Related Research Articles

Alexander II was a king of Epirus, and the son of Pyrrhus and Lanassa, the daughter of the Sicilian tyrant Agathocles.
This article concerns the period 289 BC – 280 BC.
This article concerns the period 279 BC – 270 BC.

Berenice I was Queen of Egypt by marriage to Ptolemy I Soter. She became the second queen, after Eurydice, of the Ptolemaic dynasty of Egypt.

Hiero II was the Greek tyrant of Syracuse, Magna Graecia, from 275 to 215 BC, and the illegitimate son of a Syracusan noble, Hierocles, who claimed descent from Gelon. He was a former general of Pyrrhus of Epirus and an important figure of the First Punic War. He figures in the story of famed thinker Archimedes shouting "Eureka".

Pyrrhus was a Greek king and statesman of the Hellenistic period. He was king of the Greek tribe of Molossians, of the royal Aeacid house, and later he became king of Epirus. He was one of the strongest opponents of early Rome, and had been regarded as one of the greatest generals of antiquity. Several of his victorious battles caused him unacceptably heavy losses, from which the term "Pyrrhic victory" was coined.

Lysimachus was a Thessalian officer and successor of Alexander the Great, who in 306 BC, became King of Thrace, Asia Minor and Macedon.

Ptolemy Ceraunus was a member of the Ptolemaic dynasty and briefly king of Macedon. As the son of Ptolemy I Soter, he was originally heir to the throne of Ptolemaic Egypt, but he was displaced in favour of his younger brother Ptolemy II Philadelphus. He fled to King Lysimachus of Thrace and Macedon where he was involved in court intrigue that led to the fall of that kingdom in 281 BC to Seleucus I, whom he then assassinated. He then seized the throne of Macedon, which he ruled for seventeen months before his death in battle against the Gauls in early 279 BC. His epithet Ceraunus is Greek for "Thunderbolt" and referred to his impatient, impetuous, and destructive character.
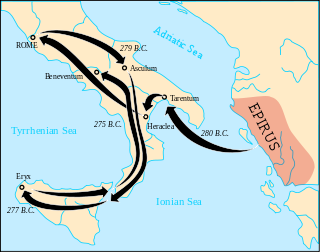
The Pyrrhic War was largely fought between the Roman Republic and Pyrrhus, the violent king of Epirus, who had been asked by the people of the Greek city of Tarentum in southern Italy to help them in their war against the Romans.

Bintanath was the firstborn daughter and later Great Royal Wife of the Egyptian Pharaoh Ramesses II.
Ptolemy, king of Epirus was the second son of Alexander II, king of Epirus, and Olympias, grandson of the great Pyrrhus and brother of Phthia of Macedon. He was named in honour of his late uncle Ptolemy. He succeeded to the throne on the death of his elder brother, Pyrrhus II of Epirus, but reigned only a very short time, having set out on a military expedition, during the course of which he fell sick and died or, according to Polyaenus, he was treasonably assassinated. The date of his reign cannot be fixed with certainty, but as he was a contemporary of Demetrius II, king of Macedonia, it may be placed between 239 and 229 BC. He was succeeded by Deidamia II or Pyrrhus III.

The city of Carthage was founded in the 9th century BC on the coast of Northwest Africa, in what is now Tunisia, as one of a number of Phoenician settlements in the western Mediterranean created to facilitate trade from the city of Tyre on the coast of what is now Lebanon. The name of both the city and the wider republic that grew out of it, Carthage developed into a significant trading empire throughout the Mediterranean. The date from which Carthage can be counted as an independent power cannot exactly be determined, and probably nothing distinguished Carthage from the other Phoenician colonies in Northwest Africa and the Mediterranean during 800–700 BC. By the end of the 7th century BC, Carthage was becoming one of the leading commercial centres of the West Mediterranean region. After a long conflict with the emerging Roman Republic, known as the Punic Wars, Rome finally destroyed Carthage in 146 BC. A Roman Carthage was established on the ruins of the first. Roman Carthage was eventually destroyed—its walls torn down, its water supply cut off, and its harbours made unusable—following its conquest by Arab invaders at the close of the 7th century. It was replaced by Tunis as the major regional centre, which has spread to include the ancient site of Carthage in a modern suburb.
Bircenna was an Illyrian princess and later an Epirote queen.

The Epirote League was an ancient Greek coalition, or koinon, of Epirote tribes.
Gelo was the eldest son of Hiero II, king of Syracuse, Magna Graecia.
Lanassa was a daughter of king Agathocles of Syracuse, Sicily, Magna Graecia, perhaps by his second wife Alcia. In 295 BC, Agathocles married Lanassa to King Pyrrhus of Epirus. Agathocles himself escorted his daughter with his fleet to Epirus to her groom. Lanassa brought the island of Corcyra as dowry into the marriage. The couple had two sons: Alexander and Helenus. However, Lanassa could not accept her husband's polygamous lifestyle, and so she left Pyrrhus in 291 BC, went to Corcyra, and offered this island as dowry to Demetrius I Poliorcetes, then king of Macedonia, if he would become her new husband. The courted diadoch came to Corcyra, married Lanassa, and occupied the island. After the death of Agathocles Pyrrhus, as former husband of Lanassa, asserted hereditary claims to Sicily. On the basis of these claims, the inhabitants of Syracuse asked Pyrrhus in 279 BC for assistance against Carthage.
Antigone was a Greek Macedonian noblewoman. Through her mother's second marriage she was a member of the Ptolemaic dynasty and through her marriage to Pyrrhus she was queen of Epirus.
Olympias was a queen consort and regent of Epirus.
Deidamia or Deidameia or Laodamia was the Queen regnant of Epirus in 234 - 233 BC. She was the daughter of Pyrrhus II of Epirus, king of Epirus.
Theoxena was a Greek Macedonian noblewoman. Through her mother's second marriage, she was a member of the Ptolemaic dynasty and through marriage was a queen of Sicily, Magna Graecia.
References
- Citations
- Sources
- Paus. vi. 12. § 3 ; Polyb. vii. 4. § 5 ; Justin. xxv iii. 3. § 4 ; Vales, ad Diod. Exc. p. 568.)
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Smith, William, ed. (1870). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology .
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Smith, William, ed. (1870). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology .{{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty |title= (help)