A mining accident is an accident that occurs during the process of mining minerals or metals. Thousands of miners die from mining accidents each year, especially from underground coal mining, although accidents also occur in hard rock mining. Coal mining is considered much more hazardous than hard rock mining due to flat-lying rock strata, generally incompetent rock, the presence of methane gas, and coal dust. Most of the deaths these days occur in developing countries, and rural parts of developed countries where safety measures are not practiced as fully. A mining disaster is an incident where there are five or more fatalities.
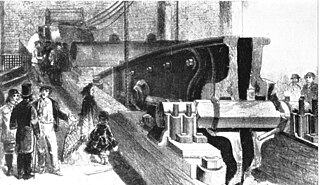
The Hartley Colliery disaster was a coal mining accident in Northumberland, England, that occurred on 16 January 1862 and resulted in the deaths of 204 men and children. The beam of the pit's pumping engine broke and fell down the shaft, trapping the men below. The disaster prompted a change in British law that required all collieries to have at least two independent means of escape.

The Oaks explosion, which happened at a coal mine in West Riding of Yorkshire on 12 December 1866, remains the worst mining disaster in England. A series of explosions caused by firedamp ripped through the underground workings at the Oaks Colliery at Hoyle Mill near Stairfoot in Barnsley killing 361 miners and rescuers. It was the worst mining disaster in the United Kingdom until the 1913 Senghenydd explosion in Wales.

Wet Earth Colliery was a coal mine located on the Manchester Coalfield, in Clifton, Greater Manchester. The colliery site is now the location of Clifton Country Park. The colliery has a unique place in British coal mining history; apart from being one of the earliest pits in the country, it is the place where engineer James Brindley made water run uphill.
The South Yorkshire Coalfield is so named from its position within Yorkshire. It covers most of South Yorkshire, West Yorkshire and a small part of North Yorkshire. The exposed coalfield outcrops in the Pennine foothills and dips under Permian rocks in the east. Its most famous coal seam is the Barnsley Bed. Coal has been mined from shallow seams and outcrops since medieval times and possibly earlier.

Chatterley Whitfield Colliery is a disused coal mine on the outskirts of Chell, Staffordshire in Stoke on Trent, England. It was the largest mine working the North Staffordshire Coalfield and was the first colliery in the UK to produce one million tons of saleable coal in a year.
The West Stanley Pit disasters refers to two explosions at the West Stanley colliery. West Stanley colliery was a coal mine near Stanley, with the mine opening in 1832 and closing in 1936. Over the years several seams were worked through four shafts: Kettledrum pit, Lamp pit, Mary pit and New pit. In 1882 an underground explosion killed 13 men and in 1909 another explosion killed 168 men.
Nantgarw Colliery was a coal mine and later developed Coking coal works, located in the village on Nantgarw, Mid Glamorgan, Wales located just north of Cardiff.

The Twin Shaft disaster occurred in the Newton Coal Company's Twin Shaft Colliery in Pittston, Pennsylvania, United States, on June 28, 1896, when a massive cave-in killed fifty-eight miners.

The Knockshinnoch disaster was a mining accident that occurred in September 1950 in the village of New Cumnock, Ayrshire, Scotland. A glaciated lake filled with liquid peat and moss flooded pit workings, trapping more than a hundred miners underground. For several days rescue teams worked non-stop to reach the trapped men. Most were eventually rescued three days later, but 13 died. The disaster was an international media event.

The Ingleton Coalfield is in North Yorkshire, close to its border with Lancashire in north-west England. Isolated from other coal-producing areas, it is one of the smallest coalfields in Great Britain.
Pendleton Colliery was a coal mine operating on the Manchester Coalfield after the late 1820s on Whit Lane in Pendleton, Salford, then in the historic county of Lancashire, England.
The Tarenni Colliery and its associated workings, are a series of coal mines and pits located between the villages of Godre'r Graig and Cilybebyll located in the valley of the River Tawe, in Neath Port Talbot county borough, South Wales.
Hapton Valley Colliery was a coal mine on the edge of Hapton near Burnley in Lancashire, England. Its first shafts were sunk in the early 1850s and it had a life of almost 130 years, surviving to be the last deep mine operating on the Burnley Coalfield.
Sodepur Area is one of the 14 operational areas of Eastern Coalfields Limited located mainly in Asansol subdivision of Paschim Bardhaman district and partly of Raghunathpur subdivision in Purulia district, both in the state of West Bengal, India.
Kunustoria Area is one of the 14 operational areas of Eastern Coalfields Limited located in Asansol subdivision of Paschim Bardhaman district in the state of West Bengal, India.
The Diglake Colliery Disaster, was a coal-mining disaster at what was Audley Colliery in Bignall End, North Staffordshire, on 14 January 1895. A flood of water rushed into the mine and caused the deaths of 77 miners. Only three bodies were recovered, with efforts to retrieve the dead hampered by floodwater. 73 bodies are still entombed underground.
The Hill End Colliery fire was an underground coal-seam fire. it burned from, at latest, August 1930 to at least early 1945, and most probably as late as June 1949. The impact of the fire was magnified by its close proximity to the mining town of Cessnock, New South Wales, Australia. The worst and most spectacular outbreak of the fire occurred on 8, 9 and 10 March 1933.








