Related Research Articles

In marketing, a product is an object, or system, or service made available for consumer use as of the consumer demand; it is anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy the desire or need of a customer. In retailing, products are often referred to as merchandise, and in manufacturing, products are bought as raw materials and then sold as finished goods. A service is also regarded as a type of product.
Procurement is the process of locating and agreeing to terms and purchasing goods, services, or other works from an external source, often with the use of a tendering or competitive bidding process. The term may also refer to a contractual obligation to "procure", i.e. to "ensure" that something is done. When a government agency buys goods or services through this practice, it is referred to as government procurement or public procurement.
Business software is any software or set of computer programs used by business users to perform various business functions. These business applications are used to increase productivity, measure productivity, and perform other business functions accurately.
The Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System, also known as the Harmonized System (HS) of tariff nomenclature is an internationally standardized system of names and numbers to classify traded products. It came into effect in 1988 and has since been developed and maintained by the World Customs Organization (WCO), an independent intergovernmental organization based in Brussels, Belgium.
The United Nations Standard Products and Services Code (UNSPSC) is a taxonomy of products and services for use in eCommerce. It is a four-level hierarchy coded as an eight-digit number, with an optional fifth level adding two more digits.
Purchasing is the procurement process a business or organization uses to acquire goods or services to accomplish its goals. Although there are several organizations that attempt to set standards in the purchasing process, processes can vary greatly between organizations.
E-procurement is a collective term used to refer to a range of technologies which can be used to automate the internal and external processes associated with procurement, strategic sourcing and purchasing.
Commercial-off-the-shelf or commercially available off-the-shelf (COTS) products are packaged or canned (ready-made) hardware or software, which are adapted aftermarket to the needs of the purchasing organization, rather than the commissioning of custom-made, or bespoke, solutions. A related term, Mil-COTS, refers to COTS products for use by the U.S. military.
Web analytics is the measurement, collection, analysis, and reporting of web data to understand and optimize web usage. Web analytics is not just a process for measuring web traffic but can be used as a tool for business and market research and assess and improve website effectiveness. Web analytics applications can also help companies measure the results of traditional print or broadcast advertising campaigns. It can be used to estimate how traffic to a website changes after launching a new advertising campaign. Web analytics provides information about the number of visitors to a website and the number of page views, or creates user behavior profiles. It helps gauge traffic and popularity trends, which is useful for market research.
The Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) is the principal set of rules regarding Government procurement in the United States, and is codified at Chapter 1 of Title 48 of the Code of Federal Regulations, 48 CFR 1. It covers many of the contracts issued by the US military and NASA, as well as US civilian federal agencies.
The Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) system provides a reference method for publicly known information-security vulnerabilities and exposures. The United States' National Cybersecurity FFRDC, operated by The MITRE Corporation, maintains the system, with funding from the US National Cyber Security Division of the US Department of Homeland Security. The system was officially launched for the public in September 1999.
Procurement software refers to a range of business software designed to streamline and automate purchasing processes for businesses and organizations. By managing information flows and transactions between procuring entities, suppliers, and partners, procurement software aims to cut costs, improve efficiency, and boost organizational performance.
A request for quotation (RfQ) is a business process in which a company or public entity requests a quote from a supplier for the purchase of specific products or services. RfQ generally means the same thing as Call for bids (CfB) and Invitation for bid (IfB).
Global sourcing is the practice of sourcing from the global market for goods and services across geopolitical boundaries. Global sourcing often aims to exploit global efficiencies in the delivery of a product or service. These efficiencies include low cost skilled labor, low cost raw material, extreme international competition, new technology and other economic factors like tax breaks and low trade tariffs. Common examples of globally sourced products or services include labor-intensive manufactured products produced using low-cost Chinese labor, call centers staffed with low-cost English speaking workers in the Philippines, India and Pakistan, and IT work performed by low-cost programmers in India, Pakistan and Eastern Europe. While these are examples of low-cost country sourcing, global sourcing is not limited to low-cost countries.
A vendor management system (VMS) is an Internet-enabled, often Web-based application that acts as a mechanism for business to manage and procure staffing services – temporary, and, in some cases, permanent placement services – as well as outside contract or contingent labor. Typical features of a VMS application include order distribution, consolidated billing and significant enhancements in reporting capability that outperforms manual systems and processes.
A specification often refers to a set of documented requirements to be satisfied by a material, design, product, or service. A specification is often a type of technical standard.
Spend analysis or spend analytics is the process of collecting, cleansing, classifying and analyzing expenditure data with the purpose of decreasing procurement costs, improving efficiency, and monitoring controls and compliance. It can also be leveraged in other areas of business such as inventory management, contract management, complex sourcing, supplier management, budgeting, planning, and product development.
Invoice Processing : involves the handling of incoming invoices from arrival to payment. Invoices have many variations and types. In general, invoices are grouped into two types:
Inventory management software is a software system for tracking inventory levels, orders, sales and deliveries. It can also be used in the manufacturing industry to create a work order, bill of materials and other production-related documents. Companies use inventory management software to avoid product overstock and outages. It is a tool for organizing inventory data that before was generally stored in hard-copy form or in spreadsheets.
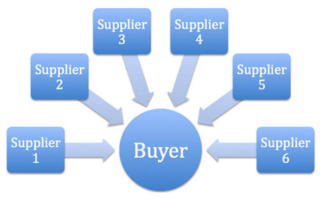
A reverse auction is a type of auction in which the traditional roles of buyer and seller are reversed. Thus, there is one buyer and many potential sellers. In an ordinary auction also known as a forward auction, buyers compete to obtain goods or services by offering increasingly higher prices. In contrast, in a reverse auction, the sellers compete to obtain business from the buyer and prices will typically decrease as the sellers underbid each other.
References
- ↑ NIGP Code sample, NIGP Code sample
- ↑ Walters, John (2009-04-11). "Planting the seeds for a green Code". Planting the seeds for a green Code. Archived from the original on 2009-04-11. Retrieved 2019-07-06.