
A chordate is an animal of the phylum Chordata. All chordates possess 5 synapomorphies, or primary characteristics, at some point during their larval or adulthood stages that distinguish them from all other taxa. These 5 synapomorphies include a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. The name “chordate” comes from the first of these synapomorphies, the notochord, which plays a significant role in chordate structure and movement. Chordates are also bilaterally symmetric, have a coelom, possess a circulatory system, and exhibit metameric segmentation.

The true finches are small to medium-sized passerine birds in the family Fringillidae. Finches have stout conical bills adapted for eating seeds and nuts and often have colourful plumage. They occupy a great range of habitats where they are usually resident and do not migrate. They have a worldwide distribution except for Australia and the polar regions. The family Fringillidae contains more than two hundred species divided into fifty genera. It includes species known as siskins, canaries, redpolls, serins, grosbeaks and euphonias.

Penguins are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the southern hemisphere: only one species, the Galápagos penguin, is found north of the Equator. Highly adapted for life in the water, penguins have countershaded dark and white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch while swimming underwater. They spend roughly half of their lives on land and the other half in the sea.

Nightjars are medium-sized nocturnal or crepuscular birds in the family Caprimulgidae and order Caprimulgiformes, characterised by long wings, short legs, and very short bills. They are sometimes called goatsuckers, due to the ancient folk tale that they sucked the milk from goats, or bugeaters, their primary source of food being insects. Some New World species are called nighthawks. The English word "nightjar" originally referred to the European nightjar.

The even-toed ungulates are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many other even-toed ungulates digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do.

Birds of prey, also known as raptors, include species of bird that primarily hunt and feed on vertebrates that are large relative to the hunter. Additionally, they have keen eyesight for detecting food at a distance or during flight, strong feet equipped with talons for grasping or killing prey, and powerful, curved beaks for tearing flesh. The term raptor is derived from the Latin word rapio, meaning to seize or take by force. In addition to hunting live prey, many birds, such as fish eagles, vultures, and condors, eat carrion.

Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk with a crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants of a species are either male or female. Cycads vary in size from having trunks only a few centimeters to several meters tall. They typically grow very slowly and live very long, with some specimens known to be as much as 1,000 years old. Because of their superficial resemblance, they are sometimes mistaken for palms or ferns, but they are not closely related to either group.

In zoological nomenclature, a type species is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus.
Parallel evolution is the similar development of a trait in distinct species that are not closely related, but share a similar original trait in response to similar evolutionary pressure.

A reedbed or reed bed is a natural habitat found in floodplains, waterlogged depressions and estuaries. Reedbeds are part of a succession from young reeds colonising open water or wet ground through a gradation of increasingly dry ground. As reedbeds age, they build up a considerable litter layer that eventually rises above the water level and that ultimately provides opportunities for shrubland or woodland invasion.
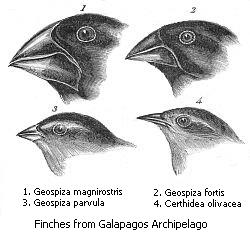
Divergent evolution or divergent selection is the accumulation of differences between closely related populations within a species, leading to speciation. Divergent evolution is typically exhibited when two populations become separated by a geographic barrier and experience different selective pressures that drive adaptations to their new environment. After many generations and continual evolution, the populations become less able to interbreed with one another. The American naturalist J. T. Gulick (1832–1923) was the first to use the term "divergent evolution", with its use becoming widespread in modern evolutionary literature. Classic examples of divergence in nature are the adaptive radiation of the finches of the Galapagos or the coloration differences in populations of a species that live in different habitats such as with pocket mice and fence lizards.

In biology, a species complex is a group of closely related organisms that are so similar in appearance that the boundaries between them are often unclear. Terms that are sometimes used synonymously but have more precise meanings are cryptic species for two or more species hidden under one species name, sibling species for two cryptic species that are each other's closest relative, and species flock for a group of closely related species that live in the same habitat. As informal taxonomic ranks, species group, species aggregate, macrospecies, and superspecies are also in use.

Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Around 99% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with over 95% belonging to the teleost subgrouping.

Ichthyornithes is an extinct group of toothed avialans very closely related to the common ancestor of all modern birds. They are known from fossil remains found throughout the late Cretaceous period of North America, though only one species, Ichthyornis dispar, is represented by complete enough fossils to have been named. Ichthyornitheans became extinct at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, along with enantiornitheans, all other non-avian dinosaurs, and many other animal and plant groups.

Banksia kingii is an extinct species of tree or shrub in the plant genus Banksia. It is known only from fossil leaves and fruiting "cones" found in Late Pleistocene sediment at Melaleuca Inlet in western Tasmania. These were discovered by Deny King in the workings of his tin mine. The climate was most likely as cool as or cooler than it is at Melaleuca now , and possibly wetter, over 2400 mm annually.
Novopsocus is a genus in the Pseudocaeciliidae family, with, until 2008, one described species endemic to New Guinea. It was later found that the specimens of two different species had been mixed, and an individual of a third species was found. The genus is characterised by a flat head with a sharp vertex, narrow, strap-like wings, and antennae with a broad, flattened first flagellar segment in the males of two species.
Novopsocus caeciliae is a species of Novopsocus from New Guinea known from a single male thus far, found in the lowlands near Baitabag, Madang Province. Its hypandrium is similar to that of Novopsocus magnus, and thus differs from the hypandrium of Novopsocus stenopterus. It is the smallest of all three Novopsocus species.
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined.
Novopsocus magnus is a species of Pseudocaeciliidae that lives on the island of New Guinea. Males of this species were first thought by Thornton (1984) to be males of N. stenopterus, but Cuénoud (2008) showed that it is indeed a separate species by identifying real males of N. stenopterus and actual females of N. magnus. It is the largest species of the genus, and its males have peculiar antennae, with a first flagellar segment strongly broadened and flattened.
Protea restionifolia, which is also known as the Reed-leaf sugarbush, is a flowering shrub endemic to the Western Cape province of South Africa where it is found from the upper part of the Breede River Valley through the Bot River Valley to Wolseley and the Koue Bokkeveld Mountains.












