
The Australian Aboriginal languages consist of around 290–363 languages belonging to an estimated 28 language families and isolates, spoken by Aboriginal Australians of mainland Australia and a few nearby islands. The relationships between these languages are not clear at present. Despite this uncertainty, the Indigenous Australian languages are collectively covered by the technical term "Australian languages", or the "Australian family".
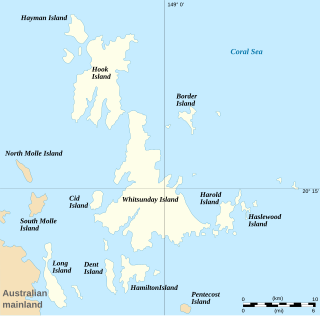
The Whitsunday Islands are a collection of continental islands of various sizes off the central coast of Queensland, Australia, approximately 900 kilometres north of Brisbane. The northernmost of the islands are situated off the coast by the town of Bowen while the southernmost islands are off the coast by Proserpine. The island group is centered on Whitsunday Island, while the group's commercial center is Hamilton Island. The traditional owners of the area are the Ngaro people and the Gia people whose Juru Clan has the only legally recognized native title in the region.
Many Australian Aboriginal cultures have or traditionally had a manually coded language, a signed counterpart of their oral language. This appears to be connected with various speech taboos between certain kin or at particular times, such as during a mourning period for women or during initiation ceremonies for men, as was also the case with Caucasian Sign Language but not Plains Indian Sign Language, which did not involve speech taboo, or deaf sign languages, which are not encodings of oral language. There is some similarity between neighboring groups and some contact pidgin similar to Plains Indian Sign Language in the American Great Plains.
Australian Aboriginal English (AAE) refers to a dialect of Australian English used by a large section of the Indigenous Australian population. It is made up of a number of varieties which developed differently in different parts of Australia. These varieties are generally said to fit along a continuum ranging from light forms, close to Standard Australian English, to heavy forms, closer to Kriol. There are generally distinctive features of accent, grammar, words and meanings, as well as language use. AAE is not to be confused with Kriol, which is a separate language from English spoken by over 30,000 people in Australia. Speakers have been noted to tend to change between different forms of AAE depending on whom they are speaking to, e.g. striving to speak more like Australian English when speaking to a non-Indigenous English-speaking person.
Hook Island is one of the Whitsunday Islands off the coast of the Australian state of Queensland. The island is almost uninhabited, quite rugged and almost completely contained within a section of the Whitsunday Islands National Park. The island has two prominent geographical features on the southern side of Hook Island; the Nara and Macona inlets, two fjord-like recesses that are used as anchorages for the Whitsunday tourist fleet. The island's northern coast is noted for its colourful underwater coral growths, to which snorkelling and diving enthusiasts are attracted.

Aboriginal Australians are the various indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland, Tasmania, and often the Tiwi people. This group contains many distinct peoples that have developed across Australia for over 50,000 years. These peoples have a broadly shared, though complex, genetic history, but it is only in the last two hundred years that they have been defined and started to self identify as a single group. The definition of the term "Aboriginal" has changed over time and place, with the importance of family lineage, self identification and community acceptance all being of varying importance. In the past, Aboriginal Australians lived over large sections of the continental shelf and were isolated on many of the smaller offshore islands when the land was inundated at the start of the inter-glacial. However, they are considered distinct from the Torres Strait Islander people, despite extensive cultural exchange.
Lindeman Island is an island in the Lindeman Group of the Whitsunday Islands off the coast of Queensland, Australia. The island was named by Captain Bedwell after his sub-lieutenant, George Sidney Lindeman whilst aboard the Royal Navy vessel HMS Virago.
Indigenous Australians are the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples of Australia, descended from groups that existed in Australia and surrounding islands before British colonisation. The time of arrival of the first Indigenous Australians is a matter of debate among researchers. The earliest conclusively human remains found in Australia are those of Mungo Man LM3 and Mungo Lady, which have been dated to around 50,000 years BP. Recent archaeological evidence from the analysis of charcoal and artefacts revealing human use suggests a date as early as 65,000 BP. Luminescence dating has suggested habitation in Arnhem Land as far back as 60,000 years BP. Genetic research has inferred a date of habitation as early as 80,000 years BP. Other estimates have ranged up to 100,000 years and 125,000 years BP.

Gumbaynggir language is an Australian Aboriginal language. It is spoken by the Gumbaynggirr, who are native to the Mid North Coast of New South Wales.
Narangga is an extinct Australian Aboriginal language formerly spoken by the Narungga people in Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. As a result of the colonisation of Australia, the Narangga language fell into disuse within several generations. Nevertheless, Narangga continued to be documented into the 20th century and the 1980s saw a community reclamation of the Narangga language by the Aboriginal community. As a result of revival efforts, the language along with Narangga culture is now being taught around the Yorke Peninsula, from Moonta and Maitland Area Schools to Point Pearce.
The Ngaro were a seafaring Australian Aborigine group of people that inhabited the Whitsunday Islands and coastal regions of Queensland, in an area that archaeologically shows evidence of human habitation since 9000 BP. Ngaro society was destroyed by warfare with traders, colonists, and the Australian Native Police. The Native Police Corps forcibly relocated the remaining Ngaro aborigines in 1870 to a penal colony on Palm Island or to the lumber mills of Brampton Island as forced laborers.
Alfred Ngaro is a New Zealand politician and, since the 2011 election, a member of the New Zealand House of Representatives. He is a member of the National Party and the first Cook Islander who was elected to Parliament in New Zealand.

Barngarla, formerly known as Parnkalla, is an Aboriginal language of Eyre Peninsula, South Australia, Australia.
Guugu Yalandji (Kuku-Yalanji) is an Australian Aboriginal language of Queensland. It is the traditional language of the Kuku Yalanji people. Despite conflicts between the Kuku Yalanji people and British settlers in Queensland, the Kuku Yalanji language has a healthy number of speakers, and that number is increasing. Though the language is threatened, the language use is vigorous and children are learning it in schools. All generations of speakers have a positive languages attitudes. The Kuku Yalanji still practice their traditional religion, and they have rich oral traditions. Many people in the Kuku Yalanji community also use English, but use is discouraged. 100 Kuku Yalanji speakers can both read and write in Kuku Yalanji.

Anaiwan (Anēwan) is an extinct Australian Aboriginal language of New South Wales. Since 2017, there has been a revival program underway to bring the language back.
Biri is an extinct Australian Aboriginal language of Queensland. A grammar of Biri proper was written before the language became extinct.

The Proserpine River is a river in Whitsunday Region of Queensland, Australia.
The Gia were an indigenous Australian tribe of the state of Queensland. Some doubt exists as to their distinct identity, and little is known of them.








