
Nicotine is a naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants and is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As a pharmaceutical drug, it is used for smoking cessation to relieve withdrawal symptoms. Nicotine acts as a receptor agonist at most nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), except at two nicotinic receptor subunits where it acts as a receptor antagonist.

Smoking cessation, usually called quitting smoking or stopping smoking, is the process of discontinuing tobacco smoking. Tobacco smoke contains nicotine, which is addictive and can cause dependence. As a result, nicotine withdrawal often makes the process of quitting difficult.
Nicotine polacrilex is nicotine bound to an ion-exchange resin. It is added to gum and hard lozenges used for nicotine replacement therapy in smoking cessation, such as in the Nicorette range of products. The use of the polymer as a delivery system maximizes the amount of nicotine released and absorbed by the oral mucosa. 80 to 90 percent of the nicotine released from the gum is absorbed by the mouth. Side effects of the gum include bad taste, nausea, dyspepsia, and stomatitis.

Snus is a Swedish tobacco product and non-tobacco nicotine product consumed by placing a pouch of powdered tobacco leaves or powdered non-tobacco plant fibers under the lip for nicotine to be absorbed through the oral mucosa. Whereas the nicotine in tobacco-based snus derives from tobacco leaves, the nicotine in non-tobacco snus can be either natural or synthesized.
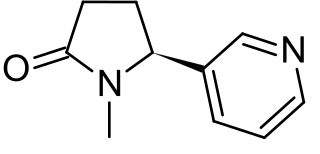
Cotinine is an alkaloid found in tobacco and is also the predominant metabolite of nicotine, typically used as a biomarker for exposure to tobacco smoke. Cotinine is currently being studied as a treatment for depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Cotinine was developed as an antidepressant as a fumaric acid salt, cotinine fumarate, to be sold under the brand name Scotine, but it was never marketed.

Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) is a medically approved way to treat people with tobacco use disorder by taking nicotine through means other than tobacco. It is used to help with quitting smoking or stopping chewing tobacco. It increases the chance of quitting tobacco smoking by about 55%. Often it is used along with other behavioral techniques. NRT has also been used to treat ulcerative colitis. Types of NRT include the adhesive patch, chewing gum, lozenges, nose spray, and inhaler. The use of multiple types of NRT at a time may increase effectiveness.

Xerostomia, also known as dry mouth, is a subjective complaint of dryness in the mouth, which may be associated with a change in the composition of saliva, or reduced salivary flow, or have no identifiable cause.

A nicotine patch is a transdermal patch that releases nicotine into the body through the skin. It is used in nicotine replacement therapy (NRT), a process for smoking cessation. Endorsed and approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), it is considered one of the safer NRTs available for the treatment of tobacco use disorder.
Nicotine gum is a chewing gum containing the active ingredient nicotine polacrilex. It is a type of nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) used alone or in combination with other pharmacotherapy for smoking cessation and for quitting smokeless tobacco.
Nicorette is the brand name of a number of products for nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) that contain nicotine polacrilex. Developed in the late 1970s in Sweden by AB Leo in the form of a chewing gum, Nicorette was the first nicotine replacement product on the market.

A metered-dose inhaler (MDI) is a device that delivers a specific amount of medication to the lungs in the form of a short burst of aerosolized medicine that is usually self-administered by the patient via inhalation. It is the most commonly used delivery system for treating asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other respiratory diseases. The medication in a metered dose inhaler is most commonly a bronchodilator, corticosteroid or a combination of both for treating asthma and COPD. Other medications less commonly used but also administered by MDI are mast cell stabilizers, such as cromoglicate or nedocromil.

Smokeless tobacco is a tobacco product that is used by means other than smoking. Their use involves chewing, sniffing, or placing the product between gum and the cheek or lip. Smokeless tobacco products are produced in various forms, such as chewing tobacco, snuff, snus, and dissolvable tobacco products. Smokeless tobacco is widely used in South Asia and this accounts for about 80% of global consumption. All smokeless tobacco products contain nicotine and are therefore highly addictive. Quitting smokeless tobacco use is as challenging as smoking cessation.

Varenicline, sold under the brand names Chantix and Champix among others, is a medication used for smoking cessation and for the treatment of dry eye syndrome. It is a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist. When activated, this receptor releases dopamine in the nucleus accumbens, the brain's reward center, thereby reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms with smoking cessation, although less pronounced than a full agonist.

Nicotine withdrawal is a group of symptoms that occur in the first few weeks after stopping or decreasing use of nicotine. Symptoms include intense cravings for nicotine, anger or irritability, anxiety, depression, impatience, trouble sleeping, restlessness, hunger, weight gain, and difficulty concentrating. Withdrawal symptoms make it harder to quit nicotine products, and most methods for quitting smoking involve reducing nicotine withdrawal. Quit smoking programs can make it easier to quit. Nicotine withdrawal is recognized in both the American Psychiatric Association Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM) and the WHO International Classification of Diseases (ICD).
Tobacco harm reduction (THR) is a public health strategy to lower the health risks to individuals and wider society associated with using tobacco products. It is an example of the concept of harm reduction, a strategy for dealing with the use of drugs. Tobacco smoking is widely acknowledged as a leading cause of illness and death, and reducing smoking is vital to public health.

Nicotine dependence is a state of substance dependence on nicotine. It is a chronic, relapsing disease characterized by a compulsive craving to use the drug despite social consequences, loss of control over drug intake, and the emergence of withdrawal symptoms. Tolerance is another component of drug dependence. Nicotine dependence develops over time as an individual continues to use nicotine. While cigarettes are the most commonly used tobacco product, all forms of tobacco use—including smokeless tobacco and e-cigarette use—can cause dependence. Nicotine dependence is a serious public health problem because it leads to continued tobacco use and the associated negative health effects. Tobacco use is one of the leading preventable causes of death worldwide, causing more than 8 million deaths per year and killing half of its users who do not quit. Current smokers are estimated to die an average of 10 years earlier than non-smokers.
Nicotine Anonymous (NicA) is a twelve-step program founded in 1982 for people desiring to quit smoking and live free of nicotine. As of July 2017, there are over 700 face-to-face meetings in 32 countries worldwide with the majority of these meetings occurring in the United States, Iran, India, Canada, Brazil, the United Kingdom, Australia, Russia and in various online community and social media platforms.. NicA maintains that total abstinence from nicotine is necessary for recovery. NicA defines abstinence as “a state that begins when all use of nicotine ceases.
NiQuitin is a range of nicotine replacement products designed to help smokers quit by replacing the nicotine supplied by cigarettes with a lower, steadier level in order to relieve withdrawal. This is to help users wean off nicotine gradually. Nicotine replacement therapy products are indicated as temporary aids for cigarette smokers who want to give up smoking. They serve as alternative sources of nicotine and provide relief of nicotine withdrawal symptoms in nicotine-dependent individuals who are acutely withdrawing from cigarette smoking.
The health effects of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) include a range of potential risks such as exposure to toxic chemicals, the possibility of increased likelihood of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, and concerns about their possible role in cancer development. Upon their introduction, there were marketing claims that they were a safer alternative to traditional tobacco products.
The scientific community in the United States and Europe are primarily concerned with the possible effect of electronic cigarette use on public health. There is concern among public health experts that e-cigarettes could renormalize smoking, weaken measures to control tobacco, and serve as a gateway for smoking among youth. The public health community is divided over whether to support e-cigarettes, because their safety and efficacy for quitting smoking is unclear. Many in the public health community acknowledge the potential for their quitting smoking and decreasing harm benefits, but there remains a concern over their long-term safety and potential for a new era of users to get addicted to nicotine and then tobacco. There is concern among tobacco control academics and advocates that prevalent universal vaping "will bring its own distinct but as yet unknown health risks in the same way tobacco smoking did, as a result of chronic exposure", among other things.











