
Kennewick Man or Ancient One was a Native American man who lived during the early Holocene, whose skeletal remains were found washed out on a bank of the Columbia River in Kennewick, Washington, on July 28, 1996. Radiocarbon tests show the man lived about 8,400 to 8,690 years Before Present, making his skeleton one of the most complete ever found this old in the Americas, and thus of high scientific interest for understanding the peopling of the Americas.
Neanderthals became extinct around 40,000 years ago. Hypotheses on the causes of the extinction include violence, transmission of diseases from modern humans which Neanderthals had no immunity to, competitive replacement, extinction by interbreeding with early modern human populations, natural catastrophes, climate change and inbreeding depression. It is likely that multiple factors caused the demise of an already low population.

Alois Ferdinand Hrdlička, after 1918 changed to Aleš Hrdlička, was a Czech anthropologist who lived in the United States after his family had moved there in 1881. He was born in Humpolec, Bohemia.
John Darnton is an American journalist who wrote for the New York Times. He is a two-time winner of the Polk Award, of which he is now the curator, and the 1982 Pulitzer Prize for International Reporting. He also moonlights as a novelist, writing scientific and medical thrillers.

Iceman is a 1984 American sci-fi drama film from Universal Pictures directed by Fred Schepisi, written by John Drimmer and Chip Proser, and starring Timothy Hutton, Lindsay Crouse, and John Lone. The film follows the discovery of a prehistoric Neanderthal caveman frozen in ice and what happens after scientists are able to bring him back to life. It was filmed in color with Dolby sound and has a running time of 100 minutes. The DVD version was released in 2004.

James Paul Czajkowski, better known by his pen name of James Rollins, is an American veterinarian and writer of action-adventure/thriller, mystery, and techno-thriller novels who gave up his veterinary practice in Sacramento, California to be a full-time author. Rollins' experiences and expertise as an amateur spelunker and a certified scuba diver have provided content for some of his novels, which are often set in underground or underwater locations. Under the pen name James Clemens, he has also published fantasy novels, such as Wit'ch Fire, Wit'ch Storm, Wit'ch War, Wit'ch Gate, Wit'ch Star, Shadowfall (2005), and Hinterland (2006).

Return To Eden is a 1988 science fiction novel by American writer Harry Harrison.

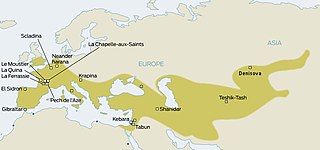
La Ferrassie 1 (LF1) is a male Neanderthal skeleton estimated to be 58–50,000 years old. It was discovered at the La Ferrassie site in France by Louis Capitan and Denis Peyrony in 1909. The skull is the most complete Neanderthal skull ever found. With a cranial capacity of 1641 cm3, it is the second largest hominid skull ever discovered, after Amud 1.
Neanderthals have been depicted in popular culture since the early 20th century. Early depictions conveyed and perpetuated notions of proverbially crude, low-browed cavemen; since the latter part of the 20th century, some depictions have modeled more sympathetic reconstructions of the genus Homo in the Middle Paleolithic era. In popular idiom, people sometimes use the word "Neanderthal" as an insult - to suggest that a person so designated combines a deficiency in intelligence and a tendency to use brute force. The term may also imply that a person is old-fashioned or attached to outdated ideas, much in the same way as the terms "dinosaur" or "Yahoo".

Snakeman, also known as The Snake King, is a Syfy original film that premiered April 8, 2005, on the Syfy channel.
The Neanderthal genome project is an effort of a group of scientists to sequence the Neanderthal genome, founded in July 2006.

Hermann Schaaffhausen was a German anatomist, anthropologist, and paleoanthropologist.

War Before Civilization: the Myth of the Peaceful Savage is a book by Lawrence H. Keeley, a professor of archaeology at the University of Illinois at Chicago who specialized in prehistoric Europe. The book deals with warfare conducted throughout human history by societies with little technology. In the book, Keeley aims to stop the apparent trend in seeing modern civilization as bad, by setting out to prove that prehistoric societies were often violent and engaged in frequent warfare that was highly destructive to the cultures involved.

Mikhail Mikhaylovich Gerasimov was a Soviet archaeologist and anthropologist who discovered the Mal'ta–Buret' culture and developed the first technique of forensic sculpture based on findings of anthropology, archaeology, paleontology, and forensic science. He studied the skulls and meticulously reconstructed the faces of more than 200 people, ranging from the earliest excavated homo sapiens and neanderthals, to the Middle Ages' monarchs and dignitaries, including emperor Timur (Tamerlane), Yaroslav the Wise, Ivan the Terrible, and Friedrich Schiller.

The Tukudeka or Mountain Sheepeaters are a band of Shoshone within the Eastern Shoshone and the Northern Shoshone. Before the reservation era, they traditionally lived in the central Sawtooth Range of Idaho and the mountains of what is now northwest Wyoming. Bands were very fluid and nomadic, and they often interacted with and intermarried other bands of Shoshone. Today the Tukudeka are enrolled in the federally recognized Shoshone-Bannock Tribes of the Fort Hall Reservation of Idaho and the Eastern Shoshone of the Wind River Indian Reservation in Wyoming.

Mugharet el-Zuttiyeh is a prehistoric archaeological site in Upper Galilee, Israel. It is situated 800 m (2,600 ft) from the Nahal Amud outlet, approximately 30 m (98 ft) above the wadi bed. It was found to house a fossil today known as the "Galilee skull" or "The Yabrudian Man".

Levkas Man is a thriller novel by British author Hammond Innes published in 1971. It tells the story of a doctor who goes to the Greek island of Lefkada (Levkas) with his adopted son to prove a theory about prehistoric man.

Engis 2 refers to part of an assemblage, discovered in 1829 by Dutch physician and naturalist Philippe-Charles Schmerling in the lower of the Schmerling Caves. The pieces that make up Engis 2 are a partially preserved calvaria (cranium) and associated fragments of an upper and a lower jaw, a maxillary bone and an upper incisor tooth of a two to three year old Neanderthal child. The Schmerling Caves are situated just north of the Belgian municipality Engis, whence the name of this group. In 1833 Schmerling described and publicized the find, which included animal bones and stone tools. Recognizing their old age, he associated them with the "Ethiopian Type" of the diluvial period. Although it was not recognized as such until 1936, the publication represents the first scientific description of a Neanderthal fossil.

Krapina Neanderthal site, also known as Hušnjakovo Hill is a Paleolithic archaeological site located near Krapina, Croatia.















