Related Research Articles
An intelligence quotient (IQ) is a total score derived from a set of standardised tests or subtests designed to assess human intelligence. The abbreviation "IQ" was coined by the psychologist William Stern for the German term Intelligenzquotient, his term for a scoring method for intelligence tests at University of Breslau he advocated in a 1912 book.
The Stanford–Binet Intelligence Scales is an individually administered intelligence test that was revised from the original Binet–Simon Scale by Alfred Binet and Théodore Simon. It is in its fifth edition (SB5), which was released in 2003.
Intellectual giftedness is an intellectual ability significantly higher than average. It is a characteristic of children, variously defined, that motivates differences in school programming. It is thought to persist as a trait into adult life, with various consequences studied in longitudinal studies of giftedness over the last century. These consequences sometimes includes stigmatizing and social exclusion. There is no generally agreed definition of giftedness for either children or adults, but most school placement decisions and most longitudinal studies over the course of individual lives have followed people with IQs in the top 2.5 percent of the population—that is, IQs above 130. Definitions of giftedness also vary across cultures.
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) is an IQ test designed to measure intelligence and cognitive ability in adults and older adolescents.
Cognitive tests are assessments of the cognitive capabilities of humans and other animals. Tests administered to humans include various forms of IQ tests; those administered to animals include the mirror test and the T maze test. Such testing is used in psychology and psychometrics, as well as other fields studying human and animal intelligence.
The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) is an individually administered intelligence test for children between the ages of 6 and 16. The Fifth Edition is the most recent version.

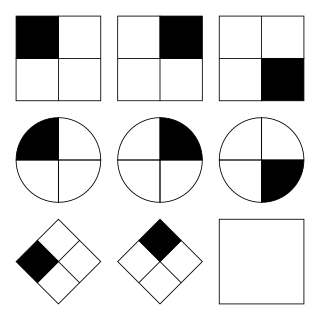
Raven's Progressive Matrices or RPM is a non-verbal test typically used to measure general human intelligence and abstract reasoning and is regarded as a non-verbal estimate of fluid intelligence. It is one of the most common tests administered to both groups and individuals ranging from 5-year-olds to the elderly. It comprises 60 multiple choice questions, listed in order of increasing difficulty. This format is designed to measure the test taker's reasoning ability, the eductive ("meaning-making") component of Spearman's g.
The Differential Ability Scales (DAS) is a nationally normed, and individually administered battery of cognitive and achievement tests. Into its second edition (DAS-II), the test can be administered to children ages 2 years 6 months to 17 years 11 months across a range of developmental levels.
The Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence (WPPSI) is an intelligence test designed for children ages 2 years 6 months to 7 years 7 months developed by David Wechsler in 1967. It is a descendant of the earlier Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale and the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children tests. Since its original publication the WPPSI has been revised three times in 1989, 2002, and 2012. The latest version, WPPSI–IV, published by Pearson Education, is a revision of the WPPSI-R and the WPPSI-III. It provides subtest and composite scores that represent intellectual functioning in verbal and performance cognitive domains, as well as providing a composite score that represents a child's general intellectual ability.
The Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children (KABC) is a clinical instrument for assessing cognitive development. Its construction incorporates several recent developments in both psychological theory and statistical methodology. The test was developed by Alan S. Kaufman and Nadeen L. Kaufman in 1983 and revised in 2004. The test has been translated and adopted for many countries, such as the Japanese version of the K-ABC by the Japanese psychologists Tatsuya Matsubara, Kazuhiro Fujita, Hisao Maekawa, and Toshinori Ishikuma.
The Culture Fair Intelligence Test (CFIT) was created by Raymond Cattell in 1949 as an attempt to measure cognitive abilities devoid of sociocultural and environmental influences. Scholars have subsequently concluded that the attempt to construct measures of cognitive abilities devoid of the influences of experiential and cultural conditioning is a challenging one. Cattell proposed that general intelligence (g) comprises both fluid intelligence (Gf) and crystallized intelligence (Gc). Whereas Gf is biologically and constitutionally based, Gc is the actual level of a person's cognitive functioning, based on the augmentation of Gf through sociocultural and experiential learning.
The Otis–Lennon School Ability Test (OLSAT), published by the successor of Harcourt Assessment—Pearson Education, Inc., a subsidiary of Pearson PLC—is, according to the publisher, a test of abstract thinking and reasoning ability of children pre-K to 18. The Otis-Lennon is group-administered, multiple choice, taken with pencil and paper, measures verbal, quantitative, and spatial reasoning ability. The test yields verbal and nonverbal scores, from which a total score is derived, called a School Ability Index (SAI). The SAI is a normalized standard score with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 16. With the exception of pre-K, the test is administered in groups.

IQ classification is the practice of categorizing human intelligence, as measured by intelligence quotient (IQ) tests, into categories such as "superior" or "average".
The Das–Naglieri cognitive assessment system (CAS) test is an individually administered test of cognitive functioning for children and adolescents ranging from 5 through 17 years of age that was designed to assess the planning, attention, simultaneous and successive cognitive processes as described in the PASS theory of intelligence.
The Cognitive Abilities Test (CogAT) is a group-administered K–12 assessment published by Riverside Insights and intended to estimate students' learned reasoning and problem solving abilities through a battery of verbal, quantitative, and nonverbal test items. The test purports to assess students' acquired reasoning abilities while also predicting achievement scores when administered with the co-normed Iowa Tests. The test was originally published in 1954 as the Lorge-Thorndike Intelligence Test, after the psychologists who authored the first version of it, Irving Lorge and Robert L. Thorndike. The CogAT is one of several tests used in the United States to help teachers or other school staff make student placement decisions for gifted education programs, and is accepted for admission to Intertel, a high IQ society for those who score at or above the 99th percentile on a test of intelligence.
The Reynolds Intellectual Assessment Scales (RIAS) is an individually administered test of intelligence that includes a co-normed, supplemental measure of memory. It is appropriate for individuals ages 3–94.
The Woodcock–Johnson Tests of Cognitive Abilities is a set of intelligence tests first developed in 1977 by Richard Woodcock and Mary E. Bonner Johnson. It was revised in 1989, again in 2001, and most recently in 2014; this last version is commonly referred to as the WJ IV. They may be administered to children from age two right up to the oldest adults. The previous edition WJ III was praised for covering "a wide variety of cognitive skills".
The Planning, Attention-Arousal, Simultaneous and Successive (P.A.S.S.) theory of intelligence, first proposed in 1975 by Das, Kirby and Jarman (1975), and later elaborated by Das, Naglieri & Kirby (1994) and Das, Kar & Parrilla (1996), challenges g-theory, on the grounds that the brain is made up of interdependent but separate functional systems. Neuroimaging studies and clinical studies of individuals with brain lesions make it clear that the brain is modularized; for example, damage to a particular area of the left temporal lobe will impair spoken and written language's production. Damage to an adjacent area will have the opposite impact, preserving the individual's ability to produce but not understand speech and text.
TestingMom.com is an online test prep for parents of gifted education and testing along with skill building, founded in 2010. Testing Mom membership services include expert advice, tele-seminars, practice questions, as well as books and games. The online programs help parents of children pre-K to 8th grade with skill building activities for school success and testing success. The platform also has content for common core testing and state testing.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human intelligence:
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Naglieri Nonverbal Ability Test | Third Edition".
- ↑ "Intertel - Join us". www.intertel-iq.org. Retrieved 2021-03-20.
- ↑ "Qualifying test scores". American Mensa. Retrieved 2021-03-20.
- ↑ "Gifted & Talented (G&T) Frequently Asked Questions - Assessment" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-10-29. Retrieved 2013-10-28.
- ↑ "New Gifted and Talented Test Leaves Parents Stumped - DNAinfo.com New York". Archived from the original on 2013-01-21. Retrieved 2013-02-15.
- ↑ Lohman, David F; Korb, Katrina K; Lakin, Joni (Fall 2008), "Identifying Academically Gifted English-Language Learners Using Nonverbal Tests: A Comparison of the Raven, NNAT, and CogAT", Gifted Child Quarterly (52): 275–296, doi:10.1177/0016986208321808, S2CID 32309883