
5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand.
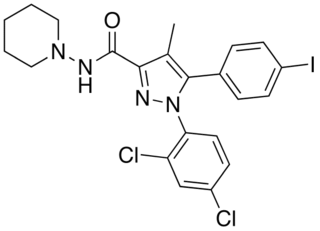
AM-251 is an inverse agonist at the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. AM-251 is structurally very close to rimonabant; both are biarylpyrazole cannabinoid receptor antagonists. In AM-251, the p-chloro group attached to the phenyl substituent at C-5 of the pyrazole ring is replaced with a p-iodo group. The resulting compound exhibits slightly better binding affinity for the CB1 receptor (with a Ki value of 7.5 nM) than rimonabant, which has a Ki value of 11.5 nM, AM-251 is, however, about two-fold more selective for the CB1 receptor when compared to rimonabant. Like rimonabant, it is additionally a μ-opioid receptor antagonist that attenuates analgesic effects.
SB-242084 is a psychoactive drug and research chemical which acts as a selective antagonist for the 5HT2C receptor. It has anxiolytic effects, and enhances dopamine signalling in the limbic system, as well as having complex effects on the dopamine release produced by cocaine, increasing it in some brain regions but reducing it in others. It has been shown to increase the effectiveness of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class of antidepressants, and may also reduce their side effects. In animal studies, SB-242084 produced stimulant-type activity and reinforcing effects, somewhat similar to but much weaker than cocaine or amphetamines.
ORG-20599 is a synthetic neuroactive steroid, with sedative effects resulting from its action as a GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator and, at higher concentrations, agonist. It was developed for use as an anaesthetic agent but was never marketed for this purpose, although it is still used in scientific research.

5-Iodowillardiine is a selective agonist for the kainate receptor, with only limited effects at the AMPA receptor. It is selective for kainate receptors composed of GluR5 subunits. It is an excitotoxic neurotoxin in vivo, but has proved highly useful for characterising the subtypes and function of the various kainate receptors in the brain and spinal cord.

2-Methyl-6-(phenylethynyl)pyridine (MPEP) is a research drug which was one of the first compounds found to act as a selective antagonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. After being originally patented as a liquid crystal for LCDs, it was developed by the pharmaceutical company Novartis in the late 1990s. It was found to produce neuroprotective effects following acute brain injury in animal studies, although it was unclear whether these results were purely from mGluR5 blockade as it also acts as a weak NMDA antagonist, and as a positive allosteric modulator of another subtype mGlu4, and there is also evidence for a functional interaction between mGluR5 and NMDA receptors in the same populations of neurons. It was also shown to produce antidepressant and anxiolytic effects in animals, and to reduce the effects of morphine withdrawal, most likely due to direct interaction between mGluR5 and the μ-opioid receptor.

SB-699551 is a drug which was the first compound developed to act as a selective antagonist for the serotonin receptor 5-HT5A, with selectivity of around 100x over other serotonin receptor subtypes. Multiple therapeutic roles have been suggested for 5-HT5A ligands due to the presence of this receptor in several areas of the brain, but research is still at an early stage, In animal studies, SB-699551 was found to block cue-mediated responding to LSD, again suggesting an antipsychotic type of activity. It also reduces the viability of certain types of cancer cells in vitro, suggesting the 5-HT5A receptor as a possible target for novel chemotherapy drugs.

BW-723C86 is a tryptamine derivative drug which acts as a 5-HT2B receptor agonist. It has anxiolytic effects in animal studies, and is also used for investigating the function of the 5-HT2B receptor in a range of other tissues.

DCPG ((S)-3,4-DCPG) is a drug used in scientific research, which acts as a potent and subtype-selective agonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR8. It has anticonvulsant effects in animal studies, and has also been investigated as a possible treatment for hyperalgesia.

Dazopride (AHR-5531) is an antiemetic and gastroprokinetic agent of the benzamide class which was never marketed. It acts as a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist and 5-HT4 receptor agonist. In addition to its gastrointestinal effects, dazopride facilitates learning and memory in mice.
Gevotroline (WY-47,384) is an atypical antipsychotic with a tricyclic structure which was under development for the treatment of schizophrenia by Wyeth-Ayerst. It acts as a balanced, modest affinity D2 and 5-HT2 receptor antagonist and also possesses high affinity for the sigma receptor. It was well tolerated and showed efficacy in phase II clinical trials but was never marketed.
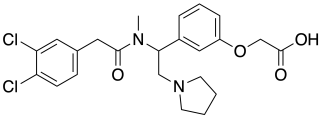
ICI-204,448 is a drug which acts as a potent and peripherally selective κ-opioid agonist, with possible uses in the treatment of heart attack as well as anti-itching effects. It is used in research to distinguish centrally from peripherally mediated kappa opioid receptor effects.

Ro10-5824 is a drug which acts as a dopamine receptor partial agonist selective for the D4 subtype, and has nootropic effects in animal studies.

Quinelorane is a drug which acts as a dopamine agonist for the D2 and D3 receptor.
Besonprodil (CI-1041) is a drug which acts as an NMDA antagonist, selective for the NR2B subunit. It is under development as a supplemental medication for Parkinson's disease, and has been shown in animals to be effective in counteracting the dyskinesias associated with long term treatment with levodopa and related drugs.

PNU-142633 is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of migraine. It exerts its effect as a selective, high affinity 5-HT1D receptor antagonist. PNU-142633 is well tolerated after oral administration.

ST-1936 (2-methyl-5-chloro-N,N-dimethyltryptamine) is a tryptamine derivative which is used in scientific research. It acts as a selective 5-HT6 receptor agonist, with a Ki of 13 nM, and much weaker action at 5-HT2B and 5-HT7 subtypes. In animal studies it has been found to increase dopamine and noradrenaline mediated signalling but decreases glutamatergic transmission, and has antidepressant effects.

SB-243213 is a research chemical which acts as a selective inverse agonist for the 5HT2C receptor and has anxiolytic effects. It has better than 100x selectivity for 5-HT2C over all other receptor subtypes tested, and a longer duration of action compared to older 5-HT2C antagonist ligands.

AZD 9272 is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. It was unsuccessful in human trials as an analgesic, but continues to be widely used in research especially as its radiolabelled forms.
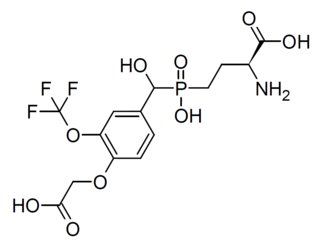
LSP2-9166 is a drug which acts as a selective agonist for the group III metabotropic glutamate receptors, with a reasonably potent EC50 of 70nM at mGluR4 and 220nM at mGluR7, and weaker activity of 1380nM at mGluR6 and 4800nM at mGluR8. It has anticonvulsant effects in animal studies, and reduces self-administration of various addictive drugs.


















