
The macrolides are a class of natural products that consist of a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. The lactone rings are usually 14-, 15-, or 16-membered. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. Some macrolides have antibiotic or antifungal activity and are used as pharmaceutical drugs. Macrolides are bacteriostatic in that they suppress or inhibit bacterial growth rather than killing bacteria completely.
Cerulenin is an antifungal antibiotic that inhibits fatty acid and steroid biosynthesis. It was the first natural product antibiotic known to inhibit lipid synthesis. In fatty acid synthesis, it has been reported to bind in equimolar ratio to b-keto-acyl-ACP synthase, one of the seven moieties of fatty acid synthase, blocking the interaction of malonyl-CoA. It also has the related activity of stimulating fatty acid oxidation through the activation of CPT1, another enzyme normally inhibited by malonyl-CoA. Inhibition involves covalent thioacylation that permanently inactivates the enzymes. These two behaviors may increase the availability of energy in the form of ATP, perhaps sensed by AMPK, in the hypothalamus.

The avermectins are a series of drugs and pesticides used to treat parasitic worms and insect pests. They are a group of 16-membered macrocyclic lactone derivatives with potent anthelmintic and insecticidal properties. These naturally occurring compounds are generated as fermentation products by Streptomyces avermitilis, a soil actinomycete. Eight different avermectins were isolated in four pairs of homologue compounds, with a major (a-component) and minor (b-component) component usually in ratios of 80:20 to 90:10. Other anthelmintics derived from the avermectins include ivermectin, selamectin, doramectin, eprinomectin, and abamectin.

Gliotoxin is a sulfur-containing mycotoxin that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines produced by several species of fungi, especially those of marine origin. It is the most prominent member of the epipolythiopiperazines, a large class of natural products featuring a diketopiperazine with di- or polysulfide linkage. These highly bioactive compounds have been the subject of numerous studies aimed at new therapeutics. Gliotoxin was originally isolated from Gliocladium fimbriatum, and was named accordingly. It is an epipolythiodioxopiperazine metabolite.
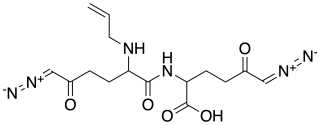
Alazopeptin is an antibiotic, with moderate anti-trypanosomal and antitumor activity. It was originally isolated from Streptacidiphilus griseoplanus, sourced from soil near Williamsburg, Iowa. It is also isolated from Kitasatospora azatica. It is still largely produced via fermentation broths of that organism. Structurally, alazopeptin is a tripeptide and contains 2 molecules of 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine and one molecule of L-alanine. In 2021 the biosynthetic pathway of alazopeptin was elucidated.
Streptomyces avermitilis is a species of bacteria in the genus Streptomyces. This bacterium was discovered by Satoshi Ōmura in Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan.

Andrastin A is a farnesyltransferase inhibitor isolate of Penicillium species including Penicillium albocoremium and Penicillium roqueforti. It has been produced bio-synthetically by porting the relevant gene sequence into Aspergillus oryzae.

Guadinomines are anti-infective compounds produced by Streptomyces sp. K01-0509. Guadinomine B is the most potent known inhibitor of the Type III secretion system (TTSS) of Gram-negative bacteria. The guadinomine (gdn) biosynthetic gene cluster includes 26 open reading frames spanning 51.2 kb. Streptomyces sp. K01-0509 produces several derivatives named guadinomines A, B, C1, C2, D, and guadinomic acid.
Fungal isolates have been researched for decades. Because fungi often exist in thin mycelial monolayers, with no protective shell, immune system, and limited mobility, they have developed the ability to synthesize a variety of unusual compounds for survival. Researchers have discovered fungal isolates with anticancer, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory, and other bio-active properties. The first statins, β-Lactam antibiotics, as well as a few important antifungals, were discovered in fungi.
Medicinal fungi are fungi that contain metabolites or can be induced to produce metabolites through biotechnology to develop prescription drugs. Compounds successfully developed into drugs or under research include antibiotics, anti-cancer drugs, cholesterol and ergosterol synthesis inhibitors, psychotropic drugs, immunosuppressants and fungicides.
Penicillium herquei is an anamorph, filamentous species of the genus of Penicillium which produces citreorosein, emodin, hualyzin, herquline B, janthinone, citrinin and duclauxin,.
Penicillium pinophilum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from a radio set in Papua New Guinea. Penicillium pinophilum produces 3-O-methylfunicone and mycophenolic acid

Satoshi Ōmura is a Japanese biochemist. He is known for the discovery and development of hundreds of pharmaceuticals originally occurring in microorganisms. In 2015, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine jointly with William C. Campbell for their role in the discovery of avermectins and ivermectin, the world's first endectocide and a safe and highly effective microfilaricide. It is believed that the large molecular size of ivermectin prevents it from crossing the blood/aqueous humour barrier, and renders the drug an important treatment of helminthically-derived blindness.
Streptomyces aculeolatus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from the Tottori prefecture in Japan. Streptomyces aculeolatus produces naphthablin.
Streptomyces fumanus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from alluvial soil. Streptomyces fumanus produces dioxapyrrolomycin, pyrrolomycin G, pyrrolomycin H, pyrrolomycin I, pyrrolomycin J and fumaquinone.
Streptomyces actuosus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces actuosus produces nosiheptide and staurosporin.
Streptomyces nitrosporeus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from garden soil in Japan. Streptomyces nitrosporeus produces Benzastatin E, Benzastatin F, Benzastatin G Nitrosporeusine A and Nitrosporeusine B and the antibiotics nitrosporin and virantomycin and the inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme foroxymithine. Streptomyces nitrosporeus can degrade cellulose.
Streptomyces pseudovenezuelae is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from lead polluted soil in China. Streptomyces pseudovenezuelae produces chloramphenicol and setomimycin.
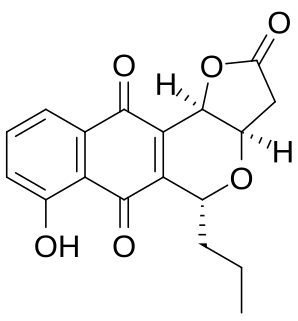
Frenolicin B is an antibiotic and antitumor agent with the molecular formula C18H16O6 which is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces roseofulvus. Frenolicin B is a selective inhibitor of glutaredoxin 3 and peroxiredoxin 1.

Spicamycin is an antibiotic with the molecular formula C30H51N7O7 which is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces alanosinicus. Spicamycin also shows antitumor activity.









