Related Research Articles

Penpont is a village about 2 miles (3 km) west of Thornhill in Dumfriesshire, in the Dumfries and Galloway region of Scotland. It is near the confluence of the Shinnel Water and Scaur Water rivers in the foothills of the Southern Uplands. It has a population of about 400 people.

Clan Armstrong is a Scottish clan of the Scottish Borders.

Liddesdale, the valley of the Liddel Water, in the County of Roxburgh, southern Scotland, extends in a south-westerly direction from the vicinity of Peel Fell to the River Esk, a distance of 21 miles (34 km). The Waverley route of the North British Railway ran down the dale, and the Catrail, or Picts' Dyke, crosses its head.

William II de Soules, Lord of Liddesdale and Butler of Scotland, was a Scottish Border noble during the Wars of Scottish Independence. William was the elder son of Nicholas II de Soules, Lord of Liddesdale and Butler of Scotland, and a cousin of Alexander Comyn, Earl of Buchan. He was the nephew of John de Soules, Guardian of Scotland.

Cummertrees is a coastal village and civil parish of Annandale in the historical county of Dumfriesshire in Dumfries and Galloway. It lies about 1 mile (1.6 km) inland, on the Pow Water to the northwest of Powfoot, 12 miles (19 km) from Dumfries and 3 miles (5 km) from Annan.

The Lord of Liddesdale was a magnate in the medieval Kingdom of Scotland; the territorial lordship of Liddesdale was first created by David I of Scotland, perhaps between 1113 and 1124 when the latter was Prince of the Cumbrians. From an early period the caput of the lordship was Hermitage Castle, the strength of Liddesdale. King David gave the territory to Ranulf de Soules, a knight from the Cotentin Peninsula. It was forfeited by the Soulis family in the 14th century and eventually passed to the Douglases, only to be lost to the Hepburns by order of James IV. Archibald Douglas, 5th Earl of Angus was remunerated for this loss by the lordship of Bothwell Castle, although the Hepburn Earls of Bothwell retained the territorial designation

Sir Ingram de Umfraville was a Scottish noble who played a particularly chequered role in the Wars of Scottish Independence, changing sides between England and Scotland multiple times, throughout the conflict.
Ranulf de Soules was a Norman knight who came to Scotland with David I and served as his cupbearer.
George Gordon was a 16th-century Scottish prelate.
George Vaus was a Scottish prelate of the late 15th and early 16th century.
Tomás mac Ailein, sometimes known as Thomas of Galloway, was an illegitimate son of Alan of Galloway, Constable of Scotland and the last Mac Fearghusa Lord of Galloway. After the death of his father, who left no legitimate sons, King Alexander II of Scotland planned to divide the lordship between the husbands of Alan's three daughters.

Dunscore is a small village which lies 9 miles (14 km) northwest of Dumfries on the B729, in Dumfriesshire, in the District Council Region of Dumfries and Galloway, southwest Scotland.

Tynron is a village and civil parish in Dumfries and Galloway, south-west Scotland, lying in a hollow of the Shinnel Water, 2 miles (3.2 km) from Moniaive.
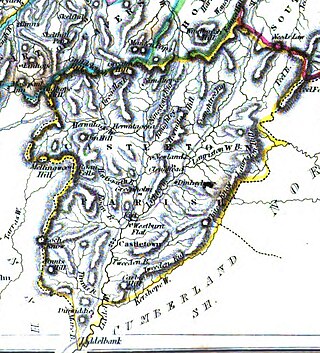
Castleton is a civil parish in the Scottish Borders area of Scotland, in the former Roxburghshire, in the extreme south of the Borders area. It is bounded by Northumberland (England), Dumfries and Galloway, and the parishes of Hobkirk, Southdean and Teviothead. The village of Castleton was commenced in 1793. It was built as a result of the land clearances in the 1790s when people were forced to move from Old Castleton village. While the parish retained the name Castleton, the village later became identified as New Castleton or Newcastleton. The parish is also known by its older name Liddesdale
Sir Andrew Murray (1298–1338), also known as Sir Andrew Moray, or Sir Andrew de Moray, was a Scottish military and political leader who supported King David II of Scotland against Edward Balliol and King Edward III of England during the Second War of Scottish Independence. He held the lordships of Avoch and Petty in north Scotland, and Bothwell in west-central Scotland. In 1326 he married Christina Bruce, a sister of King Robert I of Scotland. Murray was twice chosen as Guardian of Scotland, first in 1332, and again from 1335 on his return to Scotland after his release from captivity in England. He held the guardianship until his death in 1338.

Liddel Strength is an ancient monument near Carwinley, Cumbria, in northwest England. It consists of the earthwork remains of an Anglo-Norman border fortification destroyed by the Scots in 1346 and fragmentary remains of a pele tower subsequently built upon the site. It lies on a cliff on the south bank of the Liddel Water, overlooking the Liddel Water's confluence with the River Esk; the last high ground before the Esk reaches the Solway Plain. The Liddel Water and the Esk (downstream) form the modern Anglo-Scottish border; formerly they were the southern boundary of the Debatable Lands.
Robert Service (1854–1911) was a British nurseryman and naturalist.

De Soules is the surname of an old Norman noble family originating from Soulles, also known as the House of de Soules.

Ingram de Balliol, Lord of Redcastle and Urr in Scotland, Dalton in England and Tours-en-Vimeu in France was an Anglo Scoto-French noble.
Ludovic McLellan Mann (1869–1955) was a Scottish archaeologist and antiquarian.
References
- McAndrew, Bruce A. (2006). Scotland's historic heraldry. Woodbridge: Boydell Press. ISBN 1-84383-261-5. OCLC 71264510.
- McMichael, Thomas (1947). "The Feudal Family of de Soules" (PDF). Transactions and Journal of Proceedings of the Dumfriesshire and Galloway Natural History & Antiquarian Society. Dumfriesshire and Galloway Natural History and Antiquarian Society, 1947–1948. 26 (Third series ed.).
- Transactions and Journal of Proceedings of the Dumfriesshire and Galloway Natural History & Antiquarian Society and the Dumfriesshire and Galloway Natural History and Antiquarian Society. 1915.
{{cite journal}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - Transactions of the Hawick Archaeological Society. Hawick Archaeological Society. 1863.
{{cite journal}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)