Related Research Articles

Body identification is a subfield of forensic science that uses a variety of scientific and non-scientific methods to identify a body. Forensic purposes are served by rigorous scientific forensic identification techniques, but these are generally preceded by formal identification. This involves requesting a family member or friend of the victim to visually identify the body.

The Combined DNA Index System (CODIS) is the United States national DNA database created and maintained by the Federal Bureau of Investigation. CODIS consists of three levels of information; Local DNA Index Systems (LDIS) where DNA profiles originate, State DNA Index Systems (SDIS) which allows for laboratories within states to share information, and the National DNA Index System (NDIS) which allows states to compare DNA information with one another.
The University of North Texas Center for Human Identification is a national resource for the identification of missing and unidentified persons at the University of North Texas Health Science Center. UNTCHI combines the services of a forensic DNA laboratory, a forensic anthropology laboratory, and the Forensic Services Unit (FSU). The center operates the National Missing and Unidentified Persons System (NamUs) and Project EDAN which helps identify human remains.

Marcia Lenore Sossoman (King) (June 9, 1959 – April 22, 1981) was a 21-year-old Arkansas woman who was murdered in April 1981 and whose body was discovered in Troy, Ohio approximately 48 hours after her murder. Her body remained unidentified for 36 years before being identified via DNA analysis and genetic genealogy in April 2018. King was one of the first unidentified decedents to be identified via this method of forensic investigation.

Vernon County Jane Doe is an American murder victim whose body was found on May 4, 1984. Her identity remains unknown. Her hands had been removed, likely to prevent identification by means of fingerprinting.
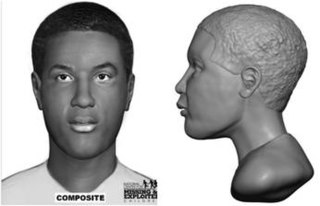
John Ingram Brandenburg Jr. and Keith Lavell Bibbs were two young murder victims formerly known as the Newton County John Does whose remains were discovered by mushroom foragers in Lake Village, Newton County, Indiana, on October 18 and 19, 1983. Both victims were discovered alongside two other murder victims whose bodies were identified within months of their discovery. All four were victims of the serial killer Larry Eyler.

Sahara Sue is the informal nickname given to a murder victim who was found in Las Vegas, Nevada, on August 14, 1979. Her identity is unknown. She was nicknamed "Sahara Sue" because her body was found near the Sahara Hotel in Las Vegas, at the intersection of Sahara and Las Vegas Boulevard. Recent developments indicate she may have used the name "Shawna" or "Shauna" when she was alive.

Perry County Jane Doe, also nicknamed "Girl with the Turquoise Jewelry" is an unidentified woman whose body was found on June 20, 1979, in Watts Township, Perry County, Pennsylvania, near the Juniata River. The cause of her death is not known, but it was considered to be suspicious by the authorities. Her name is still not known, despite efforts to identify her. She is the only unidentified decedent in the county.

Unidentified decedent or unidentified person is a term in American English used to describe a corpse of a person whose identity cannot be established by police and medical examiners. In many cases, it is several years before the identities of some UIDs are found, while in some cases, they are never identified. A UID may remain unidentified due to lack of evidence as well as absence of personal identification such as a driver's license. Where the remains have deteriorated or been mutilated to the point that the body is not easily recognized, a UID's face may be reconstructed to show what they had looked like before death. UIDs are often referred to by the placeholder names "John Doe" or "Jane Doe".
The Redhead murders is the media epithet used to refer to a series of unsolved homicides of redheaded females in the United States between October 1978 and 1992, believed to have been committed by an unidentified male serial killer. The murders believed to be related have occurred in states including Tennessee, Arkansas, Kentucky, Mississippi, Pennsylvania, and West Virginia. The murders may have continued until 1992. The victims, many remaining unidentified for years, were usually women with reddish hair, whose bodies were abandoned along major highways in the United States. Officials believe that the women were likely hitchhiking or may have engaged in sex work.

Sharon Lee Gallegos was a formerly unidentified American murder victim known as Little Miss Nobody whose body was found in Congress, Yavapai County, Arizona on July 31, 1960. Her remains were estimated to have been discovered within one to two weeks of the date of her murder. Due to the advanced state of decomposition of the child's remains, the specific cause of death of Gallegos has never been established, although her death has always been considered to be a homicide.
Patricia Spencer and Pamela Hobley were two American teenagers who went missing on Halloween, Friday, October 31, 1969 in Oscoda, Iosco County, Michigan after presumably committing truancy together, as they had both been seen walking in each other's company shortly before. The pair were aged 16 and 15, respectively, and "were not considered friends" at the time they disappeared. Their bodies were never recovered, yet it is believed by authorities that both of their lives had ended with homicide.

David Arthur Stack was an American man who was murdered while hitchhiking from his home in Broomfield, Colorado to California. Stack was murdered by an unknown assailant or assailants in Wendover, Utah. His body was found approximately one day after his murder in a landfill in rural Tooele County, although he remained an unidentified decedent for 39 years until 2015 when his body was identified via a comparison of both dental records and genetic testing.

Cynthia "Cindy" Gastelle was a formerly unidentified American murder victim who disappeared on April 3, 1980. Her body was found two years later, but remained unidentified for 30 years before matching of mitochondrial DNA entered into the national DNA database provided her identity.
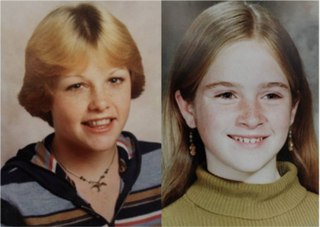
The murders of Kerry Ann Graham and Francine Marie Trimble are currently unsolved crimes that occurred in December 1978, when both girls—aged 15 and 14 respectively—disappeared after leaving their homes in Forestville, California, to visit a shopping mall in Santa Rosa. Their remains were discovered in July 1979 approximately 80 mi (130 km) north of Forestville, concealed within duct-taped garbage bags and buried within an embankment of a heavily overgrown woodland area located beside a remote section of Highway 20, 12 mi (19 km) from the city of Willits.

DNA Doe Project is an American nonprofit volunteer organization formed to identify unidentified deceased persons using forensic genealogy. Volunteers identify victims of automobile accidents, homicide, and unusual circumstances and persons who committed suicide under an alias. The group was founded in 2017 by Colleen M. Fitzpatrick and Margaret Press.
Margaret Ellen (Maggie) Fox was a 14-year-old American girl who vanished under suspicious circumstances in Burlington, New Jersey, in 1974.
Carl Koppelman is an American professional accountant and unpaid volunteer forensic sketch artist. Since 2009, Koppelman has drawn over 250 reconstructions and age progressions of missing and unidentified people.

Linda Marie Pagano, formerly known as Strongsville Jane Doe, was an American murder victim from Akron, Ohio who was an unidentified decedent for 44 years. Following an argument with her stepfather on September 1, 1974, Pagano left her stepfather's apartment and was never seen again. On February 5, 1975, partial skeletal remains of a white female were found by three boys in a park in Strongsville, Ohio. After remaining unidentified, the bones were buried in an unmarked grave. Due to a clerical error, the bones were never entered into databases of unidentified decedents, and the case was largely forgotten about. In 2016, a college student doing genealogy research of her own family rediscovered the unidentified body. After posting about it online, the case gained the attention of Carl Koppelman, a forensic sketch artist. The new attention to the case led to a connection being made by the Akron police, and in June 2018 the remains were conclusively identified as Linda Pagano.
References
- ↑ Augenstein, Seth (12 December 2017). "NamUs Law in New York Makes State 4th to Require Entries". Forensic Magazine. Retrieved 2 September 2019.
- ↑ Boncek, Marianna (August 2017). "NamUs and the Law (or lack thereof.) | Marianna Boncek" . Retrieved 2 September 2019.
- ↑ "'Francine's Law' for missing persons signed by Gov. Stitt". 2 News Oklahoma. 17 April 2019. Retrieved 11 December 2021.
- ↑ "About NamUs". www.namus.gov. Retrieved 2018-06-15.