Related Research Articles

Endocrinology is a branch of biology and medicine dealing with the endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions known as hormones. It is also concerned with the integration of developmental events proliferation, growth, and differentiation, and the psychological or behavioral activities of metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, sleep, digestion, respiration, excretion, mood, stress, lactation, movement, reproduction, and sensory perception caused by hormones. Specializations include behavioral endocrinology and comparative endocrinology.

The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems.

Gigantism, also known as giantism, is a condition characterized by excessive growth and height significantly above average. In humans, this condition is caused by over-production of growth hormone in childhood.

Ghrelin is a hormone primarily produced by enteroendocrine cells of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the stomach, and is often called a "hunger hormone" because it increases the drive to eat. Blood levels of ghrelin are highest before meals when hungry, returning to lower levels after mealtimes. Ghrelin may help prepare for food intake by increasing gastric motility and stimulating the secretion of gastric acid.

Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas. Pituitary adenomas represent from 10% to 25% of all intracranial neoplasms and the estimated prevalence rate in the general population is approximately 17%.

Motilin is a 22-amino acid polypeptide hormone in the motilin family that, in humans, is encoded by the MLN gene.

Adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency is a rare disorder characterized by secondary adrenal insufficiency with minimal or no cortisol production and normal pituitary hormone secretion apart from ACTH. ACTH deficiency may be congenital or acquired, and its symptoms are clinically similar to those of glucocorticoid deficiency. Symptoms consist of weight loss, diminished appetite, muscle weakness, nausea, vomiting, and hypotension. Low blood sugar and hyponatremia are possible; however, blood potassium levels typically remain normal because affected patients are deficient in glucocorticoids rather than mineralocorticoids because of their intact renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. ACTH may be undetectable in blood tests, and cortisol is abnormally low. Glucocorticoid replacement therapy is required. With the exception of stressful situations, some patients with mild or nearly asymptomatic disease may not require glucocorticoid replacement therapy. As of 2008 about two hundred cases have been described in the literature.
The Endocrine Society is a professional, international medical organization in the field of endocrinology and metabolism, founded in 1916 as The Association for the Study of Internal Secretions. The official name of the organization was changed to the Endocrine Society on January 1, 1952. It is a leading organization in the field and publishes four leading journals. It has more than 18,000 members from over 120 countries in medicine, molecular and cellular biology, biochemistry, physiology, genetics, immunology, education, industry, and allied health. The Society's mission is: "to advance excellence in endocrinology and promote its essential and integrative role in scientific discovery, medical practice, and human health."
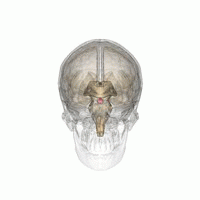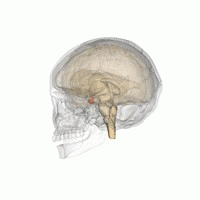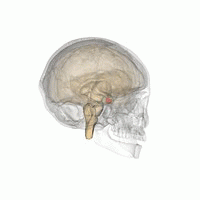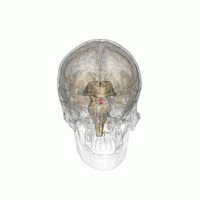
Hyperpituitarism is a condition due to the primary hypersecretion of pituitary hormones; it typically results from a pituitary adenoma. In children with hyperpituitarism, disruption of growth regulation is rare, either because of hormone hypersecretion or because of manifestations caused by local compression of the adenoma.

Menin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEN1 gene. Menin is a putative tumor suppressor associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 and has autosomal dominant inheritance. Variations in the MEN1 gene can cause pituitary adenomas, hyperparathyroidism, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, gastrinoma, and adrenocortical cancers.

George P. Chrousos is professor of Pediatrics and Endocrinology Emeritus and former chairman of the Department of Pediatrics at the Athens University Medical School, Greece. Earlier he was senior investigator, director of the Pediatric Endocrinology Section and Training Program, and chief of the Pediatric and Reproductive Endocrinology Branch of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD), National Institutes of Health (NIH). He is also clinical professor of Pediatrics, Physiology and Biophysics at Georgetown University Medical School and distinguished visiting scientist, NICHD, NIH. Dr. Chrousos was the first general director of the Foundation of Biomedical Research of the Academy of Athens (2001–2002). He holds the UNESCO Chair on Adolescent Health Care, while he held the 2011 John Kluge Chair in Technology and Society, Library of Congress, Washington, D.C.

The growth-hormone-releasing hormone receptor (GHRHR) is a G-protein-coupled receptor that binds growth hormone-releasing hormone. The GHRHR activates a Gs protein that causes a cascade of cAMP via adenylate cyclase. GHRHR is distinct from the growth hormone secretagogue receptor, where growth hormone releasing peptides act to release growth hormone.
Cyril Y. Bowers, M.D., emeritus professor of medicine at Tulane University School of Medicine, attended medical school at the University of Oregon and did an internship at the University of Washington. He then studied biochemistry at Cornell University and attended the postgraduate school of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. From 1961-2004 he was the director of the Section of Endocrinology & Metabolism in the department of medicine at Tulane University School of Medicine. Bowers has served on the editorial board of several endocrine journals, was a member of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Study Section for eight years and has written over 400 articles in peer-reviewed journals, including chapters in books and over 200 abstracts.

Dr. Hossein Gharib is a physician who specializes in thyroid disorders. He was born in Tehran, Iran, on February 2, 1940, and is a consulting physician at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
Maria Iandolo New is a professor of Pediatrics, Genomics and Genetics at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. She is an expert in congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), a genetic condition affecting the adrenal gland that can affect sexual development.

Matthias H. Tschöp is a German physician and scientist. He is the chief executive officer and scientific director of Helmholtz Zentrum München, German Research Center for Environmental Health. He is also Alexander von Humboldt Professor and chair of metabolic diseases at Technical University of Munich and serves as an adjunct professor at Yale University.

Michael O. Thorner is David C. Harrison Professor Emeritus of Internal Medicine at the University of Virginia specializing in endocrinology and metabolism. He was previously the chief of the division of endocrinology and metabolism and the chair of the department of internal medicine.

Teresa Kaye Woodruff is an American medical researcher in human reproduction and oncology, with a focus on ovarian biology, endocrinology, and women's health. She joined Michigan State University as the Provost and Executive Vice President for Academic Affairs in August 2020. Woodruff served as the interim President of Michigan State University from November 4, 2022 to March 4, 2024, following the resignation of Samuel L. Stanley. She was previously the Thomas J. Watkins Memorial Professor and Vice Chair for Research and Chief of the Division of Reproductive Science in Medicine in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at the Feinberg School of Medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago, Illinois.

Sheue-yann Cheng is an American molecular geneticist who pioneered the development of mouse models to understand the molecular basis of diseases due to mutations of thyroid hormone receptors. Cheng is a senior investigator at the National Cancer Institute and chief of the gene regulation section.
Adriana G. Ioachimescu is a Romanian-American neuroendocrinologist and professor at the Medical College of Wisconsin in the Division of Endocrinology and Molecular Medicine and the Director for Pituitary and Adrenal Disease Program, where she joined in 2023. She was born in Bucharest, Romania. Her research focuses on pituitary disorders and developing therapies for conditions like Cushing’s syndrome.
References
- 1 2 3 "Genetic aspects of pituitary tumors: A conversation with Márta Korbonits, MD, PhD, DSc". www.healio.com. Retrieved 2023-12-21.
- 1 2 "MEET YOUR NEW PRESIDENT | Society for Endocrinology". www.endocrinology.org. Retrieved 2023-12-23.
- ↑ "Márta Korbonits | Society for Endocrinology". www.endocrinology.org. Retrieved 2023-12-23.
- ↑ "Acromegaly: 'Giant gene' bond forged between US and Mid Ulster". BBC News. 2022-06-08. Retrieved 2023-12-23.
- ↑ "Scientists testing for Northern Ireland 'giant gene'". BBC News. 2013-02-04. Retrieved 2023-12-23.
- ↑ "Delbert A. Fisher Research Scholar Award/Clark T. Sawin Memorial History of Endocrinology Lecturer". www.endocrine.org. Retrieved 2023-12-21.
- ↑ "Excellence in neuroendocrinology: Márta Korbonits receives the international Rolf Gaillard Prize". www.qmul.ac.uk. 2022-09-07. Retrieved 2023-12-23.
- ↑ "Professor Márta Korbonits honoured with 2023 Laureate Award from Endocrine Society". Queen Mary University of London. 2023-06-19. Retrieved 2023-12-21.