
In molecular biology, a riboswitch is a regulatory segment of a messenger RNA molecule that binds a small molecule, resulting in a change in production of the proteins encoded by the mRNA. Thus, an mRNA that contains a riboswitch is directly involved in regulating its own activity, in response to the concentrations of its effector molecule. The discovery that modern organisms use RNA to bind small molecules, and discriminate against closely related analogs, expanded the known natural capabilities of RNA beyond its ability to code for proteins, catalyze reactions, or to bind other RNA or protein macromolecules.

Cobalamin riboswitch is a cis-regulatory element which is widely distributed in 5' untranslated regions of vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) related genes in bacteria.

The bacterial glycine riboswitch is an RNA element that can bind the amino acid glycine. Glycine riboswitches usually consist of two metabolite-binding aptamer domains with similar structures in tandem. The aptamers were originally thought to cooperatively bind glycine to regulate the expression of downstream genes. In Bacillus subtilis, this riboswitch is found upstream of the gcvT operon which controls glycine degradation. It is thought that when glycine is in excess it will bind to both aptamers to activate these genes and facilitate glycine degradation.

A purine riboswitch is a sequence of ribonucleotides in certain messenger RNA (mRNA) that selectively binds to purine ligands via a natural aptamer domain. This binding causes a conformational change in the mRNA that can affect translation by revealing an expression platform for a downstream gene, or by forming a translation-terminating stem-loop. The ultimate effects of such translational regulation often take action to manage an abundance of the instigating purine, and might produce proteins that facilitate purine metabolism or purine membrane uptake.

The SAM-II riboswitch is a RNA element found predominantly in alpha-proteobacteria that binds S-adenosyl methionine (SAM). Its structure and sequence appear to be unrelated to the SAM riboswitch found in Gram-positive bacteria. This SAM riboswitch is located upstream of the metA and metC genes in Agrobacterium tumefaciens, and other methionine and SAM biosynthesis genes in other alpha-proteobacteria. Like the other SAM riboswitch, it probably functions to turn off expression of these genes in response to elevated SAM levels. A significant variant of SAM-II riboswitches was found in Pelagibacter ubique and related marine bacteria and called SAM-V. Also, like many structured RNAs, SAM-II riboswitches can tolerate long loops between their stems.
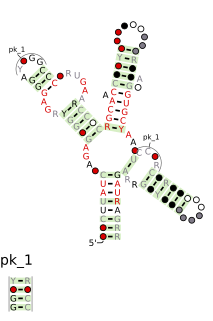
The SAM riboswitch is found upstream of a number of genes which code for proteins involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis in Gram-positive bacteria. Two SAM riboswitches in Bacillus subtilis that were experimentally studied act at the level of transcription termination control. The predicted secondary structure consists of a complex stem-loop region followed by a single stem-loop terminator region. An alternative and mutually exclusive form involves bases in the 3' segment of helix 1 with those in the 5' region of helix 5 to form a structure termed the anti-terminator form. When SAM is unbound, the anti-terminator sequence sequesters the terminator sequence so the terminator is unable to form, allowing the polymerase read-through the downstream gene. When S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) is bound to the aptamer, the anti-terminator is sequestered by an anti-anti-terminator; the terminator forms and terminates the transcription. However, many SAM riboswitches are likely to regulate gene expression at the level of translation.

The ykkC/yxkD leader is a conserved RNA structure found upstream of the ykkC and yxkD genes in Bacillus subtilis and related genes in other bacteria. The function of this family is unclear for many years although it has been suggested that it may function to switch on efflux pumps and detoxification systems in response to harmful environmental molecules. The Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis sequence AE013027 overlaps with that of purine riboswitch suggesting that the two riboswitches may work in conjunction to regulate the upstream gene which codes for TTE0584 (Q8RC62), a member of the permease family.
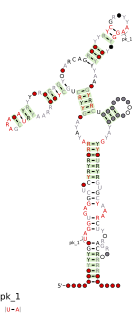
The Ykok leader or M-box is a Mg2+-sensing RNA structure that controls the expression of Magnesium ion transport proteins in bacteria. It is a distinct structure to the Magnesium responsive RNA element.
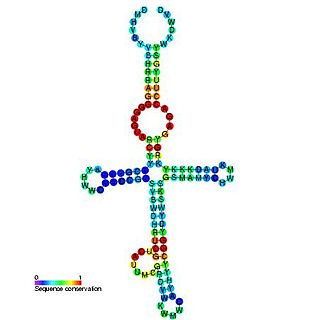
The yybP-ykoY leader RNA element was originally discovered in E. coli during a large scale screen and was named SraF. This family was later found to exist upstream of related families of protein genes in many bacteria, including the yybP and ykoY genes in B. subtilis. The specific functions of these proteins are unknown, but this structured RNA element may be involved in their genetic regulation as a riboswitch. The yybP-ykoY element was later proposed to be manganese-responsive after another associated family of genes, YebN/MntP, was shown to encode Mn2+ efflux pumps in several bacteria. Genetic data and a crystal structure confirmed that yybp-ykoY is a manganese riboswitch that directly binds Mn2+

PreQ1-II riboswitches form a class of riboswitches that specifically bind pre-queuosine1 (PreQ1), a precursor of the modified nucleoside queuosine. They are found in certain species of Streptococcus and Lactococcus, and were originally identified as a conserved RNA secondary structure called the "COG4708 motif". All known members of this riboswitch class appear to control members of COG4708 genes. These genes are predicted to encode membrane-bound proteins and have been proposed to be a transporter of preQ1, or a related metabolite, based on their association with preQ1-binding riboswitches. PreQ1-II riboswitches have no apparent similarities in sequence or structure to preQ1-I riboswitches, a previously discovered class of preQ1-binding riboswitches. PreQ1 thus joins S-adenosylmethionine as the second metabolite to be found that is the ligand of more than one riboswitch class.
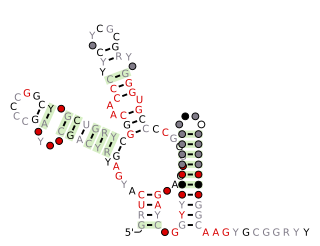
SAM-IV riboswitches are a kind of riboswitch that specifically binds S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), a cofactor used in many methylation reactions. Originally identified by bioinformatics, SAM-IV riboswitches are largely confined to the Actinomycetales, an order of Bacteria. Conserved features of SAM-IV riboswitch and experiments imply that they probably share a similar SAM-binding site to another class of SAM-binding riboswitches called SAM-I riboswitches. However, the scaffolds of these two types of riboswitch appear to be quite distinct. The structural relationship between these riboswitch types has been studied.

SAH riboswitches are a kind of riboswitch that bind S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH). When the coenzyme S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) is used in a methylation reaction, SAH is produced. SAH riboswitches typically up-regulate genes involved in recycling SAH to create more SAM. This is particularly relevant to cells, because high levels of SAH can be toxic. Originally identified by bioinformatics, SAH riboswitches are apparent in many species of bacteria, predominantly certain Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria. The atomic-resolution 3-dimensional structure of an SAH riboswitch has been solved using X-ray crystallography.

Cyclic di-GMP-I riboswitches are a class of riboswitch that specifically bind cyclic di-GMP, which is a second messenger that is used in a variety of microbial processes including virulence, motility and biofilm formation. Cyclic di-GMP-I riboswitches were originally identified by bioinformatics as a conserved RNA-like structure called the "GEMM motif". These riboswitches are present in a wide variety of bacteria, and are most common in Clostridia and certain varieties of Proteobacteria. The riboswitches are present in pathogens such as Clostridium difficile, Vibrio cholerae and Bacillus anthracis. Geobacter uraniumreducens is predicted to have 30 instances of this riboswitch in its genome. A bacteriophage that infects C. difficile is predicted to carry a cyclic di-GMP-I riboswitch, which it might use to detect and exploit the physiological state of bacteria that it infects.

The SAM–SAH riboswitch is a conserved RNA structure in certain bacteria that binds S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) and S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) and is therefore presumed to be a riboswitch. SAM–SAH riboswitches do not share any apparent structural resemblance to known riboswitches that bind SAM or SAH. The binding affinities for both compounds are similar, but binding for SAH is at least somewhat stronger. SAM–SAH riboswitches are exclusively found in Rhodobacterales, an order of alphaproteobacteria. They are always found in the apparent 5' untranslated regions of metK genes, which encode the enzyme that synthesizes SAM.

The fluoride riboswitch is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics in a wide variety of bacteria and archaea. These RNAs were later shown to function as riboswitches that sense fluoride ions. These "fluoride riboswitches" increase expression of downstream genes when fluoride levels are elevated, and the genes are proposed to help mitigate the toxic effects of very high levels of fluoride.

The glutamine riboswitch is a conserved RNA structure that was predicted by bioinformatics. It is present in a variety of lineages of cyanobacteria, as well as some phages that infect cyanobacteria. It is also found in DNA extracted from uncultivated bacteria living in the ocean that are presumably species of cyanobacteria.

The pfl RNA motif refers to a conserved RNA structure present in some bacteria and originally discovered using bioinformatics. pfl RNAs are consistently present in genomic locations that likely correspond to the 5' untranslated regions of protein-coding genes. This arrangement in bacteria is commonly associated with cis-regulatory elements. Moreover, they are in presumed 5' UTRs of multiple non-homologous genes, suggesting that they function only in these locations. Additional evidence of cis-regulatory function came from the observation that predicted rho-independent transcription terminators overlap pfl RNAs. This overlap suggests that the alternate secondary structures of pfl RNA and the transcription terminator stem-loops compete with each other, and this is a common mechanism for cis gene control in bacteria.

Cyclic di-GMP-II riboswitches form a class of riboswitches that specifically bind cyclic di-GMP, a second messenger used in multiple bacterial processes such as virulence, motility and biofilm formation. Cyclic di-GMP II riboswitches are structurally unrelated to cyclic di-GMP-I riboswitches, though they have the same function.
SAM-V riboswitch is the fifth known riboswitch to bind S-adenosyl methionine (SAM). It was first discovered in the marine bacterium Candidatus Pelagibacter ubique and can also be found in marine metagenomes. SAM-V features a similar consensus sequence and secondary structure as the binding site of SAM-II riboswitch, but bioinformatics scans cluster the two aptamers independently. These similar binding pockets suggest that the two riboswitches have undergone convergent evolution.

PreQ1-III riboswitches are a class of riboswitches that bind pre-queuosine1 (PreQ1), a precursor to the modified nucleoside queuosine. PreQ1-III riboswitches are the third class of riboswitches to be discovered that sense this ligand, and are structurally distinct from preQ1-I and preQ1-II riboswitches. Most sequenced examples of preQ1-III riboswitches are obtained from uncultivated metagenome samples, but the few examples in cultivated organisms are present in strains that are known to or suspected to be Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, a species of Gram-positive Clostridia. Known examples of preQ1-III riboswitches are found upstream of queT genes, which are expected to encode transporters of a queuosine derivative. The other two known classes of preQ1 riboswitches are also commonly found upstream of queT genes.



















