
Bromine is a chemical element with symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest halogen, and is a fuming liquid with a deep red color. At room temperature, Bromine evaporates readily to form a red to amber coloured gas. Bromine's properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jérôme Balard, its name was derived from the Ancient Greek βρῶμος ("stench"), referencing its sharp and disagreeable smell.

Sodium bromide is an inorganic compound with the formula NaBr. It is a high-melting white, crystalline solid that resembles sodium chloride. It is a widely used source of the bromide ion and has many applications.

Niobium(V) chloride, also known as niobium pentachloride, is a yellow crystalline solid. It hydrolyzes in air, and samples are often contaminated with small amounts of NbOCl3. It is often used as a precursor to other compounds of niobium. NbCl5 may be purified by sublimation.
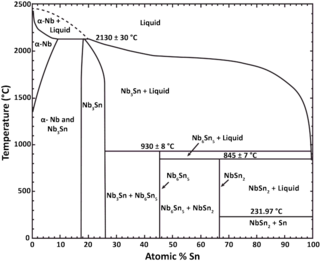
Niobium–tin (Nb3Sn) or triniobium–tin is an intermetallic compound of niobium (Nb) and tin (Sn), used industrially as a type II superconductor. This intermetallic compound is an A15 phase superconductor. It is more expensive than niobium-titanium (NbTi), but remains superconducting up to a magnetic flux density of 30 teslas [T] (300,000 G), compared to a limit of roughly 15 T for NbTi.

Tantalum(V) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula Ta2Br10. It is a diamagnetic yellow solid that hydrolyses readily. The compound adopts an edge-shared bioctahedral structure, which means that two square pyramidal TaBr5 subunits are joined by a pair of bridging bromide ligands. The pentachlorides and pentaiodides of Nb and Ta share this structural motif.

Niobium nitride is a compound of niobium and nitrogen (nitride) with the chemical formula NbN. At low temperatures NbN, niobium nitride becomes a superconductor, and is used in detectors for infrared light.

Niobium pentoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Nb2O5. It is a colourless insoluble solid that is fairly unreactive. It is the main precursor to all materials made of niobium, the dominant application being alloys, but other specialized applications include capacitors, lithium niobate, and optical glasses.

Niobium monoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula NbO. It is a grey solid with metallic conductivity.
Niobium oxide, sometimes called columbium oxide, may refer to:

Niobium dioxide, is the chemical compound with the formula NbO2. It is a bluish black non-stoichiometric solid with a composition range of NbO1.94-NbO2.09 It can be prepared by reacting Nb2O5 with H2 at 800–1350 °C. An alternative method is reaction of Nb2O5 with Nb powder at 1100 °C.

Niobium(IV) chloride, also known as niobium tetrachloride, is the chemical compound of formula NbCl4. This compound exists as dark violet crystals, is highly sensitive to air and moisture, and disproportiates into niobium(III) chloride and niobium(V) chloride when heated.

Niobium(V) fluoride, also known as niobium pentafluoride, is the inorganic compound]] with the formula NbF5. The solid consists of tetramers [NbF5]4. It is a colorless solid that is rarely used.
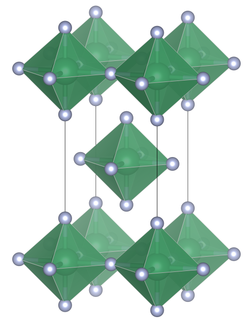
Niobium(IV) fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula NbF4; it is a nonvolatile black solid. It absorbs vapor strongly. It turns into NbO2F in moist air. NbF4 reacts with water to form a brown solution and a brown precipitate whose components are unknown. It is stable between 275 °C and 325 °C when heated in a vacuum. However, it disproportionates at 350 °C rapidly to form niobium(V) fluoride and niobium(III) fluoride:

Niobium oxychloride is the inorganic compound with the formula NbOCl3. It is a white, crystalline, diamagnetic solid. It is often found as an impurity in samples of niobium pentachloride, a common reagent in niobium chemistry.

Niobium(V) ethoxide is an metalorganic compound with formula Nb2(OC2H5)10. It is a colorless solid that dissolves in some organic solvents but hydrolyzes readily. It is mainly used for the sol-gel processing of materials containing niobium oxides.

Niobium diselenide or niobium(IV) selenide is a layered transition metal dichalcogenide with formula NbSe2. Niobium diselenide is a lubricant, and a superconductor at temperatures below 7.2 K that exhibit a charge density wave (CDW). NbSe2 crystallizes in several related forms, and can be mechanically exfoliated into monatomic layers, similar to other transition metal dichalcogenide monolayers. Monolayer NbSe2 exhibits very different properties from the bulk material, such as of Ising superconductivity, quantum metallic state, and strong enhancement of the CDW.
Organoniobium chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing niobium-carbon (Nb-C) bonds. Organoniobium compounds often have niobium in the oxidation state +5. A convenient starting material is niobium(V) chloride. Organoniobium(V) compounds are often strongly oxophilic. Organoniobium and organotantalum chemistry are similar, except that the tantalum compounds are more resistant to reduction.















