
Surrealism is a cultural movement that developed in Europe in the aftermath of World War I in which artists depicted unnerving, illogical scenes and developed techniques to allow the unconscious mind to express itself. Its aim was, according to leader André Breton, to "resolve the previously contradictory conditions of dream and reality into an absolute reality, a super-reality", or surreality. It produced works of painting, writing, theatre, filmmaking, photography, and other media.

Max Ernst was a German painter, sculptor, printmaker, graphic artist, and poet. A prolific artist, Ernst was a primary pioneer of the Dada movement and Surrealism in Europe. He had no formal artistic training, but his experimental attitude toward the making of art resulted in his invention of frottage—a technique that uses pencil rubbings of textured objects and relief surfaces to create images—and grattage, an analogous technique in which paint is scraped across canvas to reveal the imprints of the objects placed beneath. Ernst is noted for his unconventional drawing methods as well as for creating novels and pamphlets using the method of collages. He served as a soldier for four years during World War I, and this experience left him shocked, traumatised and critical of the modern world. During World War II he was designated an "undesirable foreigner" while living in France.

Marguerite "Peggy" Guggenheim was an American art collector, bohemian and socialite. Born to the wealthy New York City Guggenheim family, she was the daughter of Benjamin Guggenheim, who went down with the Titanic in 1912, and the niece of Solomon R. Guggenheim, who established the Solomon R. Guggenheim Foundation. Guggenheim collected art in Europe and America between 1938 and 1946. She exhibited this collection as she built it; in 1949, she settled in Venice, where she lived and exhibited her collection for the rest of her life. The Peggy Guggenheim Collection is a modern art museum on the Grand Canal in Venice, Italy, and is one of the most visited attractions in Venice.
Gordon Onslow Ford was one of the last surviving members of the 1930s Paris surrealist group surrounding André Breton.

Loplop, or more formally, Loplop, Father Superior of the Birds, is the name of a birdlike character that was an alter ego of the Dada-Surrealist artist Max Ernst. Ernst had a ongoing fascination with birds, which often appear in his work. Loplop functioned as a familiar animal. William Rubin wrote of Ernst "Among his more successful works of the thirties are a series begun in 1930 around the theme of his alter ego, Loplop, Superior of the Birds." Loplop is an iconic image of surrealist art, the painting Loplop Introduces Loplop (1930) appears on the front cover of the Gaëtan Picon's book Surrealist and Surrealism 1919-1939, and the drawing and collage Loplop Presents (1932) was used as the frontispiece of Patrick Waldberg's book Surrealism.

Meret Elisabeth Oppenheim was a German-born Swiss Surrealist artist and photographer.

Dorothea Margaret Tanning was an American painter, printmaker, sculptor, writer, and poet. Her early work was influenced by Surrealism.

Valentine Hugo (1887–1968) was a French artist and writer. She was born Valentine Marie Augustine Gross, only daughter to Auguste Gross and Zélie Démelin, in Boulogne-sur-Mer. She is best known for her work with the Russian ballet and with the French Surrealists. Hugo died in Paris.

Sir Roland Algernon Penrose was an English artist, historian and poet. He was a major promoter and collector of modern art and an associate of the surrealists in the United Kingdom. During the Second World War he put his artistic skills to practical use as a teacher of camouflage.

Mary Leonora Carrington was a British-born surrealist painter and novelist. She lived most of her adult life in Mexico City and was one of the last surviving participants in the surrealist movement of the 1930s. Carrington was also a founding member of the women's liberation movement in Mexico during the 1970s.
Stupid was a short-lived grouping of constructivist artists, formed in Cologne in 1919. The founding members were Willy Fick, Heinrich Hoerle, Angelika Hoerle, Anton Räderscheidt, Marta Hegemann, and Franz Wilhelm Seiwert.
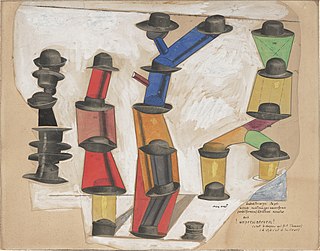
The Hat Makes the Man (1920) is a collage by the German dadaist/surrealist Max Ernst. It is composed of cut out images of hats from catalogues linked by gouache and pencil outlines to create abstract anthropomorphic figures. There are inscriptions in ink that read "seed-covered stacked-up man seedless waterformer ('edelformer') well fitting nervous system also tightly fitting nerves! ." The idea for this work began as a sculpture made from wooden hat molds.

The Elephant Celebes is a 1921 painting by the German Dadaist and surrealist Max Ernst. It is among the most famous of Ernst's early surrealist works and "undoubtedly the first masterpiece of Surrealist painting in the de Chirico tradition." It combines the vivid dreamlike atmosphere of Surrealism with the collage aspects of Dada.

A rubbing (frottage) is a reproduction of the texture of a surface created by placing a piece of paper or similar material over the subject and then rubbing the paper with something to deposit marks, most commonly charcoal or pencil but also various forms of blotted and rolled ink, chalk, wax, and many other substances. For all its simplicity, the technique can be used to produce blur-free images of minuscule elevations and depressions on areas of any size in a way that can hardly be matched by even the most elaborate, state-of-the-art methods. In this way, surface elevations measuring only a few thousandths of a millimeter can be made visible.

The Collection of Modern and Contemporary Art is a collection of paintings, graphic art and sculptures in the Vatican Museums.
Jesus Fuertes was a Cubist painter, who was initiated into the world of art by Salvador Dalí, and was described as a "true genius" by Pablo Picasso. Fuertes often chose women and cats as his subject matter. Several of his well-known works involve the use of shades of blue, which earned him the nickname "Painter of Blue".

The Exposition Internationale du Surréalisme was an exhibition by surrealist artists that took place from January 17 to February 24, 1938, in the generously equipped Galérie Beaux-Arts, run by Georges Wildenstein, at 140, Rue du Faubourg Saint-Honoré in Paris. It was organised by the French writer André Breton, the surrealists' brain and theorist, and Paul Éluard, the best known poet of the movement. The catalogue listed, along with the above, Marcel Duchamp as generator and arbitrator, Salvador Dalí and Max Ernst as technical advisers, Man Ray as head lighting technician and Wolfgang Paalen as responsible for the design of the entrance and main hall with "water and foliage". The exhibition was staged in three sections, showing paintings and objects as well as unusually decorated rooms and mannequins which had been redesigned in various ways. With this holistic presentation of surrealist art work the movement wrote exhibition history.

Nadrealizam danas i ovde was the official magazine of the Serbian surrealists from the 1930s. It was known as NDIO for short.

Xenia Cage was an American surrealist sculptor. Her work has been described as on the “cutting edge of surrealism in sculpture” for her time.
Portrait of Max Ernst, also known as Bird Superior – Portrait of Max Ernst, is an oil on canvas painting by English artist Leonora Carrington, created c. 1939. The painting was made when the two artists were having a short-lived affair. It is held at the Scottish National Gallery of Modern Art, who purchased it in 2018. It was the first work by the artist acquired by the museum.
















