Functionality
This is the hardware that is connected to the mobile phone network that communicates directly with mobile handsets. In contrast with GSM base stations, Node B uses WCDMA/TD-SCDMA as the air interface technology. As in all cellular systems, such as UMTS and GSM, the Node B contains radio frequency transmitter(s) and the receiver(s) used to communicate directly with mobile devices, which move freely around it. In this type of cellular network, the mobile devices cannot communicate directly with each other but have to communicate with the NodeB.
Traditionally, the Node Bs have minimum functionality, and are controlled by an RNC (Radio Network Controller). However, this is changing with the emergence of High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA), where some logic (e.g., retransmission) is handled on the Node B for lower response times.

The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is a standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to describe the protocols for second-generation (2G) digital cellular networks used by mobile devices such as mobile phones and tablets. GSM is also a trade mark owned by the GSM Association. GSM may also refer to the Full Rate voice codec.

General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a packet oriented mobile data standard on the 2G cellular communication network's global system for mobile communications (GSM). GPRS was established by European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) in response to the earlier CDPD and i-mode packet-switched cellular technologies. It is now maintained by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP).
The Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is a third generation mobile cellular system for networks based on the GSM standard. Developed and maintained by the 3GPP, UMTS is a component of the International Telecommunication Union IMT-2000 standard set and compares with the CDMA2000 standard set for networks based on the competing cdmaOne technology. UMTS uses wideband code-division multiple access (W-CDMA) radio access technology to offer greater spectral efficiency and bandwidth to mobile network operators.

A wireless network is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes. Wireless networking allows homes, telecommunications networks and business installations to avoid the costly process of introducing cables into a building, or as a connection between various equipment locations. Admin telecommunications networks are generally implemented and administered using radio communication. This implementation takes place at the physical level (layer) of the OSI model network structure.

3G is the third generation of wireless mobile telecommunications technology. It is the upgrade over 2G, 2.5G, GPRS and 2.75G Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution networks, offering faster data transfer, and better voice quality. This network was superseded by 4G, and later on by 5G. This network is based on a set of standards used for mobile devices and mobile telecommunications use services and networks that comply with the International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000) specifications by the International Telecommunication Union. 3G finds application in wireless voice telephony, mobile Internet access, fixed wireless Internet access, video calls and mobile TV.
The GPRS core network is the central part of the general packet radio service (GPRS) which allows 2G, 3G and WCDMA mobile networks to transmit Internet Protocol (IP) packets to external networks such as the Internet. The GPRS system is an integrated part of the GSM network switching subsystem.
The Radio Network Controller (RNC) is a governing element in the UMTS radio access network (UTRAN) and is responsible for controlling the Node Bs that are connected to it. The RNC carries out radio resource management, some of the mobility management functions and is the point where encryption is done before user data is sent to and from the mobile. The RNC connects to the Circuit Switched Core Network through Media Gateway (MGW) and to the SGSN in the Packet Switched Core Network.
A base transceiver station (BTS) is a piece of equipment that facilitates wireless communication between user equipment (UE) and a network. UEs are devices like mobile phones (handsets), WLL phones, computers with wireless Internet connectivity, or antennas mounted on buildings or telecommunication towers. The network can be that of any of the wireless communication technologies like GSM, CDMA, wireless local loop, Wi-Fi, WiMAX or other wide area network (WAN) technology.

A cellular network or mobile network is a telecommunications network where the link to and from end nodes is wireless and the network is distributed over land areas called cells, each served by at least one fixed-location transceiver. These base stations provide the cell with the network coverage which can be used for transmission of voice, data, and other types of content. A cell typically uses a different set of frequencies from neighboring cells, to avoid interference and provide guaranteed service quality within each cell.
GSM frequency bands or frequency ranges are the cellular frequencies designated by the ITU for the operation of GSM mobile phones and other mobile devices.
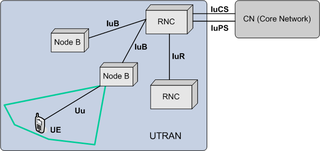
UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN) is a collective term for the network and equipment that connects mobile handsets to the public telephone network or the Internet. It contains the base stations, which are called Node B's and Radio Network Controllers (RNCs) which make up the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) radio access network. This communications network, commonly referred to as 3G, can carry many traffic types from real-time Circuit Switched to IP based Packet Switched. The UTRAN allows connectivity between the UE and the core network.
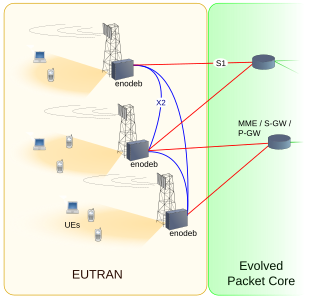
E-UTRA is the air interface of 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Long Term Evolution (LTE) upgrade path for mobile networks. It is an acronym for Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access, also known as the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access in early drafts of the 3GPP LTE specification. E-UTRAN is the combination of E-UTRA, user equipment (UE), and a Node B.

In telecommunications, a femtocell is a small, low-power cellular base station, typically designed for use in a home or small business. A broader term which is more widespread in the industry is small cell, with femtocell as a subset. It connects to the service provider's network via broadband ; current designs typically support four to eight simultaneously active mobile phones in a residential setting depending on version number and femtocell hardware, and eight to sixteen mobile phones in enterprise settings. A femtocell allows service providers to extend service coverage indoors or at the cell edge, especially where access would otherwise be limited or unavailable. Although much attention is focused on WCDMA, the concept is applicable to all standards, including GSM, CDMA2000, TD-SCDMA, WiMAX and LTE solutions.

High Speed Packet Access (HSPA) is an amalgamation of two mobile protocols—High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) and High Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA)—that extends and improves the performance of existing 3G mobile telecommunication networks using the WCDMA protocols. A further-improved 3GPP standard called Evolved High Speed Packet Access was released late in 2008, with subsequent worldwide adoption beginning in 2010. The newer standard allows bit rates to reach as high as 337 Mbit/s in the downlink and 34 Mbit/s in the uplink; however, these speeds are rarely achieved in practice.
The UMTS frequency bands are radio frequencies used by third generation (3G) wireless Universal Mobile Telecommunications System networks. They were allocated by delegates to the World Administrative Radio Conference (WARC-92) held in Málaga-Torremolinos, Spain between 3 February 1992 and 3 March 1992. Resolution 212 (Rev.WRC-97), adopted at the World Radiocommunication Conference held in Geneva, Switzerland in 1997, endorsed the bands specifically for the International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000) specification by referring to S5.388, which states "The bands 1,885-2,025 MHz and 2,110-2,200 MHz are intended for use, on a worldwide basis, by administrations wishing to implement International Mobile Telecommunications 2000 (IMT-2000). Such use does not preclude the use of these bands by other services to which they are allocated. The bands should be made available for IMT-2000 in accordance with Resolution 212 ." To accommodate the reality that these initially defined bands were already in use in various regions of the world, the initial allocation has been amended multiple times to include other radio frequency bands.

Evolved High Speed Packet Access, HSPA+, HSPA (Plus) or HSPAP, is a technical standard for wireless broadband telecommunication. It is the second phase of HSPA which has been introduced in 3GPP release 7 and being further improved in later 3GPP releases. HSPA+ can achieve data rates of up to 42.2 Mbit/s. It introduces antenna array technologies such as beamforming and multiple-input multiple-output communications (MIMO). Beam forming focuses the transmitted power of an antenna in a beam towards the user's direction. MIMO uses multiple antennas at the sending and receiving side. Further releases of the standard have introduced dual carrier operation, i.e. the simultaneous use of two 5 MHz carriers. HSPA+ is an evolution of HSPA that upgrades the existing 3G network and provides a method for telecom operators to migrate towards 4G speeds that are more comparable to the initially available speeds of newer LTE networks without deploying a new radio interface. HSPA+ should not be confused with LTE though, which uses an air interface based on orthogonal frequency-division modulation and multiple access.
The HTC Touch 3G is a Windows Mobile smartphone developed by the High Tech Computer Corporation of Taiwan. It was announced in September 2008 and released the following November. Part of the HTC Touch Family, it features quad band GSM and dual band UMTS connectivity, as well as a version of the proprietary TouchFLO 3D user interface developed by HTC.
WSDMA is a high bandwidth channel access method, developed for multi-transceiver systems such as active array antennas. WSDMA is a beamforming technique suitable for overlay on the latest air-interface protocols including WCDMA and OFDM. WSDMA enabled systems can determine the angle of arrival (AoA) of received signals to spatially divide a cell sector into many sub-sectors. This spatial awareness provides information necessary to maximise Carrier to Noise+Interference Ratio (CNIR) link budget, through a range of digital processing routines. WSDMA facilitates a flexible approach to how uplink and downlink beamforming is performed and is capable of spatial filtering known interference generating locations.

E-UTRAN Node B, also known as Evolved Node B, is the element in E-UTRA of LTE that is the evolution of the element Node B in UTRA of UMTS. It is the hardware that is connected to the mobile phone network that communicates directly wirelessly with mobile handsets (UEs), like a base transceiver station (BTS) in GSM networks.











