
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmosphere, the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers to day-to-day temperature, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions, whereas climate is the term for the averaging of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, "weather" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth.

College Bowl is a radio, television, and student quiz show. College Bowl first aired on the NBC Radio Network in 1953 as College Quiz Bowl. It then moved to American television broadcast networks, airing from 1959 to 1963 on CBS and from 1963 to 1970 on NBC. In 1977, the president of College Bowl, Richard Reid, developed it into a non-televised national championship competition on campuses across America through an affiliation with the Association of College Unions International (ACUI), which lasted for 31 years. In 1989, College Bowl introduced a (sponsored) version of College Bowl for historically black colleges and universities (HBCUs) called Honda Campus All-Star Challenge (HCASC) which is ongoing. In 2007, College Bowl produced a new version and format of the game as an international championship in Africa, called Africa Challenge. The College Bowl Campus Program and National Championship ran until 2008.

Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the conditions of the atmosphere for a given location and time. People have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia and formally since the 19th century.
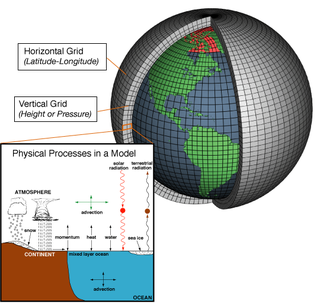
A general circulation model (GCM) is a type of climate model. It employs a mathematical model of the general circulation of a planetary atmosphere or ocean. It uses the Navier–Stokes equations on a rotating sphere with thermodynamic terms for various energy sources. These equations are the basis for computer programs used to simulate the Earth's atmosphere or oceans. Atmospheric and oceanic GCMs are key components along with sea ice and land-surface components.

In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor, so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation; their water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate, so fog and mist do not fall. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated with water vapor: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called showers.

METAR is a format for reporting weather information. A METAR weather report is predominantly used by aircraft pilots, and by meteorologists, who use aggregated METAR information to assist in weather forecasting.

Numerical weather prediction (NWP) uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic results. A number of global and regional forecast models are run in different countries worldwide, using current weather observations relayed from radiosondes, weather satellites and other observing systems as inputs.

Ensemble forecasting is a method used in or within numerical weather prediction. Instead of making a single forecast of the most likely weather, a set of forecasts is produced. This set of forecasts aims to give an indication of the range of possible future states of the atmosphere.

In atmospheric science, an atmospheric model is a mathematical model constructed around the full set of primitive, dynamical equations which govern atmospheric motions. It can supplement these equations with parameterizations for turbulent diffusion, radiation, moist processes, heat exchange, soil, vegetation, surface water, the kinematic effects of terrain, and convection. Most atmospheric models are numerical, i.e. they discretize equations of motion. They can predict microscale phenomena such as tornadoes and boundary layer eddies, sub-microscale turbulent flow over buildings, as well as synoptic and global flows. The horizontal domain of a model is either global, covering the entire Earth, or regional (limited-area), covering only part of the Earth. Atmospheric models also differ in how they compute vertical fluid motions; some types of models are thermotropic, barotropic, hydrostatic, and non-hydrostatic. These model types are differentiated by their assumptions about the atmosphere, which must balance computational speed with the model's fidelity to the atmosphere it is simulating.

The WxChallenge is a weather forecasting competition among colleges in North America. The competition is run by the University of Oklahoma. In its first official semester, fall 2006, there were 1,262 participants from 53 institutions. A similar competition, the National Collegiate Weather Forecasting Contest, recently ended, partially due to this competition.
In weather forecasting, model output statistics (MOS) is a multiple linear regression technique in which predictands, often near-surface quantities, are related statistically to one or more predictors. The predictors are typically forecasts from a numerical weather prediction (NWP) model, climatic data, and, if applicable, recent surface observations. Thus, output from NWP models can be transformed by the MOS technique into sensible weather parameters that are familiar to a layperson.
A wind power forecast corresponds to an estimate of the expected production of one or more wind turbines in the near future, up to a year. Forecast are usually expressed in terms of the available power of the wind farm, occasionally in units of energy, indicating the power production potential over a time interval.

The quantitative precipitation forecast is the expected amount of melted precipitation accumulated over a specified time period over a specified area. A QPF will be created when precipitation amounts reaching a minimum threshold are expected during the forecast's valid period. Valid periods of precipitation forecasts are normally synoptic hours such as 00:00, 06:00, 12:00 and 18:00 GMT. Terrain is considered in QPFs by use of topography or based upon climatological precipitation patterns from observations with fine detail. Starting in the mid-to-late 1990s, QPFs were used within hydrologic forecast models to simulate impact to rivers throughout the United States. Forecast models show significant sensitivity to humidity levels within the planetary boundary layer, or in the lowest levels of the atmosphere, which decreases with height. QPF can be generated on a quantitative, forecasting amounts, or a qualitative, forecasting the probability of a specific amount, basis. Radar imagery forecasting techniques show higher skill than model forecasts within 6 to 7 hours of the time of the radar image. The forecasts can be verified through use of rain gauge measurements, weather radar estimates, or a combination of both. Various skill scores can be determined to measure the value of the rainfall forecast.

Kentucky is situated in the Upland South region of the United States. A significant portion of eastern Kentucky is part of Appalachia.

The climate of New York (state) is generally humid continental, while the extreme southeastern portion of the state lies in the warmer humid subtropical climate zone. Winter temperatures average below freezing during January and February in much of the state of New York, but several degrees above freezing along the Atlantic coastline, including New York City and Long Island.

Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water for hydroelectric power plants, crop irrigation, and suitable conditions for many types of ecosystems.

Mubi North is a Local Government Area of Adamawa State, Nigeria. The town is the location of the Adamawa State University and the Federal Polytechnic, Mubi.
Seoul, the capital of South Korea, features a dry-winter humid continental climate (Dwa) in the 0°C isotherm according to the Köppen climate classification. If the -3°C isotherm is used, the climate is a dry-winter humid subtropical climate (Cwa) and there are four highly distinct seasons. In summer, the influence of the North Pacific high-pressure system brings hot, humid weather with temperatures soaring as high as 35 °C (95 °F) on occasion. In winter, the city is topographically influenced by expanding Siberian High-pressure zones and prevailing west winds bring colder air to Korea. The bitterly cold days are commonly known to come in three-day cycles regulated by rising and falling pressure systems. The most pleasant seasons for most people in the city are spring and autumn, when azure skies and comfortable temperatures are typical. Most of Seoul's precipitation falls in the summer monsoon period between June and September, as a part of East Asian monsoon season.
A prognostic chart is a map displaying the likely weather forecast for a future time. Such charts generated by atmospheric models as output from numerical weather prediction and contain a variety of information such as temperature, wind, precipitation and weather fronts. They can also indicate derived atmospheric fields such as vorticity, stability indices, or frontogenesis. Forecast errors need to be taken into account and can be determined either via absolute error, or by considering persistence and absolute error combined.

The climate of Seattle is temperate, classified in the warm-summer (in contrast to hot-summer) subtype of the Mediterranean zone by the most common climate classification although some sources put the city in the oceanic zone. It has cool, wet winters and warm, dry summers, covering characteristics of both. The climate is sometimes characterized as a "modified Mediterranean" climate because it is cooler and wetter than a "true" Mediterranean climate, but shares the characteristic dry summer and the associated reliance upon cooler-season precipitation. The city is part of USDA hardiness zone 9a, with surrounding pockets falling under 8b.














