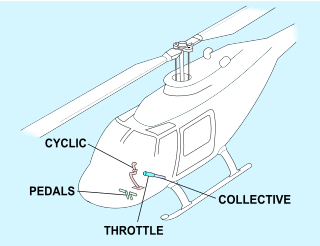
Helicopter flight controls are used to achieve and maintain controlled aerodynamic helicopter flight. Changes to the aircraft flight control system transmit mechanically to the rotor, producing aerodynamic effects on the rotor blades that make the helicopter move in a desired way. To tilt forward and back (pitch) or sideways (roll) requires that the controls alter the angle of attack of the main rotor blades cyclically during rotation, creating differing amounts of lift at different points in the cycle. To increase or decrease overall lift requires that the controls alter the angle of attack for all blades collectively by equal amounts at the same time, resulting in ascent, descent, acceleration and deceleration.

The tail rotor is a smaller rotor mounted vertically or near-vertically at the tail of a traditional single-rotor helicopter, where it rotates to generate a propeller-like horizontal thrust in the same direction as the main rotor's rotation. The tail rotor's position and distance from the helicopter's center of mass allow it to develop enough thrust leverage to counter the reactional torque exerted on the fuselage by the spinning of the main rotor. Without the tail rotor or other anti-torque mechanisms, the helicopter would be constantly spinning in the opposite direction of the main rotor when flying.

On a helicopter, the main rotor or rotor system is the combination of several rotary wings with a control system, that generates the aerodynamic lift force that supports the weight of the helicopter, and the thrust that counteracts aerodynamic drag in forward flight. Each main rotor is mounted on a vertical mast over the top of the helicopter, as opposed to a helicopter tail rotor, which connects through a combination of drive shaft(s) and gearboxes along the tail boom. The blade pitch is typically controlled by the pilot using the helicopter flight controls. Helicopters are one example of rotary-wing aircraft (rotorcraft). The name is derived from the Greek words helix, helik-, meaning spiral; and pteron meaning wing.

A rotary-wing aircraft, rotorwing aircraft or rotorcraft is a heavier-than-air aircraft with rotary wings that spin around a vertical mast to generate lift. The assembly of several rotor blades mounted on a single mast is referred to as a rotor. The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) defines a rotorcraft as "supported in flight by the reactions of the air on one or more rotors".

MD Helicopters, LLC. is an American aerospace manufacturer. It produces light utility helicopters for commercial and military use. The company was a subsidiary of Hughes Aircraft until 1984, when McDonnell Douglas acquired it and renamed it McDonnell Douglas Helicopter Systems. It later became MD Helicopters in 1999 after McDonnell Douglas merged with Boeing.

The MD Helicopters MD 500 series is an American family of light utility civilian and military helicopters. The MD 500 was developed from the Hughes 500, a civilian version of the US Army's OH-6A Cayuse/Loach. The series currently includes the MD 500E, MD 520N, and MD 530F.

The MD Helicopters MD Explorer is a light twin-engined utility helicopter designed and initially produced by the American rotorcraft specialist McDonnell Douglas Helicopter Systems.

A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft and many forms of short take-off and landing (STOL) or short take-off and vertical landing (STOVL) aircraft cannot perform without a runway.

The MD Helicopters MD 600N is a light utility civilian helicopter designed in the United States. It is a stretched eight-seat development of the five-seat MD 520N helicopter.

A powered lift aircraft takes off and lands vertically under engine power but uses a fixed wing for horizontal flight. Like helicopters, these aircraft do not need a long runway to take off and land, but they have a speed and performance similar to standard fixed-wing aircraft in combat or other situations.

The Cierva W.9 was a British 1940s experimental helicopter with a three-blade tilting-hub controlled main rotor, and torque compensation achieved using a jet of air discharged from the rear port side of the fuselage. The design was not further developed into production, and the prototype crashed in 1946.
The Fiat Model 7002 was a 1960s Italian general-purpose helicopter with a tip jet driven rotor built by Fiat Aviazione. Only one aircraft was built.

The Sud-Ouest SO.1221 Djinn is a French two-seat light helicopter designed and manufactured by aircraft manufacturer Sud-Ouest (SNCASO), which was later merged into Sud Aviation. It was the first production French helicopter, as well as being one of the first practical European helicopters to be produced. The Djinn was also the first rotorcraft to harness tip-jet propulsion to enter production, and the first production turbine powered helicopter.

A monocopter or gyropter is a rotorcraft that uses a single rotating blade. The concept is similar to the whirling helicopter seeds that fall from some trees. The name gyropter is sometimes applied to monocopters in which the entire aircraft rotates about its center of mass as it flies. The name "monocopter" has also been applied to the personal jet pack constructed by Andreas Petzoldt.

The Bell 30 is the prototype for the first commercial helicopter, and the first helicopter built by the Bell Aircraft Company. Designed by Arthur M. Young, the type served as a demonstration testbed for the successful Bell 47.
The Nord 1750 Norelfe was a 1950s French three-seat helicopter built by Nord Aviation and designed by Jean Cantinieau.

The Dornier Do 32E was a simple, collapsible one-man helicopter, designed for military use in Germany in the 1960s. Despite initial hopes of large orders and some proposed civilian roles, only three flew.

The Matra-Cantinieau MC-101 was an early 1950s French experimental two seat helicopter of conventional tail rotor configuration but with its engine mounted close to the main rotor, above the seating.
The Nord 1700 Norélic or SNCAN N.1700 Norélic was a French helicopter with several novel control features. Only one prototype was built, though it was intended to lead to series production.
The SNCASE SE-3110 or Sud-Est SE-3110 was a French two seat experimental helicopter with unusual twin, angled tail rotors, first flown in 1950. After brief tests SNCASE decided to concentrate on a closely related but single-tail-rotor design.





















