
Victoria is an incorporated town in Lunenburg County, Virginia, United States. The population was 1,725 at the 2010 census, which was down from the 1,821 reported in 2000.

The Virginian Railway was a Class I railroad located in Virginia and West Virginia in the United States. The VGN was created to transport high quality "smokeless" bituminous coal from southern West Virginia to port at Hampton Roads.

The Norfolk and Western Railway, commonly called the N&W, was a US class I railroad, formed by more than 200 railroad mergers between 1838 and 1982. It was headquartered in Roanoke, Virginia, for most of its existence. Its motto was "Precision Transportation"; it had a variety of nicknames, including "King Coal" and "British Railway of America". In 1986, N&W merged with Southern Railway to form today's Norfolk Southern Railway.

The Norfolk and Petersburg Railroad was built between Norfolk and Petersburg, Virginia and was completed by 1858. The line was 85 miles (137 km) of 5 ft track gauge.

The Southside Railroad was formed in Virginia in 1846. Construction was begun in 1849 and completed in 1854. The 5 ft gauge railroad connected City Point, a port on the James River with the farm country south and west of Petersburg, Virginia, to Lynchburg, Virginia, a distance of about 132 miles (212 km).
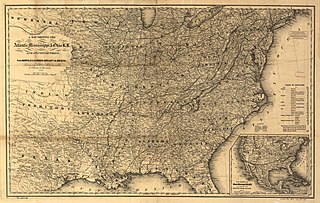
Atlantic, Mississippi and Ohio Railroad (AM&O) was formed in 1870 in Virginia from three east–west railroads which traversed across the southern portion of the state. Organized and led by former Confederate general William Mahone (1826-1895), the 428-mile (689 km) line linked Norfolk with Bristol, Virginia by way of Suffolk, Petersburg, Lynchburg, and Salem. The AM&O was promoted as a trade link to the west, and further expansion was envisioned with the goal of increasing Virginia's Ohio Valley and Mississippi Valley commerce. It was heavily backed by investors from England and Scotland.
The Seaboard and Roanoke Railroad was organized in 1833 to extend from the area of the rapids of the Roanoke River at its fall line near Weldon, North Carolina to Portsmouth, Virginia, across the Elizabeth River from Norfolk on the harbor of Hampton Roads.

The Pocahontas was a named overnight passenger train, operated by the Norfolk and Western Railway (N&W) in the United States. It made its inaugural operation on November 21, 1926, with two trains; Nos. 3 and 4, which both ran 676 miles (1,088 km) daily at night on the N&W mainline between Norfolk, Virginia, and Cincinnati, Ohio, with a through-connection to and from Chicago, Illinois. The Pocahontas replaced an earlier passenger train called the Norfolk-Chicago Express, which bears the same train numbers.

The Powhatan Arrow was a named flagship passenger train operated by the Norfolk and Western Railway (N&W) in the United States. Debuting on April 28, 1946, the daily westbound No. 25 and the eastbound No. 26 connected Norfolk, Virginia, and Cincinnati, Ohio, covering 676 miles (1,088 km) in about 15 hours and 45 minutes behind streamlined 4-8-4 class J steam locomotives. In late 1949, N&W re-equipped the Powhatan Arrow consist with new lightweight passenger cars, dining cars, and observation cars from the Pullman-Standard Company. It was advertised as the "most beautiful train in the east."

The Cavalier was one of the named passenger trains of the Norfolk and Western Railway. Originally running from Norfolk, Virginia, to Cincinnati, Ohio, by 1957 trains 15 and 16 had been cut back to a Petersburg, Virginia, to Portsmouth, Ohio run. Service to Norfolk was maintained by combining train 15 with train 27, and train 16 with train 22, the eastbound Cannonball.

Kemper Street station, also known as Lynchburg station, is an intermodal transit station in Lynchburg, Virginia, United States. It serves Amtrak while an adjacent bus transfer center serves Greater Lynchburg Transit Company and Greyhound buses. Kemper Street Station is located at 825 Kemper Street.

The Virginia Museum of Transportation (VMT) is a museum in Downtown Roanoke, Virginia, that is devoted to the topic of transportation.
Located in the southeastern corner of the state, Norfolk is economically and culturally important to Virginia. A variety of transportation modes have developed around the city's importance and somewhat unusual geography.

Norfolk and Western 1218 is a preserved four-cylinder simple articulated 2-6-6-4 steam locomotive, built in June 1943 by the Norfolk and Western's (N&W) Roanoke Shops in Roanoke, Virginia as part of the N&W's class "A" fleet of fast freight locomotives. It was retired from regular revenue service in July 1959, and was later restored by Norfolk Southern for excursion service for their steam program, pulling excursions throughout the eastern United States from 1987 to 1991. It is currently on display at the Virginia Museum of Transportation in Roanoke, Virginia.

The Hilltopper was a passenger train operated by Amtrak in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It ran daily from South Station in Boston, Massachusetts to Catlettsburg station in Catlettsburg, Kentucky. The 1,674 mi (2,694 km) run made 34 stops in 11 states and the District of Columbia.

The Pelican was a named train of the Southern Railway which ran from New York City to New Orleans and back until 1970.

Norfolk and Western 611, also known as the "Spirit of Roanoke" and the "Queen of Steam", is the only surviving example of Norfolk and Western's (N&W) class J 4-8-4 type "Northern" streamlined steam locomotives. Built in May 1950 at N&W's Roanoke Shops in Roanoke, Virginia, it was one of the last mainline passenger steam locomotives built in the United States and represents a pinnacle of American steam locomotive technology.

The Mountaineer was a passenger train operated by Amtrak between Norfolk, Virginia, and Chicago, Illinois, via Cincinnati, Ohio. It was the first train to use the Norfolk and Western Railway's tracks since the creation of Amtrak in 1971 and followed the route of the Pocahontas, the N&W's last passenger train. Service began in 1975 and ended in 1977. A new train, the Hilltopper, operated over much of the Mountaineer's route but was itself discontinued in 1979.
The 21st Century Steam program was conducted by the Norfolk Southern Railway from 2011 to 2015, featuring four classic steam locomotives pulling passenger excursions along Norfolk Southern rails in the eastern United States. The last train was to be Southern 4501's Piedmont Limited excursion trip from Atlanta, Georgia, to Toccoa, Georgia, but cancelled on October 1 due to Hurricane Joaquin.

Roanoke station is a train station in Roanoke, Virginia, the current southern terminus of Amtrak's Northeast Regional line. Built in 2017, it follows several other Roanoke passenger stations that operated from the 1850s to 1979. The unstaffed station consists of a single high-level platform with no station building or waiting room available for passengers. All tickets must be purchased in advance; there is no Quik-Trak kiosk at the station.


















