
Biogas is a gaseous renewable energy source produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste, wastewater, and food waste. Biogas is produced by anaerobic digestion with anaerobic organisms or methanogens inside an anaerobic digester, biodigester or a bioreactor. The gas composition is primarily methane and carbon dioxide and may have small amounts of hydrogen sulfide, moisture and siloxanes. The methane can be combusted or oxidized with oxygen. This energy release allows biogas to be used as a fuel; it can be used in fuel cells and for heating purpose, such as in cooking. It can also be used in a gas engine to convert the energy in the gas into electricity and heat.
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide, in various ratios. The gas often contains some carbon dioxide and methane. It is principally used for producing ammonia or methanol. Syngas is combustible and can be used as a fuel. Historically, it has been used as a replacement for gasoline, when gasoline supply has been limited; for example, wood gas was used to power cars in Europe during WWII.
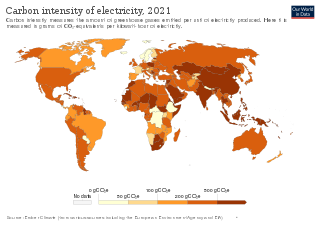
An emission intensity is the emission rate of a given pollutant relative to the intensity of a specific activity, or an industrial production process; for example grams of carbon dioxide released per megajoule of energy produced, or the ratio of greenhouse gas emissions produced to gross domestic product (GDP). Emission intensities are used to derive estimates of air pollutant or greenhouse gas emissions based on the amount of fuel combusted, the number of animals in animal husbandry, on industrial production levels, distances traveled or similar activity data. Emission intensities may also be used to compare the environmental impact of different fuels or activities. In some case the related terms emission factor and carbon intensity are used interchangeably. The jargon used can be different, for different fields/industrial sectors; normally the term "carbon" excludes other pollutants, such as particulate emissions. One commonly used figure is carbon intensity per kilowatt-hour (CIPK), which is used to compare emissions from different sources of electrical power.

The methanol economy is a suggested future economy in which methanol and dimethyl ether replace fossil fuels as a means of energy storage, ground transportation fuel, and raw material for synthetic hydrocarbons and their products. It offers an alternative to the proposed hydrogen economy or ethanol economy, although these concepts are not exclusive. Methanol can be produced from a variety of sources including fossil fuels as well as agricultural products and municipal waste, wood and varied biomass. It can also be made from chemical recycling of carbon dioxide.
Coal liquefaction is a process of converting coal into liquid hydrocarbons: liquid fuels and petrochemicals. This process is often known as "Coal to X" or "Carbon to X", where X can be many different hydrocarbon-based products. However, the most common process chain is "Coal to Liquid Fuels" (CTL).

Synthetic fuel or synfuel is a liquid fuel, or sometimes gaseous fuel, obtained from syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, in which the syngas was derived from gasification of solid feedstocks such as coal or biomass or by reforming of natural gas.

A carbon footprint (or greenhouse gas footprint) is a calculated value or index that makes it possible to compare the total amount of greenhouse gases that an activity, product, company or country adds to the atmosphere. Carbon footprints are usually reported in tonnes of emissions (CO2-equivalent) per unit of comparison. Such units can be for example tonnes CO2-eq per year, per kilogram of protein for consumption, per kilometer travelled, per piece of clothing and so forth. A product's carbon footprint includes the emissions for the entire life cycle. These run from the production along the supply chain to its final consumption and disposal.

Gas to liquids (GTL) is a refinery process to convert natural gas or other gaseous hydrocarbons into longer-chain hydrocarbons, such as gasoline or diesel fuel. Methane-rich gases are converted into liquid synthetic fuels. Two general strategies exist: (i) direct partial combustion of methane to methanol and (ii) Fischer–Tropsch-like processes that convert carbon monoxide and hydrogen into hydrocarbons. Strategy ii is followed by diverse methods to convert the hydrogen-carbon monoxide mixtures to liquids. Direct partial combustion has been demonstrated in nature but not replicated commercially. Technologies reliant on partial combustion have been commercialized mainly in regions where natural gas is inexpensive.
The United States produces mainly biodiesel and ethanol fuel, which uses corn as the main feedstock. The US is the world's largest producer of ethanol, having produced nearly 16 billion gallons in 2017 alone. The United States, together with Brazil accounted for 85 percent of all ethanol production, with total world production of 27.05 billion gallons. Biodiesel is commercially available in most oilseed-producing states. As of 2005, it was somewhat more expensive than fossil diesel, though it is still commonly produced in relatively small quantities, in comparison to petroleum products and ethanol fuel.

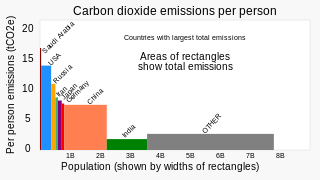
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide, from burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is one of the most important factors in causing climate change. The largest emitters are China followed by the United States. The United States has higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 GtC, of which 484±20 GtC from fossil fuels and industry, and 219±60 GtC from land use change. Land-use change, such as deforestation, caused about 31% of cumulative emissions over 1870–2022, coal 32%, oil 24%, and gas 10%.

The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG, followed by the United States with 11%, then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG, more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and, amongst the top eight emitters, is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person.

Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CH4. It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel, although capturing and storing it is hard because it is a gas at standard temperature and pressure.
Fugitive emissions are leaks and other irregular releases of gases or vapors from a pressurized containment – such as appliances, storage tanks, pipelines, wells, or other pieces of equipment – mostly from industrial activities. In addition to the economic cost of lost commodities, fugitive emissions contribute to local air pollution and may cause further environmental harm. Common industrial gases include refrigerants and natural gas, while less common examples are perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, and nitrogen trifluoride.

The environmental impact of the petroleum industry is extensive and expansive due to petroleum having many uses. Crude oil and natural gas are primary energy and raw material sources that enable numerous aspects of modern daily life and the world economy. Their supply has grown quickly over the last 150 years to meet the demands of the rapidly increasing human population, creativity, knowledge, and consumerism.

Türkmennebit, also known by the translation of the name as Turkmenoil or Turkmenneft, is the national oil company of Turkmenistan. It was established by a presidential decree reorganising parts of the former Ministry of Oil and Gas in July 1996, and has its headquarters in Ashgabat. The chairman of the company is Guychgeldi Baygeldiyev. The main oil fields operated by Türkmennebit are Goturdepe, Barsa-gelmez, Nebitdag, Körpeje, Gamyşlyja, Çeleken and Kemer, mainly in Balkan Province near the Caspian Sea.
Carbon-neutral fuel is fuel which produces no net-greenhouse gas emissions or carbon footprint. In practice, this usually means fuels that are made using carbon dioxide (CO2) as a feedstock. Proposed carbon-neutral fuels can broadly be grouped into synthetic fuels, which are made by chemically hydrogenating carbon dioxide, and biofuels, which are produced using natural CO2-consuming processes like photosynthesis.
China's greenhouse gas emissions are the largest of any country in the world both in production and consumption terms, and stem mainly from coal burning, including coal power, coal mining, and blast furnaces producing iron and steel. When measuring production-based emissions, China emitted over 14 gigatonnes (Gt) CO2eq of greenhouse gases in 2019, 27% of the world total. When measuring in consumption-based terms, which adds emissions associated with imported goods and extracts those associated with exported goods, China accounts for 13 gigatonnes (Gt) or 25% of global emissions. According to the Carbon Majors Database, Chinese state coal production alone accounts for 14% of historic global emissions.

Greenhouse gas emissionsbyRussia are mostly from fossil gas, oil and coal. Russia emits 2 or 3 billion tonnes CO2eq of greenhouse gases each year; about 4% of world emissions. Annual carbon dioxide emissions alone are about 12 tons per person, more than double the world average. Cutting greenhouse gas emissions, and therefore air pollution in Russia, would have health benefits greater than the cost. The country is the world's biggest methane emitter, and 4 billion dollars worth of methane was estimated to leak in 2019/20.












