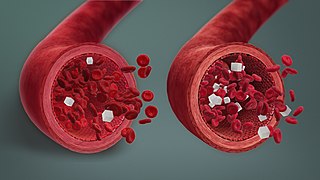
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L), symptoms associated with hypoglycemia, and resolution of symptoms when blood sugar returns to normal. Hypoglycemia may result in headache, tiredness, clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, fast heart rate, sweating, shakiness, nervousness, hunger, loss of consciousness, seizures, or death. Symptoms typically come on quickly.

An insulin pump is a medical device used for the administration of insulin in the treatment of diabetes mellitus, also known as continuous subcutaneous insulin therapy. The device configuration may vary depending on design. A traditional pump includes:

Blood glucose monitoring is the use of a glucose meter for testing the concentration of glucose in the blood (glycemia). Particularly important in diabetes management, a blood glucose test is typically performed by piercing the skin to draw blood, then applying the blood to a chemically active disposable 'test-strip'. The other main option is continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). Different manufacturers use different technology, but most systems measure an electrical characteristic and use this to determine the glucose level in the blood. Skin-prick methods measure capillary blood glucose, whereas CGM correlates interstitial fluid glucose level to blood glucose level. Measurements may occur after fasting or at random nonfasting intervals, each of which informs diagnosis or monitoring in different ways.

The blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, blood glucose level, or glycemia is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis.
Glycated hemoglobin, also known as HbA1c, glycohemoglobin, glycosylated hemoglobin, or simply A1c, is a form of hemoglobin (Hb) that is chemically linked to a sugar. Most monosaccharides, including glucose, galactose and fructose, spontaneously bond with hemoglobin when present in the bloodstream. However, glucose is only 21% as likely to do so as galactose and 13% as likely to do so as fructose, which may explain why glucose is used as the primary metabolic fuel in humans.

A glucose meter, also referred to as a "glucometer", is a medical device for determining the approximate concentration of glucose in the blood. It can also be a strip of glucose paper dipped into a substance and measured to the glucose chart. It is a key element of glucose testing, including home blood glucose monitoring (HBGM) performed by people with diabetes mellitus or hypoglycemia. A small drop of blood, obtained from slightly piercing a fingertip with a lancet, is placed on a disposable test strip that the meter reads and uses to calculate the blood glucose level. The meter then displays the level in units of mg/dL or mmol/L.
The term diabetes includes several different metabolic disorders that all, if left untreated, result in abnormally high concentrations of a sugar called glucose in the blood. Diabetes mellitus type 1 results when the pancreas no longer produces significant amounts of the hormone insulin, usually owing to the autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. Diabetes mellitus type 2, in contrast, is now thought to result from autoimmune attacks on the pancreas and/or insulin resistance. The pancreas of a person with type 2 diabetes may be producing normal or even abnormally large amounts of insulin. Other forms of diabetes mellitus, such as the various forms of maturity-onset diabetes of the young, may represent some combination of insufficient insulin production and insulin resistance. Some degree of insulin resistance may also be present in a person with type 1 diabetes.
Many types of glucose tests exist and they can be used to estimate blood sugar levels at a given time or, over a longer period of time, to obtain average levels or to see how fast body is able to normalize changed glucose levels. Eating food for example leads to elevated blood sugar levels. In healthy people, these levels quickly return to normal via increased cellular glucose uptake which is primarily mediated by increase in blood insulin levels.
Automated insulin delivery systems are automated systems designed to assist people with insulin-requiring diabetes, by automatically adjusting insulin delivery in response to blood glucose levels. Currently available systems can only deliver a single hormone—insulin. Other systems currently in development aim to improve on current systems by adding one or more additional hormones that can be delivered as needed, providing something closer to the endocrine functionality of the pancreas.
Insulin detemir, sold under the brand name Levemir among others, is a long-acting modified form of medical insulin used to treat both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. It is used by injection under the skin. It is effective for up to 24 hours.
Noninvasive glucose monitoring (NIGM) is the measurement of blood glucose levels, required by people with diabetes to prevent both chronic and acute complications from the disease, without drawing blood, puncturing the skin, or causing pain or trauma. The search for a successful technique began about 1975 and has continued to the present without a clinically or commercially viable product.
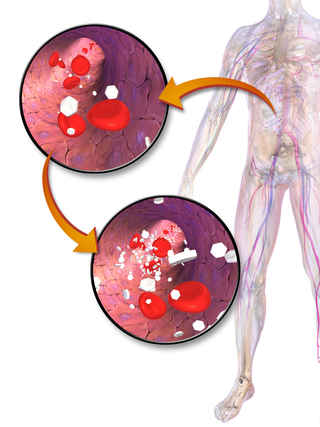
Prediabetes is a component of metabolic syndrome and is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels that fall below the threshold to diagnose diabetes mellitus. It usually does not cause symptoms but people with prediabetes often have obesity, dyslipidemia with high triglycerides and/or low HDL cholesterol, and hypertension. It is also associated with increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Prediabetes is more accurately considered an early stage of diabetes as health complications associated with type 2 diabetes often occur before the diagnosis of diabetes.
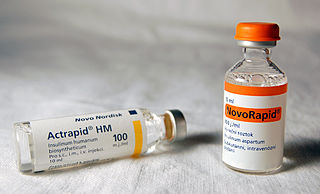
As a medication, insulin is any pharmaceutical preparation of the protein hormone insulin that is used to treat high blood glucose. Such conditions include type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and complications of diabetes such as diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic states. Insulin is also used along with glucose to treat hyperkalemia. Typically it is given by injection under the skin, but some forms may also be used by injection into a vein or muscle. There are various types of insulin, suitable for various time spans. The types are often all called insulin in the broad sense, although in a more precise sense, insulin is identical to the naturally occurring molecule whereas insulin analogues have slightly different molecules that allow for modified time of action. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2021, it was the 179th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2 million prescriptions.
DexCom, Inc. is a company that develops, manufactures, produces, and distributes continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems for diabetes management. It operates internationally with headquarters in San Diego, California, and has manufacturing facilities in Mesa, Arizona and Batu Kawan, Malaysia.
Tandem Diabetes Care is an American medical device manufacturer based in San Diego, California. The company develops medical technologies for the treatment of diabetes and specifically insulin infusion therapy.
Ambulatory glucose profile (AGP) is a single-page, standardized report for interpreting a patient's daily glucose and insulin patterns. AGP provides both graphic and quantitative characterizations of daily glucose patterns. First developed by Drs. Roger Mazze and David Rodbard, with colleagues at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in 1987, AGP was initially used for the representation of episodic self-monitored blood glucose (SMBG). The first version included a glucose median and inter-quartile ranges graphed as a 24-hour day. Dr. Mazze brought the original AGP to the International Diabetes Center (IDC) in the late 1980s. Since then, IDC has built the AGP into the internationally recognized standard for glucose pattern reporting.
GlySens, a biomedical technology company, is a privately owned corporation developing a long term internal continuous glucose monitor in order to effectively manage and observe glucose levels in real time. The GlySens ICGM system is the world's first surgically implanted continuous glucose monitoring system to demonstrate an 18-month performance in a preclinical setting. GlySens Incorporated was founded in 1998 by David A. Gough and Joseph Lucisano, a bioengineering graduate at the University of California, San Diego. The implanted continuous glucose monitoring system uses an internal sensor equipped with electrochemical detectors to measure glucose readings via a chemical reaction between enzymes and oxygen.
Nightscout is a free and open-source project, and associated social movement, that enables accessing and working with continuous glucose monitor (CGM) data. Nightscout software aims to give users access to their real time blood sugar data by putting this data in the cloud. In addition to browser-based data visualization, Nightscout can also be used to review data from a phone or smartwatch, or to remotely monitor CGM data for individuals with type 1 diabetes. Associated with Nightscout software is a broader "CGM in the Cloud" social movement, supporting individuals seeking to access and use realtime CGM data through commercial and DIY approaches.
The Open Artificial Pancreas System (OpenAPS) project is a free and open-source project that aims to make basic artificial pancreas system (APS) technology available to everyone. The OpenAPS project was designed with the idea of quickly getting the APS technology to more people using a direct approach, rather than waiting for clinical trials to be completed and regulatory approval to be granted.

A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) is a device used for monitoring blood glucose on a continual basis instead of monitoring glucose levels periodically by drawing a drop of blood from a finger. This is known as continuous glucose monitoring. CGMs are used by people who treat their diabetes with insulin, for example people with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, or other types of diabetes, such as gestational diabetes.








