
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment in Stockholm in June 1972. Its mandate is to provide leadership, deliver science and develop solutions on a wide range of issues, including climate change, the management of marine and terrestrial ecosystems, and green economic development. The organization also develops international environmental agreements; publishes and promotes environmental science and helps national governments achieve environmental targets.

The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed regional seas and estuaries, rivers, lakes, groundwater systems (aquifers), and wetlands.
The Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO (IOC/UNESCO) was established by resolution 2.31 adopted by the General Conference of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). It first met in Paris at UNESCO Headquarters from 19 to 27 October 1961. Initially, 40 States became members of the commission. The IOC assists governments to address their individual and collective ocean and coastal management needs, through the sharing of knowledge, information and technology as well as through the co-ordination of programs and building capacity in ocean and coastal research, observations and services.
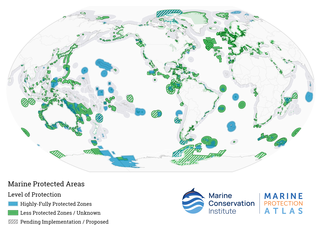
A marine protected area (MPA) is a protected area of the world's seas, oceans, estuaries or in the US, the Great Lakes. These marine areas can come in many forms ranging from wildlife refuges to research facilities. MPAs restrict human activity for a conservation purpose, typically to protect natural or cultural resources. Such marine resources are protected by local, state, territorial, native, regional, national, or international authorities and differ substantially among and between nations. This variation includes different limitations on development, fishing practices, fishing seasons and catch limits, moorings and bans on removing or disrupting marine life. MPAs can provide economic benefits by supporting the fishing industry through the revival of fish stocks, as well as job creation and other market benefits via ecotourism. The value of MPA to mobile species is unknown.
A regional fishery body (RFB) is a type of international organization that is part of an international fishery agreement or arrangement to cooperate on the sustainable use and conservation of marine living resources and/or the development of marine capture fisheries whose such capacity has been recognized by the UN Food and Agriculture Organization under the United Nations Fish Stocks Agreement.

The Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals, also known as the Convention on Migratory Species (CMS) or the Bonn Convention, is an international agreement that aims to conserve migratory species throughout their ranges. The agreement was signed under the auspices of the United Nations Environment Programme and is concerned with conservation of wildlife and habitats on a global scale.

The Convention for the Protection of the Marine Environment and the Coastal Region of the Mediterranean, originally the Convention for Protection of the Mediterranean Sea against Pollution, and often simply referred to as the Barcelona Convention, is a regional convention adopted in 1976 to prevent and abate pollution from ships, aircraft and land based sources in the Mediterranean Sea. This includes but is not limited to dumping, run-off and discharges. Signers agreed to cooperate and assist in dealing with pollution emergencies, monitoring and scientific research. The convention was adopted on 16 February 1976 and amended on 10 June 1995.
The South East Atlantic Fisheries Organisation (SEAFO) is an organization that maintains controls over fishing and fishing related acts in the Southeastern Atlantic Ocean.

The Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) concerning Conservation Measures for Marine Turtles of the Atlantic Coast of Africa is a 1998 multilateral environmental memorandum of understanding that entered into effect on 1 July 1999 under the auspices of the Convention on Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS), also known as the Bonn Convention. The MoU focuses on the protection of six marine turtle species that are estimated to have rapidly declined in numbers along the Atlantic Coast of Africa. The MoU covers 26 range States. As of May 2013, 23 range States have signed the MoU.
Partnerships in Environmental Management for the Seas of East Asia (PEMSEA) is a regional partnership programme implemented by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and executed by the United Nations Office for Project Services (UNOPS). The project, started in 1994, was originally known as Prevention and Management of Marine Pollution in the East Asian Seas (SDS-SEA).
The Port Management Association of Eastern and Southern Africa (PMAESA) is a non-profit, inter-governmental organization made up of Port Operators, Government Line Ministries, Logistics and Maritime Service Providers and other port and shipping stakeholders from the Eastern, Western and Southern African and Indian Ocean regions.
Framework Convention for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the Caspian Sea is a regional convention signed by the official representatives of the five littoral Caspian states: Azerbaijan, Iran, Kazakhstan, Russian Federation and Turkmenistan in Tehran (Iran) on 4 November 2003. The Framework Convention, also called Tehran Convention, entered into force on 12 August 2006.
Tundi Spring Agardy is a marine conservationist and the founder of Sound Seas – a Washington DC–based group specializing in working at the nexus of marine science and policy in order to safeguard ocean life.

Coastal & Marine Union (EUCC) is a nonprofit organization. It was founded in 1989 with the aim of promoting coastal management. In Europe, it had 13 national branches. EUCC's working area is Europe and its neighbouring regions, especially the Black Sea and the Mediterranean.

Western Indian Ocean Marine Science Association (WIOMSA) is a regional professional, non-governmental, non-profit, membership organization, registered in Zanzibar, Tanzania. The organization is dedicated to promoting the educational, scientific and technological development of all aspects of marine sciences throughout the region of Western Indian Ocean (Somalia, Kenya, Tanzania, Mozambique, South Africa, Comoros, Madagascar, Seychelles, Mauritius, Réunion (France)), with a view toward sustaining the use and conservation of its marine resources. The association has about 1000 individual members as well as about 50 institutional members from within and outside the region.
The Rocherpan Marine Protected Area is a small coastal conservation region on the West Coast of the Western Cape province, in the territorial waters of South Africa. It is about 25 km north of Velddrif on the road to Elands Bay, north of Dwarskersbos.

Aldo Manos was an Italian diplomat, academic and author. He was a founding member of UNEP and the United Nations office located in Kenya.
The Convention for the Protection and Development of the Marine Environment of the Wider Caribbean Region, commonly called the Cartagena Convention, is an international agreement for the protection of the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico and a portion of the adjacent Atlantic Ocean. It was adopted on 24 March 1983, entered into force on 11 October 1986 subsequent to its ratification by Antigua and Barbuda, the ninth party to do so, and has been ratified by 26 states. It has been amended by three major protocols: the Protocol Concerning Co-operation in Combating Oil Spills in the Wider Caribbean Region, the Protocol Concerning Specially Protected Areas and Wildlife to the Convention for the Protection and Development of the Marine Environment of the Wider Caribbean Region and the Protocol Concerning Pollution from Land-Based Sources and Activities to the Convention for the Protection and Development of the Marine Environment of the Wider Caribbean Region.









