with regard to Judaism. In the former case, usually presented as racial antisemitism, a person's hostility is driven by the belief that Jews constitute a distinct race with inherent traits or characteristics that are repulsive or inferior to the preferred traits or characteristics within that person's society. In the latter case, known as religious antisemitism, a person's hostility is driven by their religion's perception of Jews and Judaism, typically encompassing doctrines of supersession that expect or demand Jews to turn away from Judaism and submit to the religion presenting itself as Judaism's successor faith — this is a common theme within the other Abrahamic religions. The development of racial and religious antisemitism has historically been encouraged by anti-Judaism, though the concept itself is distinct from antisemitism.
Hinduism is an Indian religion or dharma, a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with approximately 1.2 billion followers, or 15% of the global population, known as Hindus. The word Hindu is an exonym and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, it has also been described as sanātana dharma, a modern usage, based on the belief that its origins lie beyond human history, as revealed in the Hindu texts. Another endonym is Vaidika Dharma, the dharma related to the Vedas.

India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area; the most populous country as of June 2023; and from the time of its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia.

The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a numeric commercial book identifier that is intended to be unique. Publishers purchase or receive ISBNs from an affiliate of the International ISBN Agency.

Muhammad was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monotheistic teachings of Adam, Abraham, Moses, Jesus, and other prophets. He is believed to be the Seal of the Prophets within Islam, with the Quran as well as his teachings and practices forming the basis for Islamic religious belief.

Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist and political ethicist who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule. He inspired movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific Mahātmā, first applied to him in South Africa in 1914, is now used throughout the world.

The Ottoman Empire, historically and colloquially known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. The empire also controlled an eastern region of Central Europe from the 16th to the late 17th century.

Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of 313,931 km2 (121,209 sq mi). Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous member state of the European Union. Warsaw is the nation's capital and largest metropolis. Other major cities include Kraków, Gdańsk, Wrocław, Katowice, Łódź, Poznań, Szczecin and Lublin.

The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. In the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of 7,641 islands which are broadly categorized in three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. The Philippines is bounded by the South China Sea to the west, the Philippine Sea to the east, and the Celebes Sea to the south. It shares maritime borders with Taiwan to the north, Japan to the northeast, Palau to the east and southeast, Indonesia to the south, Malaysia to the southwest, Vietnam to the west, and China to the northwest. It is the world's twelfth-most-populous country, with diverse ethnicities and cultures. Manila is the country's capital, and its most populated city is Quezon City; both are within Metro Manila.

Sex is the trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing organism produces male or female gametes. Male organisms produce small mobile gametes, while female organisms produce larger, non-mobile gametes. Organisms that produce both types of gametes are called hermaphrodites. During sexual reproduction, male and female gametes fuse to form zygotes, which develop into offspring that inherit traits from each parent.

The Six-Day War or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states from 5 to 10 June 1967.

William Shakespeare was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon". His extant works, including collaborations, consist of some 39 plays, 154 sonnets, three long narrative poems, and a few other verses, some of uncertain authorship. His plays have been translated into every major living language and are performed more often than those of any other playwright. Shakespeare remains arguably the most influential writer in the English language, and his works continue to be studied and reinterpreted.

World War II or the Second World War was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945. The vast majority of the world's countries, including all the great powers, fought as part of two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis. Many participants threw their economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind this total war, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and delivery of the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. It was by far the deadliest conflict in history, resulting in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly civilians. Millions died due to genocides, including the Holocaust, as well as starvation, massacres, and disease. In the wake of Axis defeat, Germany, Austria and Japan were occupied, and war crimes tribunals were conducted against German and Japanese leaders.

Jesus, also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many other names and titles, was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religion. Most Christians believe Jesus to be the incarnation of God the Son and the awaited Jewish messiah, the Christ that is prophesied in the Hebrew Bible.
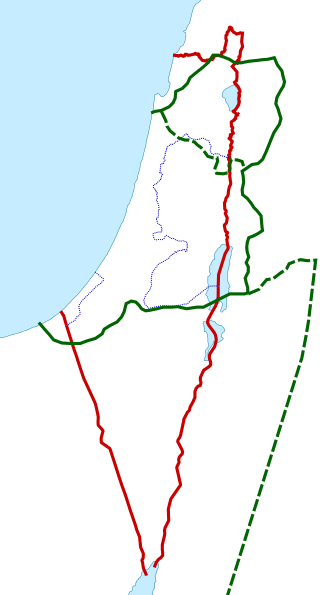
Palestine is a geographical region in West Asia. Situated in the Southern Levant, it is usually considered to include Israel and the State of Palestine, though some definitions also include parts of northwestern Jordan. Other historical names for the region include Canaan, the Promised Land, the Land of Israel, or the Holy Land.

Adolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Germany from 1933 until his suicide in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and then taking the title of Führer und Reichskanzler in 1934. During his dictatorship, he initiated World War II in Europe by invading Poland on 1 September 1939. He was closely involved in military operations throughout the war and was central to the perpetration of the Holocaust, the genocide of about six million Jews and millions of other victims.

The United States of America (USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S.) or simply America, is a country primarily located in North America and consisting of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, and nine Minor Outlying Islands. It includes 326 Indian reservations. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third-most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C., and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City.

World War I (WWI), also known as the First World War, was a global conflict fought between two coalitions, the Allied Powers and the Central Powers. Fighting took place throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia.

Islam is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centered on the Quran and the teachings of Muhammad, the religion's founder. Adherents of Islam, called Muslims, number approximately 1.9 billion globally and are the world's second-largest religious population after Christians.

The Jews or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group originating from the ancient Hebrews or Israelites, and whose traditional religion is Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, religion and community are highly interrelated, as Judaism is an ethnic religion, although not all ethnic Jews practice it. Despite this, most religious Jews regard individuals who have formally converted to Judaism as part of the community.