
Dhubri District (Pron:ˈdʊbri) is an administrative district in the Indian state of Assam. Included within the Kamatapur Autonomous Council, the district headquarters are located at Dhubri town which is situated ~290 km from Guwahati. This was also the headquarters of erstwhile undivided Goalpara district which was created in 1876 by the British government. In 1983, Goalpara district was divided into four districts and Dhubri is one among those. Dhubri district is one among the many Muslim-majority districts of Assam. In 2016, Dhubri was divided again to form South Salmara-Mankachar District.

Gee's golden langur, also known as simply the golden langur, is an Old World monkey found in a small region of Western Assam, India and the neighboring foothills of the Black Mountains of Bhutan. Long considered sacred by many Himalayan people, the golden langur was first brought to the attention of the Western world by the naturalist Edward Pritchard Gee in the 1950s. Adult males have a cream to golden coat with darker flanks while the females and juveniles are lighter. The golden langur has a black face and a long tail up to 50 cm (19.69 in) in length. It lives in high trees and has a herbivorous diet of fruits, leaves, seeds, buds, and flowers. The average group size is eight individuals, with a ratio of several females to each adult male. It is one of the most endangered primate species of India and Bhutan.

Dhubri is a town and the administrative centre of Dhubri district in the Indian state of Assam. It is an old town on the bank of the Brahmaputra river, with historical significance. In 1883, the town was first constituted as a Municipal Board under the British regime. It is situated about 277.4 kilometres (172 mi) west from Dispur, the state capital of Assam.

The Brahmaputra Valley semi-evergreen forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of Northeastern India, southern Bhutan and adjacent Bangladesh.
Edward Pritchard Gee (1904–1968) was a Cambridge educated, Anglo-Indian tea-planter and an amateur naturalist in Assam, India. He is credited with the 1953 discovery of Gee's golden langur. He is notable as an early influential wildlife conservationist, especially for his 1959 and 1963 surveys and recommendations resulting in the creation of Chitwan National Park, the first of nine national parks in Nepal.

Manas National Park is a national park, Project Tiger reserve, and an elephant reserve in Assam, India. Located in the Himalayan foothills, it borders the Royal Manas National Park in Bhutan. The park is known for its rare and endangered endemic wildlife such as the Assam roofed turtle, hispid hare, golden langur and pygmy hog. Manas is also famous for its population of the wild water buffalo. Because of its exceptional biodiversity, scenery, and variety of habitats, Manas National Park is a biosphere reserve and a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
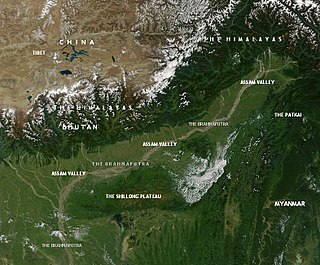
This article discusses the geological origin, geomorphic characteristics, and climate of the northeastern Indian state of Assam. Extending from 89° 42′ E to 96° E longitude and 24° 8′ N to 28° 2′ N latitude, it has an area of 78,438 km2, similar to that of Ireland or Austria.

Assam is the main and oldest state in the North-East Region of India and as the gateway to the rest of the Seven Sister States. The land of red river and blue hills, Assam comprises three main geographical areas: the Brahmaputra Valley which stretching along the length of the Brahmaputra river, the Barak Valley extending like a tail, and the intervening Karbi Plateau and North Cachar Hills. Assam shares its border with Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Tripura, Mizoram and West Bengal; and there are National Highways leading to their capital cities. It also shares international borders with Bhutan and Bangladesh and is very close to Myanmar. In ancient times Assam was known as Pragjyotisha or Pragjyotishpura, and Kamarupa.

The Kingdom of Bhutan is a small, landlocked nation nestled in the southern slopes of the Eastern Himalaya. To its north lies the Tibet Autonomous Region of China and to the west, south and east lies the Indian states of Sikkim, Bengal, Assam and Arunachal Pradesh.
Pakke Tiger Reserve, is a Project Tiger reserve in the East Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh in Northeast India. The 862 km2 (333 sq mi) reserve is protected by the Department of Environment and Forest of Arunachal Pradesh. It was known as Pakhui Tiger Reserve, but renamed in April 2001 by the Governor of Arunachal Pradesh. It has won India Biodiversity Award 2016 in the category of 'Conservation of threatened species' for its Hornbill Nest Adoption Programme.

Chakrashila Wildlife Sanctuary is a wildlife sanctuary falling under Kokrajhar district and some adjacent areas of Dhubri district of Assam, India. It is famous for the golden langur and is the second protected habitat for golden langurs in India.

Anwaruddin Choudhury is an Indian naturalist, noted for his expertise on the fauna of North-East India.

Dehing Patkai National Park is a national park in the Dibrugarh and Tinsukia districts of Assam covering an area of 231.65 km2 (89.44 sq mi) of rainforest. It was declared a wildlife sanctuary on 13 June 2004. On 13 December 2020, the Government of Assam upgraded it into a national park. On 9 June 2021, the Forest Department of Assam officially notified it as a national park. It is located in the Dehing Patkai Landscape which is a dipterocarp-dominated lowland rainforest. The rainforest stretches for more than 575 km2 (222 sq mi) in the districts of Dibrugarh, Tinsukia and Charaideo. The forest further spreads over in the Tirap and Changlang districts of Arunachal Pradesh. Dehing Patkai National Park harbours the largest stretch of lowland rainforests in India. Dehing Patkai Wildlife Sanctuary was declared as Dehing Patkai Elephant Reserve under Project Elephant. Dehing-Patkai as a potential wildlife sanctuary was identified in late 1980s during a primate survey as "Upper Dehing Wildlife Sanctuary". Subsequently during a study on white-winged wood duck in early 1990s, it was discovered as a globally important site for this duck and recommended to be upgraded to "Upper Dehing National Park".
Assam – 16th largest, 15th most populous and 26th most literate state of the 28 states of the democratic Republic of India. Assam is at 14th position in life expectancy and 8th in female-to-male sex ratio. Assam is the 21st most media exposed states in India. The Economy of Assam is largely agriculture based with 69% of the population engaged in it. Growth rate of Assam's income has not kept pace with that of India's during the Post-British Era; differences increased rapidly since the 1970s. While the Indian economy grew at 6 percent per annum over the period of 1981 to 2000, the same of Assam's grew only by 3.3 percent.

Kakoijana reserved forest is located near Abhayapuri in Bongaigaon district of Assam. The forest is famous for golden langur. The forest is 17.24 km2.
Ultapani Reserve Forest is a biodiversity area situated under Holtugaon Forest Division of Manas Biosphere reserve situated in Kokrajhar district, Assam, India.
Salkocha is a village and gram panchayat in the town of Chapar in the Dhubri district of the state of Assam, India. It is part of the Bilasipara East Assam Legislative Assembly constituency and the Dhubri Lok Sabha constituency.
Kashmira Kakati is a wildlife biologist and environmental activist working the North Eastern forests of India. In 2010, she announced the discovery of the presence of seven species of wild cats in the Jeypore-Dehing forests in Assam. Her work using camera traps to find wild cats was featured in the first episode of the BBC documentary Lost Land of the Tiger (2010).
Dehing Patkai Landscape, located in the Upper Assam, stretches for over roughly 600 square kilometres and comprises three large blocks of forests and several forest fragments. The forest is classified as a lowland Tropical Wet Evergreen Forest (Dipterocarpus-Mesua). It falls under Indo-Burma Biodiversity Hotspot. Due to its biodiversity and significance for elephant habitat, parts of the landscape are recognised as Dehing Patkai Elephant Reserve and 111 km2 is protected as the Dehing Patkai Wildlife Sanctuary since 2004.

Raimona National Park is located in extreme western part of Assam, India. It is spread across Gossaigaon and Kokrajhar subdivisions of Kokrajhar district of Bodoland Territorial Region.














