
New Zealand literature is literature, both oral and written, produced by the people of New Zealand. It often deals with New Zealand themes, people or places, is written predominantly in New Zealand English, and features Māori culture and the use of the Māori language. Before the arrival and settlement of Europeans in New Zealand in the 19th century, Māori culture had a strong oral tradition. Early European settlers wrote about their experiences travelling and exploring New Zealand. The concept of a "New Zealand literature", as distinct from English literature, did not originate until the 20th century, when authors began exploring themes of landscape, isolation, and the emerging New Zealand national identity. Māori writers became more prominent in the latter half of the 20th century, and Māori language and culture have become an increasingly important part of New Zealand literature.

The Chatham Islands are an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean about 800 km (430 nmi) east of New Zealand's South Island, administered as part of New Zealand, and consisting of about 10 islands within an approximate 60 km (30 nmi) radius, the largest of which are Chatham Island and Pitt Island (Rangiauria). They include New Zealand's easternmost point, the Forty-Fours. Some of the islands, formerly cleared for farming, are now preserved as nature reserves to conserve some of the unique flora and fauna.

The Moriori are the first settlers of the Chatham Islands. Moriori are Polynesians who came from the New Zealand mainland around 1500 CE, which was close to the time of the shift from the archaic to the classic period of Polynesian Māori culture on the mainland. Oral tradition records migration to the Chathams in the 16th century. The settlers' culture diverged from mainland Māori, and they developed a distinct Moriori language, mythology, artistic expression and way of life. Currently there are around 700 people who identify as Moriori, most of whom no longer live on the Chatham Islands. During the late 19th century some prominent anthropologists proposed that Moriori were pre-Māori settlers of mainland New Zealand, and possibly Melanesian in origin; this hypothesis has been discredited by archaeologists since the early 20th century, but continued to be referred to by critics of the Treaty of Waitangi settlement process into the 21st.

Witi Tame Ihimaera-Smiler is a New Zealand author. Raised in the small town of Waituhi, he decided to become a writer as a teenager after being convinced that Māori people were ignored or mischaracterised in literature. He was the first Māori writer to publish a collection of short stories, with Pounamu, Pounamu (1972), and the first to publish a novel, with Tangi (1973). After his early works, he took a ten-year break from writing, during which he focused on editing an anthology of Māori writing in English.

Michael King was a New Zealand historian, author, and biographer. He wrote or edited over 30 books on New Zealand topics, including the best-selling Penguin History of New Zealand, which was the most popular New Zealand book of 2004.

Christian Karlson "Karl" Stead is a New Zealand writer whose works include novels, poetry, short stories, and literary criticism. He is one of New Zealand's most well-known and internationally celebrated writers.

Patricia Frances Grace is a New Zealand writer of novels, short stories, and children's books. She began writing as a young adult, while working as a teacher. Her early short stories were published in magazines, leading to her becoming the first female Māori writer to publish a collection of short stories, Waiariki, in 1975. Her first novel, Mutuwhenua: The Moon Sleeps, followed in 1978.

Pitt Island is the second largest island in New Zealand's Chatham Islands, with an area of 65 square kilometres (25 sq mi). It lies about 770 kilometres (480 mi) to the east of New Zealand's main islands, and about 20 kilometres (12 mi) to the southeast of Chatham Island, from which it is separated by Pitt Strait. The island is hilly; its highest point rises to 241 metres (791 ft) above sea level. As of 2011, Pitt Island had a population of about 38 people.

Jacqueline Cecilia Sturm was a New Zealand poet, short story writer and librarian. She was one of the first Māori women to complete an undergraduate university degree, at Victoria University College, followed by a Masters of Arts degree in philosophy. She was also the first Māori writer to have her work published in an English anthology. Her short stories were published in several collections and student magazines in the 1950s and early 1960s, and in 1983 a women's publishing collective printed a collection of her short stories as The House of the Talking Cat. She continued to write short stories and poetry well into the early 2000s, and is regarded today as a pioneer of New Zealand literature.
Moriori, or ta rē Moriori, is a Polynesian language most closely related to New Zealand Māori. It is spoken by the Moriori, the indigenous people of New Zealand's Chatham Islands, an archipelago located east of the South Island. Moriori went extinct as a first language at the turn of the 20th century, but revitalisation attempts are ongoing.
The Polynesian Society is a non-profit organisation based at the University of Auckland, New Zealand, dedicated to the scholarly study of the history, ethnography and mythology of Oceania.

Edward Robert Tregear, Ordre des Palmes académiques was a New Zealand public servant and scholar. He was an architect of New Zealand's advanced social reforms and progressive labour legislation during the 1890s.
Ngāti Mutunga is a Māori iwi (tribe) of New Zealand, whose original tribal lands were in north Taranaki. They migrated, first to Wellington, and then to the Chatham Islands in the 1830s. The rohe of the iwi include the Chatham Islands and part of north Taranaki. The principal marae are at Urenui in Taranaki, and on the Chatham Islands.

The Ngāti Tama is a historic Māori tribe of present-day New Zealand. Their origins, according to Māori oral tradition, date back to Tama Ariki, the chief navigator on the Tokomaru waka. They are located in north Taranaki, around Poutama. River Mōhakatino marks their northern boundary with the Tainui and the Ngāti Maniapoto. The close geographical proximity of Tainui's Ngāti Toa of Kawhia and the Ngati Mutunga explains the long, continuous, and close relationship among these three tribes.
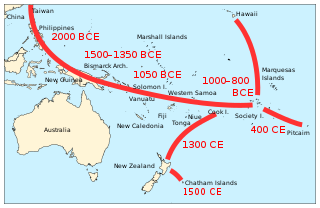
Since the early 1900s it has been accepted by archaeologists and anthropologists that Polynesians were the first ethnic group to settle in New Zealand. Before that time and until the 1920s, however, a small group of prominent anthropologists proposed that the Moriori people of the Chatham Islands represented a pre-Māori group of people from Melanesia, who once lived across all of New Zealand and were replaced by the Māori. While this claim was soon disproven by academics, it was widely incorporated into school textbooks during the 20th century, most notably in the School Journal. This theory has been followed by modern claims of a pre-Māori settlement of New Zealand by various ethnic groups. Today, such theories are considered to be pseudohistorical and negationist by scholars and historians.

Tina Makereti is a New Zealand novelist, essayist, and short story writer, editor and creative writing teacher. Her work has been widely published and she has been the recipient of writing residencies in New Zealand and overseas. Her book Once Upon a Time in Aotearoa won the inaugural fiction prize at the Ngā Kupu Ora Māori Book Awards in 2011, and Where the Rēkohu Bone Sings won the Ngā Kupu Ora Aotearoa Māori Book Award for Fiction in 2014.
The Storylines Notable Book Awards constitute an annual list of exceptional and outstanding books for children and young people published in New Zealand, by New Zealand authors and illustrators, during the previous calendar year.

Toby Morris is a New Zealand cartoonist, comics artist, illustrator and writer, best known for non-fiction online comics that often highlight social issues.
Eirlys Elisabeth Hunter is a writer and creative writing teacher in New Zealand. She was born in London, England.

The Moriori genocide was the mass murder, enslavement, and cannibalism of the Moriori people, the indigenous ethnic group of the Chatham Islands, by members of the mainland Māori New Zealand iwi Ngāti Mutunga and Ngāti Tama from 1835 to 1863. The invaders murdered around 300 Moriori and enslaved the remaining population. This, together with introduced Western diseases, caused the population to drop from 1,700 in 1835 to 100 in 1870. The last full-blood Moriori, Tommy Solomon, died in 1933. There remain just under a thousand people of mixed descent who identify as Moriori.


















