
In cellular biology, paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance, as opposed to cell signaling by endocrine factors, hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system; juxtacrine interactions; and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain.
The Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways which begin with proteins that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt is a portmanteau created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling pathways use either nearby cell-cell communication (paracrine) or same-cell communication (autocrine). They are highly evolutionarily conserved in animals, which means they are similar across animal species from fruit flies to humans.

Catenins are a family of proteins found in complexes with cadherin cell adhesion molecules of animal cells. The first two catenins that were identified became known as α-catenin and β-catenin. α-Catenin can bind to β-catenin and can also bind filamentous actin (F-actin). β-Catenin binds directly to the cytoplasmic tail of classical cadherins. Additional catenins such as γ-catenin and δ-catenin have been identified. The name "catenin" was originally selected because it was suspected that catenins might link cadherins to the cytoskeleton.
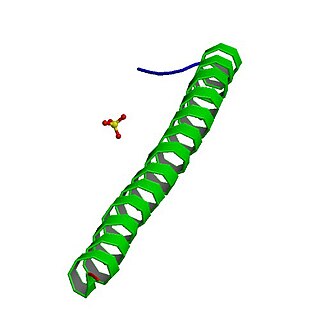
Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) also known as deleted in polyposis 2.5 (DP2.5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APC gene. The APC protein is a negative regulator that controls beta-catenin concentrations and interacts with E-cadherin, which are involved in cell adhesion. Mutations in the APC gene may result in colorectal cancer and desmoid tumors.
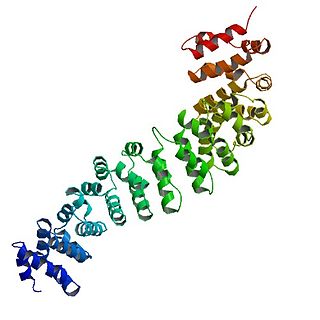
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (beta-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTNNB1 gene.

Axin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AXIN1 gene.

Proto-oncogene Wnt-1, or Proto-oncogene Int-1 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT1 gene.

Segment polarity protein dishevelled homolog DVL-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DVL1 gene.

Secreted frizzled-related protein 1, also known as SFRP1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SFRP1 gene.

Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LRP6 gene. LRP6 is a key component of the LRP5/LRP6/Frizzled co-receptor group that is involved in canonical Wnt pathway.

Protein Wnt-3a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT3A gene.

Axin-2, also known as axin-like protein (Axil), axis inhibition protein 2 (AXIN2), or conductin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AXIN2 gene.

Segment polarity protein dishevelled homolog DVL-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DVL2 gene.

Segment polarity protein dishevelled homolog DVL-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DVL3 gene.

Dishevelled (Dsh) is a family of proteins involved in canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways. Dsh is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein that acts directly downstream of frizzled receptors. It takes its name from its initial discovery in flies, where a mutation in the dishevelled gene was observed to cause improper orientation of body and wing hairs. There are vertebrate homologs in zebrafish, Xenopus (Xdsh), mice and humans. Dsh relays complex Wnt signals in tissues and cells, in normal and abnormal contexts. It is thought to interact with the SPATS1 protein when regulating the Wnt Signalling pathway.
The Nodal signaling pathway is a signal transduction pathway important in regional and cellular differentiation during embryonic development.
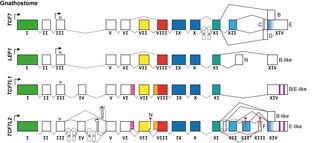
The TCF/LEF family is a group of genes that encode transcription factors which bind to DNA through a SOX-like high mobility group domain. They are involved in the Wnt signaling pathway, particularly during embryonic and stem-cell development, but also had been found to play a role in cancer and diabetes. TCF/LEF factors recruit the coactivator beta-catenin to enhancer elements of genes they target. They can also recruit members of the Groucho family of corepressors.
Naked cuticle 2 (NKD2) is a human gene that encodes the protein Nkd2, one of the Naked cuticle (Nkd) family of proteins that regulate the Wnt signaling pathway. Both Nkd1 and Nkd2 proteins can bind to Dishevelled proteins, but only Nkd2 can bind to the EGF-ligand family member TGF alpha and regulate its polarized secretion in cultured epithelial cells.
Naked cuticle (Nkd) is a conserved family of intracellular proteins encoded in most animal genomes. The original mutants were discovered by 1995 Nobel laureates Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard and Eric F. Wieschaus and colleagues in their genetic screens for pattern-formation mutants in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. The Nkd gene family was first cloned in the laboratory of Matthew P. Scott. Like many cleverly named fly mutants, the name "naked cuticle" derives from the fact that mutants lack most of the hair-like protrusions from their ventral cuticle and thus appear "naked".
In molecular biology, the protein domain, WIF N-terminal refers to the N terminal domain of the protein, WIF. It stands for, Wnt-inhibitory factor, whereby wnt is a signalling molecule also known as wingless. Wnt is a molecule in the wnt signaling pathway. The WIF domain binds to the wnt ligand since it inhibits it.