Related Research Articles

Kannada, previously also known as Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a second or third language for around 15 million non-native speakers in Karnataka.

Kannada literature is the corpus of written forms of the Kannada language, a member of the Dravidian family spoken mainly in the Indian state of Karnataka and written in the Kannada script.

Kavirajamarga is the earliest available work on rhetoric, poetics and grammar in the Kannada language. It was inspired by or written in part by the famous Rashtrakuta King Amoghavarsha I, and some historians claim it is based partly on the Sanskrit text Kavyadarsha. Some historians believe Kavirajamarga may have been co-authored by a poet in the king's court, the Kannada language theorist Sri Vijaya.
Durvinita is seen as the most successful ruler of the Western Ganga dynasty. Son of the previous ruler, Avinita, Durvinita's accession to the throne was disputed by his brother, who had gained the support of the Pallavas and Kadambas. There are Nallala and Kadagattur inscriptions that refer to this dispute. However, Durvinita managed to grab the throne by virtue of his valour.
Ponna (c. 945) was a noted Kannada poet in the court of Rashtrakuta Dynasty king Krishna III (r.939–968 CE). The emperor honoured Ponna with the title "emperor among poets" (Kavichakravarthi) for his domination of the Kannada literary circles of the time, and the title "imperial poet of two languages" for his command over Sanskrit as well. Ponna is often considered one among the "three gems of Kannada literature" for ushering it in full panoply. According to the scholar R. Narasimhacharya, Ponna is known to have claimed superiority over all the poets of the time. According to scholars Nilakanta Shastri and E.P. Rice, Ponna belonged to Vengi Vishaya in Kammanadu, Punganur, Andhra Pradesh, but later migrated to Manyakheta, the Rashtrakuta capital, after his conversion to Jainism.
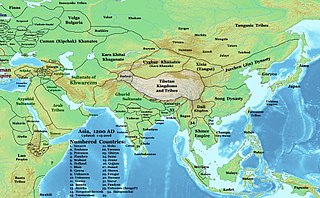
Hoysala literature is the large body of literature in the Kannada and Sanskrit languages produced by the Hoysala Empire (1025–1343) in what is now southern India. The empire was established by Nripa Kama II, came into political prominence during the rule of King Vishnuvardhana (1108–1152), and declined gradually after its defeat by the Khalji dynasty invaders in 1311.
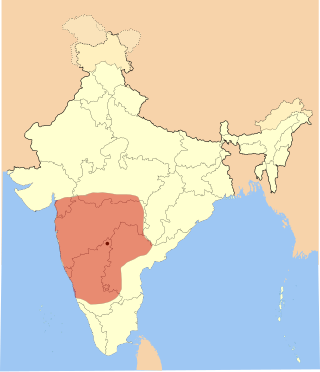
A large body of Western Chalukya literature in the Kannada language was produced during the reign of the Western Chalukya Empire in what is now southern India. This dynasty, which ruled most of the western Deccan in South India, is sometimes called the Kalyani Chalukya dynasty after its royal capital at Kalyani, and sometimes called the Later Chalukya dynasty for its theoretical relationship to the 6th-century Chalukya dynasty of Badami. For a brief period (1162–1183), the Kalachuris of Kalyani, a dynasty of kings who had earlier migrated to the Karnataka region from central India and served as vassals for several generations, exploited the growing weakness of their overlords and annexed the Kalyani. Around 1183, the last Chalukya scion, Someshvara IV, overthrew the Kalachuris to regain control of the royal city. But his efforts were in vain, as other prominent Chalukya vassals in the Deccan, the Hoysalas, the Kakatiyas and the Seunas destroyed the remnants of the Chalukya power.
Nāgavarma I (c. 990) was a noted Jain writer and poet in the Kannada language in the late 10th century. His two important works, both of which are extant, are Karnātaka Kādambari, a champu based romance novel and an adaptation of Bana's Sanskrit Kādambari, and Chandōmbudhi, the earliest available work on Kannada prosody which Nāgavarma I claims would command the respect even of poet Kalidasa. According to the scholars K.A. Nilakanta Shastri and R. Narasimhacharya, Nāgavarma I belonged to a migrant Brahmin family originally from Vengi. According to the modern Kannada poet and scholar Govinda Pai, Nāgavarma I lived from 950 CE to 1015 CE. So popular was Nāgavarma I's poetic skills that King Bhoja of Malwa presented him with horses, in appreciation of his poetic skills.

Rashtrakuta literature is the body of work created during the rule of the Rastrakutas of Manyakheta, a dynasty that ruled the southern and central parts of the Deccan, India between the 8th and 10th centuries. The period of their rule was an important time in the history of South Indian literature in general and Kannada literature in particular. This era was practically the end of classical Prakrit and Sanskrit writings when a whole wealth of topics were available to be written in Kannada. Some of Kannada's most famous poets graced the courts of the Rashtrakuta kings. Court poets and royalty created eminent works in Kannada and Sanskrit, that spanned such literary forms as prose, poetry, rhetoric, epics and grammar. Famous scholars even wrote on secular subjects such as mathematics. Rashtrakuta inscriptions were also written in expressive and poetic Kannada and Sanskrit, rather than plain documentary prose.
Medieval Kannada literature covered a wide range of subjects and genres which can broadly be classified under the Jain, Virashaiva, Vaishnava and secular traditions. These include writings from the 7th century rise of the Badami Chalukya empire to the 16th century, coinciding with the decline of Vijayanagara Empire. The earliest known literary works until about the 12th century CE were mostly authored by the Jainas along with a few works by Virashaivas and Brahmins and hence this period is called the age of Jain literature,. The 13th century CE, to the 15th century CE, saw the emergence of numerous Virashaiva and Brahminical writers with a proportional decline in Jain literary works. Thereafter, Virashaiva and Brahmin writers have dominated the Kannada literary tradition. Some of the earliest metres used by Jain writers prior to 9th century include the chattana, bedande and the melvadu metres, writings in which have not been discovered but are known from references made to them in later centuries. Popular metres from the 9th century onwards when Kannada literature is available are the champu-kavyas or just champu, vachanasangatya, shatpadi, ragale, tripadi, and kavya.

Mysore literature in Kannada is a body of literature composed in the Kannada language in the historical Kingdom of Mysore in Southern India and written in the Kannada script. The writings date from the Kingdom of Mysore, which existed from around 1600 CE until the establishment of modern India in 1947. Many of the works of this literature written on religious themes are labeled Veerashaiva or Vaishnava in acknowledgment of the two faiths that gave form to the literature and fostered it until the advent of the modern era. Despite a gradual decline in the popularity of Jainism, authors devoted to the faith produced some works of merit. Secular themes dealing with a wide range of subjects were also written on. Kannada literature flourished for a short while in the court of the neighbouring kingdom of the Nayakas of Keladi whose territory was annexed by Mysore in 1763.

Vijayanagara literature in Kannada is the body of literature composed in the Kannada language of South India during the ascendancy of the Vijayanagara Empire which lasted from the 14th through the 16th century. The Vijayanagara empire was established in 1336 by Harihara I and his brother Bukka Raya I. Although it lasted until 1664, its power declined after a major military defeat by the Shahi Sultanates in the battle of Talikota in 1565. The empire is named after its capital city Vijayanagara, whose ruins surround modern Hampi, now a World Heritage Site in Karnataka.
Extinct Kannada literature is a body of literature of the Kannada language dating from the period preceding the first extant work, Kavirajamarga.
Ratnakaravarni was a 16th-century Kannada poet and writer. He is considered to be one of the trailblazers in the native shatpadi and sangatya metric tradition that was popularised in Kannada literature during the rule of the Vijayanagara empire in modern Karnataka. His most famous writing is the story of the Jain prince Bharata and is called the Bharatesha Vaibhava. Known to be a troubled and restless person, tradition has it that Ratnakaravarni converted from his religion Jainism to Veerashaivism when a less-meritorious poet superseded him. During this brief time, he wrote the Basavapurana, a biography of the 12th century social reformer Basavanna. Later, he returned to the Jain religion and penned classics in the shataka metre. His contributions to Kannada literature are considered trend setting.
Harihara was a noted Kannada poet and writer in the 12th century. A native of Halebidu in modern Hassan district, he came from a family of accountants (Karnikas) and initially served in that capacity in the court of Hoysala King Narasimha I. Later, he moved to Hampi and authored many landmark classics. Among his important writings, the Girijakalyana written in champu metre is considered one of the enduring classics of Kannada language.
Andayya was a notable 13th-century Kannada writer during the rule of the Hoysala empire. Andayya was a Jain by faith and came from a family of accountants. His most important extant work is the Kabbigara Kava which also goes by the names Sobagina Suggi, Madana Vijaya or Kavana Gella and was written in the 1217–1235 CE period.
Bhaṭṭākalaṅka Deva was the third and the last of the notable Kannada grammarians from the medieval period. In 1604 CE, he authored a comprehensive text on old-Kannada grammar called Karnāṭaka Śabdānuśāsana in 592 Sanskrit aphorisms with glossary and commentary. The work contains useful references to prior poets and writers of Kannada literature and is considered a valuable asset to the student of old-Kannada language. A native of South Canara and a student of the Haduvalli monastery, the Jain grammarian was learned in over six languages including Kannada, Sanskrit, Prakrit and Magadhi.
Durgasimha was the minister of war and peace of Western Chalukya King Jayasimha II. Durgasimha adapted the well-known set of fables, Panchatantra, from Sanskrit language into the Kannada language in champu style. The Kannada-language version, whose central theme has a strong Jain bent, contains 60 fables, 13 of which are original stories. All the stories have morality as their theme and carry a summary section. The Kannada version is the earliest Indian vernacular version, and the author, being a minister, not surprisingly, chose to write a book on political science (Rajniti). The scholar R. Narasimhachar fixed the date of this work as c. 1025, but the modern Kannada poet and scholar Govinda Pai dated the work to 8 March 1031, based on information in the concluding stanza of the manuscript.
Asaga was a 9th-century Digambara Jain poet who wrote in Sanskrit and Kannada language. He is most known for his extant work in Sanskrit, the Vardhamana Charitra. This epic poem which runs into eighteen cantos was written in 853 CE. It is the earliest available Sanskrit biography of the last tirthankara of Jainism, Mahavira. In all, he authored at least eight works in Sanskrit. In Kannada, none of his writings, including the Karnataka Kumarasambhava Kavya that have been referenced by latter day poets have survived.
References
- Bhat, Thirumaleshwara (1993) [1993]. Govinda Pai. Sahitya Akademi. ISBN 81-7201-540-2.
- Kamath, Suryanath U. (2001) [1980]. A concise history of Karnataka : from pre-historic times to the present. Bangalore: Jupiter books. LCCN 80905179. OCLC 7796041.
- Mugali, R.S. (2006) [2006]. The Heritage of Karnataka. Lightning Source Inc. ISBN 1-4067-0232-3.
- Nagaraj, D.R. (2003). "Critical Tensions in the History of Kannada Literary Culture". In Sheldon I. Pollock (ed.). Literary Cultures in History: Reconstructions from South Asia. Berkeley and London: University of California Press. pp. 323–383. ISBN 0-520-22821-9.
- Narasimhacharya, R (1988) [1934]. History of Kannada Literature. Mysore: Government Press. Reprinted by Asian Educational Services, New Delhi. ISBN 81-206-0303-6.
- Pollock, Sheldon (2006). The Language of Gods in the World of Men: Sanskrit, Culture and Power in Pre-modern India. Berkeley and London: University of California Press. Pp. 703. ISBN 0-520-24500-8.
- Rice, B.L. (2001) [1897]. Mysore Gazetteer Compiled for Government-vol 1. New Delhi, Madras: Asian Educational Services. ISBN 81-206-0977-8.
- Rice, E.P. (1982) [1921]. A History of Kanarese Literature. New Delhi: Asian Educational Services. ISBN 81-206-0063-0.
- Sastri, K.A. Nilakanta (2002) [1955]. A history of South India from prehistoric times to the fall of Vijayanagar. New Delhi: Indian Branch, Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-560686-8.
- Singh, Nagendra K R (2001). Encyclopaedia of Jainism. Anmol Publications. ISBN 978-81-261-0691-2.
- Various (1987) [1987]. Encyclopaedia of Indian literature – vol 1. Sahitya Akademi. ISBN 81-260-1803-8.
- Various (1988) [1988]. Encyclopaedia of Indian literature – vol 2. Sahitya Akademi. ISBN 81-260-1194-7.
- Various (1992) [1992]. Encyclopaedia of Indian literature – vol 5. Sahitya Akademi. ISBN 81-260-1221-8.