Related Research Articles

The economy of Cambodia currently follows an open market system and has seen rapid economic progress in the last decade. Cambodia had a gross domestic product (GDP) of $28.54 billion in 2022. Per capita income, although rapidly increasing, is low compared with most neighboring countries. Cambodia's two largest industries are textiles and tourism, while agricultural activities remain the main source of income for many Cambodians living in rural areas. The service sector is heavily concentrated on trading activities and catering-related services. Recently, Cambodia has reported that oil and natural gas reserves have been found off-shore.

The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is one of the first and oldest specialized agencies of the UN. The ILO has 187 member states: 186 out of 193 UN member states plus the Cook Islands. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, with around 40 field offices around the world, and employs some 3,381 staff across 107 nations, of whom 1,698 work in technical cooperation programmes and projects.

Child labour is the exploitation of children through any form of work that interferes with their ability to attend regular school, or is mentally, physically, socially and morally harmful. Such exploitation is prohibited by legislation worldwide, although these laws do not consider all work by children as child labour; exceptions include work by child artists, family duties, supervised training, and some forms of work undertaken by Amish children, as well as by Indigenous children in the Americas.
Labor rights or workers' rights are both legal rights and human rights relating to labor relations between workers and employers. These rights are codified in national and international labor and employment law. In general, these rights influence working conditions in the relations of employment. One of the most prominent is the right to freedom of association, otherwise known as the right to organize. Workers organized in trade unions exercise the right to collective bargaining to improve working conditions.

The Harkin–Engel Protocol, sometimes referred to as the Cocoa Protocol, is an international agreement aimed at ending the worst forms of child labor and forced labor in the production of cocoa, the main ingredient in chocolate. The protocol was negotiated by U.S. Senator Tom Harkin and U.S. Representative Eliot Engel in response to a documentary and multiple articles in 2000 and 2001 reporting widespread child slavery and child trafficking in the production of cocoa. The protocol was signed in September 2001. Joint Statements in 2001, 2005 and 2008 and a Joint Declaration in 2010 extended the commitment to address the problem.
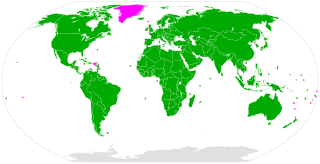
The Convention Concerning the Prohibition and Immediate Action for the Elimination of the Worst Forms of Child Labour, known in short as the Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention, was adopted by the International Labour Organization (ILO) in 1999 as ILO Convention No 182. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions.

Trafficking of children is a form of human trafficking and is defined by the United Nations as the "recruitment, transportation, harboring, and/or receipt" kidnapping of a child for the purpose of slavery, forced labour, and exploitation. This definition is substantially wider than the same document's definition of "trafficking in persons". Children may also be trafficked for adoption. Not all adoption is a form of human trafficking, but illegal or informal is. Illegal adoptions violate multiple child rights norms and principles, including the best interests of the child, the principle of subsidiarity and the prohibition of improper financial gain.
Child labour in Botswana is defined as the exploitation of children through any form of work which is harmful to their physical, mental, social and moral development. Child labour in Botswana is characterised by the type of forced work at an associated age, as a result of reasons such as poverty and household-resource allocations. Child labour in Botswana is not of higher percentage according to studies. The United States Department of Labor states that due to the gaps in the national frameworks, scarce economy, and lack of initiatives, “children in Botswana engage in the worst forms of child labour”. The International Labour Organization is a body of the United Nations which engages to develop labour policies and promote social justice issues. The International Labour Organization (ILO) in convention 138 states the minimum required age for employment to act as the method for "effective abolition of child labour" through establishing minimum age requirements and policies for countries when ratified. Botswana ratified the Minimum Age Convention in 1995, establishing a national policy allowing children at least fourteen-years old to work in specified conditions. Botswana further ratified the ILO's Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention, convention 182, in 2000.
Child labour in Eswatini is a controversial issue that affects a large portion of the country's population. Child labour is often seen as a human rights concern because it is "work that deprives children of their childhood, their potential and their dignity, and that is harmful to physical and mental development," as defined by the International Labour Organization (ILO). Additionally, child labour is harmful in that it restricts a child's ability to attend school or receive an education. The ILO recognizes that not all forms of children working are harmful, but this article will focus on the type of child labour that is generally accepted as harmful to the child involved.
Human rights in the Philippines are protected by the Constitution of the Philippines, to make sure that people in the Philippines are able to live peacefully and with dignity, safe from the abuse of any individuals or institutions, including the state.
The global march against child labour came about in 1998, following the significant response concerning the desire to end child labour. It was a grassroot movement that motivated many individuals and organizations to unite and fight against child labor, not an annual march.

Bangladesh being a first line littoral state of the Indian Ocean has a very good source of marine resources in the Bay of Bengal. The country has an exclusive economic zone of 41,000 square miles (110,000 km2), which is 73% of the country's land area. On the other hand, Bangladesh is a small and developing country overloaded with almost unbearable pressure of human population. In the past, people of Bangladesh were mostly dependent upon land-based proteins. But, the continuous process of industrialisation and urbanisation consumes the limited land area. Now there is no other way than to harvest the vast under water protein from the Bay of Bengal, which can meet the country's demand.

Child labour in Bangladesh is significant, with 4.7 million children aged 5 to 14 in the work force in 2002-03. Out of the child labourers engaged in the work force, 83% are employed in rural areas and 17% are employed in urban areas. Child labour can be found in agriculture, poultry breeding, fish processing, the garment sector and the leather industry, as well as in shoe production. Children are involved in jute processing, the production of candles, soap and furniture. They work in the salt industry, the production of asbestos, bitumen, tiles and ship breaking.

A significant proportion of children in India are engaged in child labour. In 2011, the national census of India found that the total number of child labourers, aged [5–14], to be at 10.12 million, out of the total of 259.64 million children in that age group. The child labour problem is not unique to India; worldwide, about 217 million children work, many full-time.

Child labour in Africa is generally defined based on two factors: type of work and minimum appropriate age of the work. If a child is involved in an activity that is harmful to his/her physical and mental development, he/she is generally considered as a child labourer. That is, any work that is mentally, physically, socially or morally dangerous and harmful to children, and interferes with their schooling by depriving them of the opportunity to attend school or requiring them to attempt to combine school attendance with excessively long and heavy work. Appropriate minimum age for each work depends on the effects of the work on the physical health and mental development of children. ILO Convention No. 138 suggests the following minimum age for admission to employment under which, if a child works, he/she is considered as a child laborer: 18 years old for hazardous works, and 13–15 years old for light works, although 12–14 years old may be permitted for light works under strict conditions in very poor countries. Another definition proposed by ILO's Statistical Information and Monitoring Program on Child Labor (SIMPOC) defines a child as a child labourer if he/she is involved in an economic activity, and is under 12 years old and works one or more hours per week, or is 14 years old or under and works at least 14 hours per week, or is 14 years old or under and works at least one hour per week in activities that are hazardous, or is 17 or under and works in an "unconditional worst form of child labor".
Child labor in the Philippines is the employment of children in hazardous occupations below the age of fifteen (15), or without the proper conditions and requirements below the age of fifteen (15), where children are compelled to work on a regular basis to earn a living for themselves and their families, and as a result are disadvantaged educationally and socially. So to make it short, it is called child labor when it is forced.
International labour law is the body of rules spanning public and private international law which concern the rights and duties of employees, employers, trade unions and governments in regulating Work and the workplace. The International Labour Organization and the World Trade Organization have been the main international bodies involved in reforming labour markets. The International Monetary Fund and the World Bank have indirectly driven changes in labour policy by demanding structural adjustment conditions for receiving loans or grants. Issues regarding Conflict of laws arise, determined by national courts, when people work in more than one country, and supra-national bodies, particularly in the law of the European Union, have a growing body of rules regarding labour rights.
Child labour laws are statutes placing restrictions and regulations on the work of minors.

Armenia was admitted into the United Nations on 2 March 1992, following its independence from the Soviet Union. In December 1992, the UN opened its first office in Yerevan. Since then, Armenia has signed and ratified several international treaties. There are 20 specialized agencies, programs, and funds operating in the country under the supervision of the UN Resident Coordinator. Armenia strengthened its relations with the UN by cooperating with various UN agencies and bodies such as the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, the World Food Programme, and with the financial institutions of the UN. Armenia is a candidate to preside as a non-permanent member of the UN Security Council in 2031.

Child labor, the practice of employing children under the legal age set by a government, is considered one of Brazil's most significant social issues. According to data from the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE), more than 2.7 million minors between the ages of 5 and 17 worked in the country in 2015; 79,000 were between the ages of 5 and 9. Under Brazilian law, 16 is the minimum age to enter the labor market and 14 is the minimum age to work as an apprentice.
References
- ↑ "Hazardous labour hijacks childhood of 1.28m children". New Age. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
- ↑ "Trading with tiny hands: Do we really care?". The Daily Star. 14 June 2017. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
- ↑ "Clothing and cotton still on child labour list". just-style.com. 8 October 2015. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
- ↑ "Bonded labour at dry fish units robbing children of their youth". The Business Standard. 23 January 2020. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
- ↑ "ILO supports first meeting of national child labour council". ilo.org. 26 May 2015. Retrieved 8 April 2020.