This article needs additional citations for verification .(June 2020) |
| Ninahuilca | |
|---|---|
| Highest point | |
| Coordinates | 0°21′13″S78°37′01″W / 0.3535°S 78.617°W [1] |
Ninahuilca is a volcano in the Western Cordillera of Ecuador. It is southwest of Atacazo.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(June 2020) |
| Ninahuilca | |
|---|---|
| Highest point | |
| Coordinates | 0°21′13″S78°37′01″W / 0.3535°S 78.617°W [1] |
Ninahuilca is a volcano in the Western Cordillera of Ecuador. It is southwest of Atacazo.

Quito, formally San Francisco de Quito, is the capital of Ecuador, with an estimated population of 2.8 million in its urban area. It is also the capital of the province of Pichincha. Quito is located in a valley on the eastern slopes of Pichincha, an active stratovolcano in the Andes, at an elevation of 2,850 m (9,350 ft), making it the second-highest capital city in the world.

Tungurahua is an active stratovolcano located in the Cordillera Oriental of Ecuador. The volcano gives its name to the province of Tungurahua. Volcanic activity restarted on August 19, 1999, and is ongoing as of 2017, with several major eruptions since then, the last starting on 1 February 2014.

Chimborazo is a currently inactive stratovolcano in the Cordillera Occidental range of the Andes. Its last known eruption is believed to have occurred around 550 A.D.

Cotopaxi is an active stratovolcano in the Andes Mountains, located in Latacunga city of Cotopaxi Province, about 50 km (31 mi) south of Quito, and 31 km (19 mi) northeast of the city of Latacunga, Ecuador. It is the second highest summit in Ecuador, reaching a height of 5,897 m (19,347 ft). Cotopaxi is among the highest active volcanoes in the world.

Pichincha is a stratovolcano in Ecuador. The capital Quito wraps around its eastern slopes.

The Illinizas are a pair of volcanic mountains that are located in the north of Latacunga, Cotopaxi, Ecuador. They are located in the Illinizas Ecological Reserve. These twin mountains are separated by a saddle that is about a kilometer long. The peaks are among the highest in Ecuador, with Illiniza Sur standing slightly taller than Illiniza Norte, its northern counterpart, at 5245 metres and 5126 metres respectively.

Cotopaxi is one of the provinces of Ecuador. The capital is Latacunga. The province contains the Cotopaxi Volcano, an intermittent volcano with a height of 19,347 feet (5,897 m).

Imbabura is a province located in the Andes of northern Ecuador. The capital is Ibarra. The people of the province speak Spanish, and a large portion of the population also speaks the Imbaburan Kichwa variety of the Quechua language.

Tungurahua is one of the twenty-four provinces of Ecuador. Its capital is Ambato. The province takes its name from the Tungurahua volcano, which is located within the boundaries of the provinces.

Cayambe or Volcán Cayambe is a volcano in Ecuador, in the Cordillera Central, a range of the Ecuadorian Andes. It is located in Pichincha Province, some 70 km (43 mi) northeast of Quito. It is the third-highest mountain in Ecuador, at an elevation of 5,790 m (18,996 ft) above sea level.

Sangay is an active stratovolcano in central Ecuador. It exhibits mostly strombolian activity. Geologically, Sangay marks the southern boundary of the Northern Volcanic Zone, and its position straddling two major pieces of crust accounts for its high level of activity. Sangay's approximately 500,000-year-old history is one of instability; two previous versions of the mountain were destroyed in massive flank collapses, evidence of which still litters its surroundings today.

Antisana is a stratovolcano of the northern Andes, in Ecuador. It is the fourth highest volcano in Ecuador, at 5,753 metres (18,875 ft), and is located 50 kilometres (31 mi) SE of the capital city of Quito.

Reventador is an active stratovolcano which lies in the eastern Andes of Ecuador. It lies in a remote area of the national park of the same name, which is Spanish for "exploder". Since 1541, it has erupted over 25 times, although its isolated location means that many of its eruptions have gone unreported.

Mejía is a canton in the province of Pichincha in northern Ecuador. It is named after Ecuadorian political figure José Mejía Lequerica. The canton includes a volcano in the Central Cordillera of the Ecuadorian Andes called Rumiñahui. The seat of the canton is called Machachi.

The black-breasted puffleg is a species of hummingbird native to Ecuador. It is Critically Endangered, with no more than 250 individuals remaining in the wild.

Chiles is a volcano on the border of Colombia and Ecuador. It lies 3 kilometres (2 mi) south-east of the volcano Cerro Negro de Mayasquer, and the two peaks are considered part of the same Chiles-Cerro Negro volcanic complex. The volcanoes, together with the Cumbal are andesitic in rock type. A 1936 eruption reported by the Colombian government agency Ingeominas may have been from the Ecuadorean volcano Reventador, otherwise the volcano has not erupted for around 160,000 years.
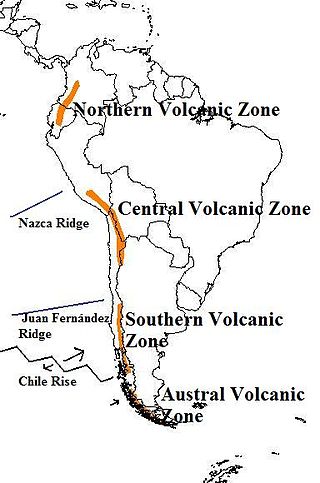
The Andean Volcanic Belt is a major volcanic belt along the Andean cordillera in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. It is formed as a result of subduction of the Nazca Plate and Antarctic Plate underneath the South American Plate. The belt is subdivided into four main volcanic zones which are separated by volcanic gaps. The volcanoes of the belt are diverse in terms of activity style, products, and morphology. While some differences can be explained by which volcanic zone a volcano belongs to, there are significant differences within volcanic zones and even between neighboring volcanoes. Despite being a type location for calc-alkalic and subduction volcanism, the Andean Volcanic Belt has a broad range of volcano-tectonic settings, as it has rift systems and extensional zones, transpressional faults, subduction of mid-ocean ridges and seamount chains as well as a large range of crustal thicknesses and magma ascent paths and different amounts of crustal assimilations.

The National Polytechnic School, also known as EPN, is a public university in Quito, Ecuador. The campus, called "José Rubén Orellana", is located at the sector center-oriental of Quito. It occupies an area of 15.2 hectares and has a built area of around 62,000 metres2. Its student body numbers approximately 10,000 of which thirty percent are women. The main campus encompasses ten teaching and research faculties, in addition to four technical and specialized institutes. EPN was founded in 1869 with the aim of becoming the first technical and technological center in the country. Since its beginnings, EPN adopted the polytechnic university model, which stresses laboratory instruction in applied science and engineering. At the campus, there are some libraries with a content primarily oriented to engineering and scientific topics.

Atacazo is a volcano of the Western Cordillera located 25 kilometers southwest of Quito, Ecuador. Atacazo is a stratovolcano formed by the action of a Late-Pleistocene to Holocene caldera. The last eruption of the Atacazo was nearly 2300 years ago.