
South Africa occupies the southern tip of Africa, its coastline stretching more than 2,850 kilometres from the desert border with Namibia on the Atlantic (western) coast southwards around the tip of Africa and then northeast to the border with Mozambique on the Indian (eastern) coast. The low-lying coastal zone is narrow for much of that distance, soon giving way to a mountainous escarpment that separates the coast from the high inland plateau. In some places, notably the province of KwaZulu-Natal in the east, a greater distance separates the coast from the escarpment. Although much of the country is classified as semi-arid, it has considerable variation in climate as well as topography. The total land area is 1,220,813 km2 (471,359 sq mi). It has the 23rd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,535,538 km2 (592,875 sq mi).

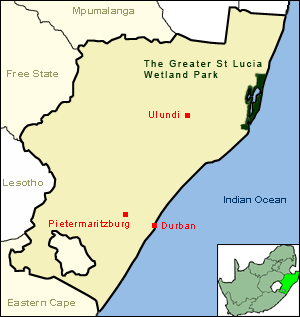
KwaZulu-Natal is a province of South Africa that was created in 1994 when the Zulu bantustan of KwaZulu and Natal Province were merged. It is located in the southeast of the country, with a long shoreline on the Indian Ocean and sharing borders with three other provinces and the countries of Mozambique, Eswatini and Lesotho. Its capital is Pietermaritzburg, and its largest city is Durban. It is the second-most populous province in South Africa, with slightly fewer residents than Gauteng.

The Drakensberg is the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, which encloses the central Southern African plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation – 2,000 to 3,482 metres within the border region of South Africa and Lesotho.

Hluhluwe–Imfolozi Park, formerly Hluhluwe–Umfolozi Game Reserve, is the oldest proclaimed nature reserve in Africa. It consists of 960 km² of hilly topography 280 kilometres (170 mi) north of Durban in central KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa and is known for its rich wildlife and conservation efforts. Operated by Ezemvelo KZN Wildlife, the park is the only state-run park in KwaZulu-Natal where each of the big five game animals can be found.
KwaZulu-Natal is one of the most diverse provinces in South Africa in terms of its fauna and flora. Many of its wide variety of ecosystems have been preserved as parks and reserves, which are popular tourist attractions. Ezemvelo KZN Wildlife is a governmental agency that maintains the wildlife conservation areas in the province.
Kosi Bay is a series of four interlinked lakes in the Maputaland area of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa.

Ndumo Game Reserve is a small South African game reserve located in the far northeast district of KwaZulu-Natal known as Maputaland. It is situated on the border with Mozambique where the Pongola River joins the Great Usutu River. It is adjacent to the Tembe Elephant Park. Ndumo is relatively remote, being over 400 kilometres (250 mi) from Durban. The town of Mkuze is 110 kilometres (68 mi) away.
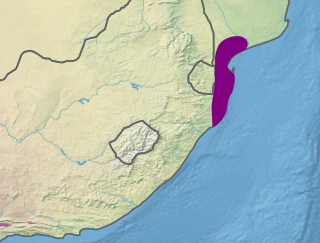
The Maputaland coastal forest mosaic is a subtropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion on the Indian Ocean coast of Southern Africa. It covers an area of 29,961 square kilometres (11,568 sq mi) in southern Mozambique, Eswatini, and the KwaZulu-Natal Province of South Africa. Mozambique's capital Maputo lies within the ecoregion.

Mkhambathi Nature Reserve is a protected area at Lusikisiki in the Eastern Cape, South Africa. It is 7,720 hectares, with the Pondoland Marine Protected Area off its coastal edge. The reserve is located in the Pondoland Centre of Plant Endemism and the greater Maputaland–Pondoland–Albany Hotspot, and is covered in open grassland, dotted with patches of indigenous forest, swamp forests and flanked by the forested ravines of the Msikaba and Mtentu rivers.

Abe Bailey Nature Reserve is a protected area in the Merafong City Local Municipality in Gauteng, South Africa. It is situated near Carletonville, beside the township of Khutsong on the West Rand. It is about 4,200 hectares in size.

Marievale Bird Sanctuary is a protected area in Gauteng, South Africa. It is about 15 km2 in size, and situated on the East Rand on the southern half of the Blesbokspruit wetland, a Ramsar site. The Blesbokspruit is a major perennial river in Gauteng which is flanked by extensive floodplains on either side. Nearby is the Suikerbosrand Nature Reserve.
Blyde River Canyon Nature Reserve is situated in the Drakensberg escarpment region of eastern Mpumalanga, South Africa. The reserve protects the Blyde River Canyon, including sections of the Ohrigstad and Blyde Rivers and the geological formations around Bourke's Luck Potholes, where the Treur River tumbles into the Blyde below. Southwards of the canyon, the reserve follows the escarpment, to include the Devil's and God's Window, the latter a popular viewpoint to the lowveld at the reserve's southern extremity.
Seekoeivlei Nature Reserve is an expansive wetland spanning some 30 km2 near the town of Memel in the Free State, South Africa. The area was declared a Ramsar site in 1999. It is unique for housing more than 250 species of birds, and the town of Memel is now a popular destination for bird enthusiasts, featuring bird hides and picnic facilities. It is also home to some hippopotamus, "seekoei" being the Afrikaans translation, as well as zebra. It lies nearly 2000 m above sea level near the Drakensberg escarpment and close to where the Free State, Mpumalanga, and KwaZulu-Natal meet.

Pigeon Valley is a Natural Heritage Park and formally declared municipal nature reserve in Durban, South Africa. It is an unusual example of an urban reserve with very high levels of biodiversity. It was established to provide protection for the Natal elm and other forest giants of the coastal climax forest. Another rare tree that occurs here is Natal forest loquat, which is endemic to the Durban area and to oNgoye Forest.

Areas of forest which grow in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa mostly on south facing slopes in higher rainfall areas, and along the humid coastal areas. Different types of forest can be identified by their species composition which depends mostly on the altitude, latitude and substrate in which they grow. South facing slopes are favourable for the development of forest as they are more shaded, and therefore cooler and retain more moisture than the northern slopes. The extra moisture on the south slopes is not only favoured by forest trees, but also helps to prevent or subdue wildfires. Fires can also be blocked by cliff faces and rocks or boulders on these slopes, and by streams or rivers at the base of the slopes. The coastal regions are conducive to forest formation, because of high rainfall and humidity which are favoured by forest trees and also help to prevent or subdue fires. The rivers of the coastal areas are also broader than further inland, which may often prevent fires from spreading long distances, and fires generally burn uphill and therefore more often away from areas at low altitude.

The Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany Hotspot (MPA) is a biodiversity hotspot, a biogeographic region with significant levels of biodiversity, in Southern Africa. It is situated near the south-eastern coast of Africa, occupying an area between the Great Escarpment and the Indian Ocean. The area is named after Maputaland, Pondoland and Albany. It stretches from the Albany Centre of Plant Endemism in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa, through the Pondoland Centre of Plant Endemism and KwaZulu-Natal Province, the eastern side of Eswatini and into southern Mozambique and Mpumalanga. The Maputaland Centre of Plant Endemism is contained in northern KwaZulu-Natal and southern Mozambique.

Matatiele Municipality is a local municipality within the Alfred Nzo District Municipality, in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. It adjoins Lesotho to the north, Elundini to the south-west, and Greater Kokstad to the east and its 4,352 km² makes the Matatiele Municipality largest of four municipalities in the district at almost half of its geographical area. According to the South African National Census of 2011, its 203,483 residents and 49,527 households makes Matatiele Municipality the second largest populated area in the Alfred Nzo District Municipality behind Mbizana.

The fauna of South Africa is diverse and largely typical of the ecosystems in Africa. South Africa is ranked sixth out of the world's 17 megadiverse countries. Many endemic species are unique to South Africa. The country is among the world leaders in conservation, but at the time wildlife is threatened by poaching and canned hunting.
The uMgeni Vlei Nature Reserve is a wetland reserve in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa that protects several threatened bird species.

















