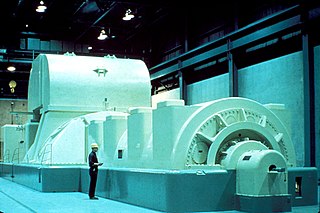
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motion-based power or fuel-based power into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. Generators provide nearly all the power for electrical grids.

A starter is a device used to rotate (crank) an internal-combustion engine so as to initiate the engine's operation under its own power. Starters can be electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic. The starter can also be another internal-combustion engine in the case, for instance, of very large engines, or diesel engines in agricultural or excavation applications.

An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature. Occasionally, a linear alternator or a rotating armature with a stationary magnetic field is used. In principle, any AC electrical generator can be called an alternator, but usually the term refers to small rotating machines driven by automotive and other internal combustion engines.

The Joint European Torus (JET) was a magnetically confined plasma physics experiment, located at Culham Centre for Fusion Energy in Oxfordshire, UK. Based on a tokamak design, the fusion research facility was a joint European project with the main purpose of opening the way to future nuclear fusion grid energy. At the time of its design JET was larger than any comparable machine.

Diamond Light Source is the UK's national synchrotron light source science facility located at the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in Oxfordshire.

A synchrotron is a particular type of cyclic particle accelerator, descended from the cyclotron, in which the accelerating particle beam travels around a fixed closed-loop path. The magnetic field which bends the particle beam into its closed path increases with time during the accelerating process, being synchronized to the increasing kinetic energy of the particles. The synchrotron is one of the first accelerator concepts to enable the construction of large-scale facilities, since bending, beam focusing and acceleration can be separated into different components. The most powerful modern particle accelerators use versions of the synchrotron design. The largest synchrotron-type accelerator, also the largest particle accelerator in the world, is the 27-kilometre-circumference (17 mi) Large Hadron Collider (LHC) near Geneva, Switzerland, built in 2008 by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN). It can accelerate beams of protons to an energy of 7 tera electronvolts (TeV or 1012 eV).

A motor–generator is a device for converting electrical power to another form. Motor–generator sets are used to convert frequency, voltage, or phase of power. They may also be used to isolate electrical loads from the electrical power supply line. Large motor–generators were widely used to convert industrial amounts of power while smaller motor–generators were used to convert battery power to higher DC voltages.

Spallation is a process in which fragments of material (spall) are ejected from a body due to impact or stress. In the context of impact mechanics it describes ejection of material from a target during impact by a projectile. In planetary physics, spallation describes meteoritic impacts on a planetary surface and the effects of stellar winds and cosmic rays on planetary atmospheres and surfaces. In the context of mining or geology, spallation can refer to pieces of rock breaking off a rock face due to the internal stresses in the rock; it commonly occurs on mine shaft walls. In the context of anthropology, spallation is a process used to make stone tools such as arrowheads by knapping. In nuclear physics, spallation is the process in which a heavy nucleus emits numerous nucleons as a result of being hit by a high-energy particle, thus greatly reducing its atomic weight. In industrial processes and bioprocessing the loss of tubing material due to the repeated flexing of the tubing within a peristaltic pump is termed spallation.

The Bevatron was a particle accelerator — specifically, a weak-focusing proton synchrotron — at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, U.S., which began operating in 1954. The antiproton was discovered there in 1955, resulting in the 1959 Nobel Prize in physics for Emilio Segrè and Owen Chamberlain. It accelerated protons into a fixed target, and was named for its ability to impart energies of billions of eV.

The Proton Synchrotron is a particle accelerator at CERN. It is CERN's first synchrotron, beginning its operation in 1959. For a brief period the PS was the world's highest energy particle accelerator. It has since served as a pre-accelerator for the Intersecting Storage Rings (ISR) and the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS), and is currently part of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) accelerator complex. In addition to protons, PS has accelerated alpha particles, oxygen and sulfur nuclei, electrons, positrons, and antiprotons.

The ISIS Neutron and Muon Source is a pulsed neutron and muon source, established 1984 at the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory of the Science and Technology Facilities Council, on the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in Oxfordshire, United Kingdom. It uses the techniques of muon spectroscopy and neutron scattering to probe the structure and dynamics of condensed matter on a microscopic scale ranging from the subatomic to the macromolecular.

Alcator C-Mod was a tokamak that operated between 1991 and 2016 at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Plasma Science and Fusion Center (PSFC). Notable for its high toroidal magnetic field, Alcator C-Mod holds the world record for volume averaged plasma pressure in a magnetically confined fusion device. Until its shutdown in 2016, it was one of the major fusion research facilities in the United States.
The Australian Synchrotron is a 3 GeV national synchrotron radiation facility located in Clayton, in the south-eastern suburbs of Melbourne, Victoria. The facility opened in 2007, and is operated by the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation.
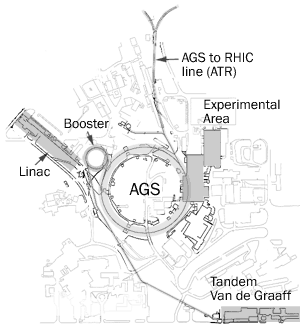
The Alternating Gradient Synchrotron (AGS) is a particle accelerator located at the Brookhaven National Laboratory in Long Island, New York, United States.

The Proton Synchrotron Booster (PSB) is the first and smallest circular proton accelerator in the accelerator chain at the CERN injection complex, which also provides beams to the Large Hadron Collider. It contains four superimposed rings with a radius of 25 meters, which receive protons with an energy of 160 MeV from the linear accelerator Linac4 and accelerate them up to 2.0 GeV, ready to be injected into the Proton Synchrotron (PS). Before the PSB was built in 1972, Linac 1 injected directly into the Proton Synchrotron, but the increased injection energy provided by the booster allowed for more protons to be injected into the PS and a higher luminosity at the end of the accelerator chain.

A dynamo is an electrical generator that creates direct current using a commutator. Dynamos were the first electrical generators capable of delivering power for industry, and the foundation upon which many other later electric-power conversion devices were based, including the electric motor, the alternating-current alternator, and the rotary converter.

The Chrysler Patriot was a turbine-electric hybrid sports-prototype racing car utilizing flywheel energy storage, built by Reynard Motorsport and SatCon Technology Corporation for Chrysler in 1993 as a concept car but with the express intent of winning the Le Mans 24 Hour Race.

A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to very high speeds and energies, and to contain them in well-defined beams.

Flywheel energy storage (FES) works by accelerating a rotor (flywheel) to a very high speed and maintaining the energy in the system as rotational energy. When energy is extracted from the system, the flywheel's rotational speed is reduced as a consequence of the principle of conservation of energy; adding energy to the system correspondingly results in an increase in the speed of the flywheel.
A Fixed-Field alternating gradient Accelerator is a circular particle accelerator concept that can be characterized by its time-independent magnetic fields and the use of alternating gradient strong focusing.
















