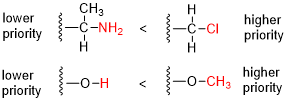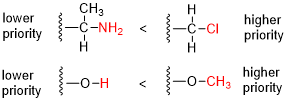
In organic chemistry, the Cahn–Ingold–Prelog (CIP) sequence rules are a standard process to completely and unequivocally name a stereoisomer of a molecule. The purpose of the CIP system is to assign an R or S descriptor to each stereocenter and an E or Z descriptor to each double bond so that the configuration of the entire molecule can be specified uniquely by including the descriptors in its systematic name. A molecule may contain any number of stereocenters and any number of double bonds, and each usually gives rise to two possible isomers. A molecule with an integer n describing the number of stereocenters will usually have 2n stereoisomers, and 2n−1 diastereomers each having an associated pair of enantiomers. The CIP sequence rules contribute to the precise naming of every stereoisomer of every organic molecule with all atoms of ligancy of fewer than 4.
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis.

The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. IUPAC's executive director heads this administrative office, currently Greta Heydenrych.
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry.
In organic chemistry, a substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule.

Nitryl is the nitrogen dioxide (NO2) moiety when it occurs in a larger compound as a univalent fragment. Examples include nitryl fluoride (NO2F) and nitryl chloride (NO2Cl).
Chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry is a systematic method of naming inorganic chemical compounds, as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry. Ideally, every inorganic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous formula can be determined. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry.
The suffix –ol is used in organic chemistry principally to form names of organic compounds containing the hydroxyl (–OH) group, mainly alcohols. The suffix was extracted from the word alcohol.

Quantities, Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry, also known as the Green Book, is a compilation of terms and symbols widely used in the field of physical chemistry. It also includes a table of physical constants, tables listing the properties of elementary particles, chemical elements, and nuclides, and information about conversion factors that are commonly used in physical chemistry. The Green Book is published by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and is based on published, citeable sources. Information in the Green Book is synthesized from recommendations made by IUPAC, the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), including recommendations listed in the IUPAP Red Book Symbols, Units, Nomenclature and Fundamental Constants in Physics and in the ISO 31 standards.
The suffix -oate is the IUPAC nomenclature used in organic chemistry to form names of compounds formed from carboxylic acids. They are of two types:
In chemical nomenclature, a preferred IUPAC name (PIN) is a unique name, assigned to a chemical substance and preferred among all possible names generated by IUPAC nomenclature. The "preferred IUPAC nomenclature" provides a set of rules for choosing between multiple possibilities in situations where it is important to decide on a unique name. It is intended for use in legal and regulatory situations.

The Compendium of Analytical Nomenclature is an IUPAC nomenclature book published by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) containing internationally accepted definitions for terms in analytical chemistry. It has traditionally been published in an orange cover, hence its informal name, the Orange Book.
In organic chemistry, Hantzsch–Widman nomenclature, also called the extended Hantzsch–Widman system, is a type of systematic chemical nomenclature used for naming heterocyclic parent hydrides having no more than ten ring members. Some common heterocyclic compounds have retained names that do not follow the Hantzsch–Widman pattern.
In chemistry, a retained name is a name for a chemical compound, that is recommended for use by a system of chemical nomenclature, but that is not exactly systematic. Retained names are often used for the most fundamental parts of a nomenclature system: almost all the chemical elements have retained names rather than being named systematically, as do the first four alkanes, benzene and most simple heterocyclic compounds. Water and ammonia are other examples of retained names.
In chemistry, a ring is an ambiguous term referring either to a simple cycle of atoms and bonds in a molecule or to a connected set of atoms and bonds in which every atom and bond is a member of a cycle. A ring system that is a simple cycle is called a monocycle or simple ring, and one that is not a simple cycle is called a polycycle or polycyclic ring system. A simple ring contains the same number of sigma bonds as atoms, and a polycyclic ring system contains more sigma bonds than atoms.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) publishes many books which contain its complete list of definitions. The definitions are divided initially into seven IUPAC Colour Books: Gold, Green, Blue, Purple, Orange, White, and Red. There is also an eighth book, the "Silver Book".
The Compendium of Macromolecular Nomenclature, by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), provides definition of polymer related terms and rules of nomenclature of polymers. It is referred to as the Purple Book. It was published in 1991 (ISBN 0-63202-8475) by Blackwell Science. The author of this book is W.V. Metanomski.

The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has published four sets of rules to standardize chemical nomenclature.

In chromatography, resolution is a measure of the separation of two peaks of different retention time t in a chromatogram.