
Aphasia, also known as dysphasia, is an impairment in a person’s ability to comprehend or formulate language because of damage to specific brain regions. The major causes are stroke and head trauma; prevalence is hard to determine, but aphasia due to stroke is estimated to be 0.1–0.4% in the Global North. Aphasia can also be the result of brain tumors, epilepsy, autoimmune neurological diseases, brain infections, or neurodegenerative diseases.

Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression, PTSD and anxiety disorders. Cognitive behavioral therapy focuses on challenging and changing cognitive distortions and their associated behaviors to improve emotional regulation and develop personal coping strategies that target solving current problems. Though it was originally designed to treat depression, its uses have been expanded to include many issues and the treatment of many mental health and other conditions, including anxiety, substance use disorders, marital problems, ADHD, and eating disorders. CBT includes a number of cognitive or behavioral psychotherapies that treat defined psychopathologies using evidence-based techniques and strategies.
Hypnotherapy, also known as hypnotic medicine, is the use of hypnosis in psychotherapy. Hypnotherapy is generally not considered to be based on scientific evidence, and is rarely recommended in clinical practice guidelines. Reviews by psychologists have found hypnosis to be effective as an adjunctive treatment for a range of conditions, such as chronic and acute pain, irritable bowel syndrome, post-traumatic stress disorder, phobias and eating disorder. ”It is regarded as a type of alternative medicine.

Anger management is a psycho-therapeutic program for anger prevention and control. It has been described as deploying anger successfully. Anger is frequently a result of frustration, or of feeling blocked or thwarted from something the subject feels is important. Anger can also be a defensive response to underlying fear or feelings of vulnerability or powerlessness. Anger management programs consider anger to be a motivation caused by an identifiable reason which can be logically analyzed and addressed.
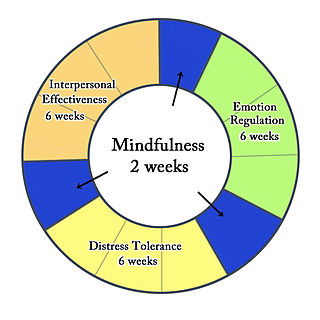
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is an evidence-based psychotherapy that began with efforts to treat personality disorders and interpersonal conflicts. Evidence suggests that DBT can be useful in treating mood disorders and suicidal ideation as well as for changing behavioral patterns such as self-harm and substance use. DBT evolved into a process in which the therapist and client work with acceptance and change-oriented strategies and ultimately balance and synthesize them—comparable to the philosophical dialectical process of thesis and antithesis, followed by synthesis.

Aaron Temkin Beck was an American psychiatrist who was a professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Pennsylvania. He is regarded as the father of cognitive therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). His pioneering methods are widely used in the treatment of clinical depression and various anxiety disorders. Beck also developed self-report measures for depression and anxiety, notably the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), which became one of the most widely used instruments for measuring the severity of depression. In 1994 he and his daughter, psychologist Judith S. Beck, founded the nonprofit Beck Institute for Cognitive Behavior Therapy, which provides CBT treatment and training, as well as research. Beck served as President Emeritus of the organization up until his death.

Physical abuse is any intentional act causing injury or trauma to another person or animal by way of bodily contact. In most cases, children are the victims of physical abuse, but adults can also be victims, as in cases of domestic violence or workplace aggression. Alternative terms sometimes used include physical assault or physical violence, and may also include sexual abuse. Physical abuse may involve more than one abuser, and more than one victim.

Perfectionism, in psychology, is a broad personality trait characterized by a person's concern with striving for flawlessness and perfection and is accompanied by critical self-evaluations and concerns regarding others' evaluations. It is best conceptualized as a multidimensional and multilayered personality characteristic, and initially some psychologists thought that there were many positive and negative aspects.
Andrew Salter was an American clinical psychologist who introduced behavior therapy, developed many of its conceptual foundations, and created numerous techniques still used today across its varied descendants, including cognitive behavioral therapy. His work in the early 1940s demystified hypnosis, interpreting it as a form of conditioning, now the widely accepted view. He was one of the founders of the Association for the Advancement of Behavioral Therapies, now the Association for Behavioral and Cognitive Therapies. He maintained an active clinical practice in Manhattan until shortly before his death. His key ideas are documented in his book, Conditioned Reflex Therapy,, originally published in 1949 and reprinted many times, with a new edition published by Watkins Press in 2019. All citations from CRT refer to this edition.
Acceptance and commitment therapy is a form of psychotherapy, as well as a branch of clinical behavior analysis. It is an empirically-based psychological intervention that uses acceptance and mindfulness strategies along with commitment and behavior-change strategies to increase psychological flexibility.

Adventure therapy is a form of psychotherapy created as early as the 1960s. It is influenced by a variety of learning and psychological theories. Experiential education is the underlying philosophy.
Steven C. Hayes is an American clinical psychologist and Nevada Foundation Professor at the University of Nevada, Reno Department of Psychology, where he is a faculty member in their Ph.D. program in behavior analysis. He is known for developing relational frame theory, an account of human higher cognition, and as the co-developer of acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), a popular evidence-based form of psychotherapy that uses mindfulness, acceptance, and values-based methods, and is the co-developer of process-based therapy (PBT), a new approach to evidence-based therapies more generally. He also coined the term clinical behavior analysis.
Cognitive therapy (CT) is a type of psychotherapy developed by American psychiatrist Aaron T. Beck. CT is one therapeutic approach within the larger group of cognitive behavioral therapies (CBT) and was first expounded by Beck in the 1960s. Cognitive therapy is based on the cognitive model, which states that thoughts, feelings and behavior are all connected, and that individuals can move toward overcoming difficulties and meeting their goals by identifying and changing unhelpful or inaccurate thinking, problematic behavior, and distressing emotional responses. This involves the individual working with the therapist to develop skills for testing and changing beliefs, identifying distorted thinking, relating to others in different ways, and changing behaviors. A cognitive case conceptualization is developed by the cognitive therapist as a guide to understand the individual's internal reality, select appropriate interventions and identify areas of distress.
Functional analysis in behavioral psychology is the application of the laws of operant and respondent conditioning to establish the relationships between stimuli and responses. To establish the function of operant behavior, one typically examines the "four-term contingency": first by identifying the motivating operations, then identifying the antecedent or trigger of the behavior, identifying the behavior itself as it has been operationalized, and identifying the consequence of the behavior which continues to maintain it.
Self-embedding is the insertion of foreign objects either into soft tissues under the skin or into muscle. Self-embedding is typically considered deliberate self-harm, also known as nonsuicidal self-injury, which is defined as "deliberate, direct destruction of tissues without suicidal intent."
Flexibility is a personality trait that describes the extent to which a person can cope with changes in circumstances and think about problems and tasks in novel, creative ways. This trait comes into play when stressors or unexpected events occur, requiring that a person change their stance, outlook, or commitment.
Experiential avoidance (EA) has been broadly defined as attempts to avoid thoughts, feelings, memories, physical sensations, and other internal experiences — even when doing so creates harm in the long run. The process of EA is thought to be maintained through negative reinforcement — that is, short-term relief of discomfort is achieved through avoidance, thereby increasing the likelihood that the avoidance behavior will persist. Importantly, the current conceptualization of EA suggests that it is not negative thoughts, emotions, and sensations that are problematic, but how one responds to them that can cause difficulties. In particular, a habitual and persistent unwillingness to experience uncomfortable thoughts and feelings is thought to be linked to a wide range of problems, as opposed to deliberately choosing discomfort, which only results in discomfort.
Augustus John Rush is an internationally renowned psychiatrist. He is a professor emeritus in Duke-NUS Medical School at the National University of Singapore (NUS), and adjunct professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Duke University School of Medicine. He has authored and edited more than 10 books, and over 600 scientific journal articles that are largely focused on the diagnosis and treatment of depressive and bipolar disorders.

Jonathan Stuart Abramowitz is an American clinical psychologist and Professor in the Department of Psychology and Neuroscience at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (UNC-CH). He is an expert on obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and anxiety disorders whose work is highly cited. He maintains a research lab and currently serves as the Director of the UNC-CH Clinical Psychology PhD Program. Abramowitz approaches the understanding and treatment of psychological problems from a cognitive-behavioral perspective.
Anne Marie Albano is a clinical psychologist known for her clinical work and research on psychosocial treatments for anxiety and mood disorders, and the impact of these disorders on the developing youth. She is the CUCARD professor of medical psychology in psychiatry at Columbia University, the founding director of the Columbia University Clinic for Anxiety and Related Disorders (CUCARD), and the clinical site director at CUCARD of the New York Presbyterian Hospital's Youth Anxiety Center.








