
The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) is a multilateral treaty to ban nuclear weapons test explosions and any other nuclear explosions, for both civilian and military purposes, in all environments. It was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on 10 September 1996, but has not entered into force, as eight specific nations have not ratified the treaty.

A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion reactions, producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter.

The Partial Test Ban Treaty (PTBT), formally known as the 1963 Treaty Banning Nuclear Weapon Tests in the Atmosphere, in Outer Space and Under Water, prohibited all test detonations of nuclear weapons except for those conducted underground. It is also abbreviated as the Limited Test Ban Treaty (LTBT) and Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (NTBT), though the latter may also refer to the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT), which succeeded the PTBT for ratifying parties.

A fusion rocket is a theoretical design for a rocket driven by fusion propulsion that could provide efficient and sustained acceleration in space without the need to carry a large fuel supply. The design requires fusion power technology beyond current capabilities, and much larger and more complex rockets.

Nuclear pulse propulsion or external pulsed plasma propulsion is a hypothetical method of spacecraft propulsion that uses nuclear explosions for thrust. It originated as Project Orion with support from DARPA, after a suggestion by Stanislaw Ulam in 1947. Newer designs using inertial confinement fusion have been the baseline for most later designs, including Project Daedalus and Project Longshot.
Antimatter-catalyzed nuclear pulse propulsion is a variation of nuclear pulse propulsion based upon the injection of antimatter into a mass of nuclear fuel to initiate a nuclear chain reaction for propulsion when the fuel does not normally have a critical mass.

Project Orion was a study conducted in the 1950s and 1960s by the United States Air Force, DARPA, and NASA into the viability of a nuclear pulse spaceship that would be directly propelled by a series of atomic explosions behind the craft. Early versions of the vehicle were proposed to take off from the ground; later versions were presented for use only in space. The design effort took place at General Atomics in San Diego, and supporters included Wernher von Braun, who issued a white paper advocating the idea. Non-nuclear tests were conducted with models, but the project was eventually abandoned for several reasons, including the 1963 Partial Test Ban Treaty, which banned nuclear explosions in space, and concerns over nuclear fallout.

Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine the performance, yield, and effects of nuclear weapons. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detonations are affected by different conditions, and how personnel, structures, and equipment are affected when subjected to nuclear explosions. However, nuclear testing has often been used as an indicator of scientific and military strength. Many tests have been overtly political in their intention; most nuclear weapons states publicly declared their nuclear status through a nuclear test.
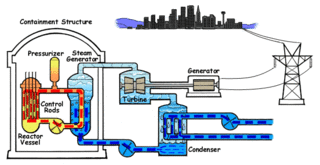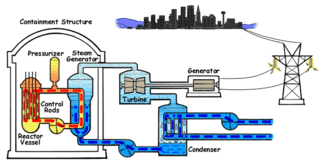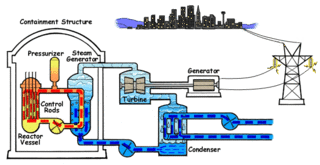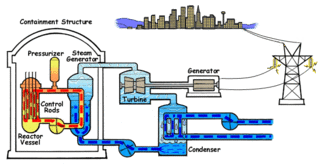
Nuclear propulsion includes a wide variety of propulsion methods that use some form of nuclear reaction as their primary power source. The idea of using nuclear material for propulsion dates back to the beginning of the 20th century. In 1903 it was hypothesized that radioactive material, radium, might be a suitable fuel for engines to propel cars, planes, and boats. H. G. Wells picked up this idea in his 1914 fiction work The World Set Free. Many aircraft carriers and submarines currently use uranium fueled nuclear reactors that can provide propulsion for long periods without refueling. There are also applications in the space sector with nuclear thermal and nuclear electric engines which could be more efficient than conventional rocket engines.

Operation Castle was a United States series of high-yield (high-energy) nuclear tests by Joint Task Force 7 (JTF-7) at Bikini Atoll beginning in March 1954. It followed Operation Upshot–Knothole and preceded Operation Teapot.
Project PACER, carried out at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) in the mid-1970s, explored the possibility of a fusion power system that would involve exploding small hydrogen bombs —or, as stated in a later proposal, fission bombs—inside an underground cavity. Its proponents claimed that the system is the only fusion power system that could be demonstrated to work using existing technology. It would also require a continuous supply of nuclear explosives and contemporary economics studies demonstrated that these could not be produced at a competitive price compared to conventional energy sources.

The militarisation of space involves the placement and development of weaponry and military technology in outer space. The early exploration of space in the mid-20th century had, in part, a military motivation, as the United States and the Soviet Union used it as an opportunity to demonstrate ballistic-missile technology and other technologies having the potential for military application. Outer space has since been used as an operating location for military spacecraft such as imaging and communications satellites, and some ballistic missiles pass through outer space during their flight. As of 2018, known deployments of weapons stationed in space include only the Almaz space-station armament and pistols such as the TP-82 Cosmonaut survival pistol.
Peaceful nuclear explosions (PNEs) are nuclear explosions conducted for non-military purposes. Proposed uses include excavation for the building of canals and harbours, electrical generation, the use of nuclear explosions to drive spacecraft, and as a form of wide-area fracking. PNEs were an area of some research from the late 1950s into the 1980s, primarily in the United States and Soviet Union.
Nuclear Explosions for the National Economy was a Soviet program to investigate peaceful nuclear explosions (PNEs). It was analogous to the United States program Operation Plowshare.

High-altitude nuclear explosions are the result of nuclear weapons testing within the upper layers of the Earth's atmosphere and in outer space. Several such tests were performed at high altitudes by the United States and the Soviet Union between 1958 and 1962.

A nuclear explosion is an explosion that occurs as a result of the rapid release of energy from a high-speed nuclear reaction. The driving reaction may be nuclear fission or nuclear fusion or a multi-stage cascading combination of the two, though to date all fusion-based weapons have used a fission device to initiate fusion, and a pure fusion weapon remains a hypothetical device. Nuclear explosions are used in nuclear weapons and nuclear testing.

Underground nuclear testing is the test detonation of nuclear weapons that is performed underground. When the device being tested is buried at sufficient depth, the nuclear explosion may be contained, with no release of radioactive materials to the atmosphere.
Operation Project 56 was a series of 4 nuclear tests conducted by the United States in 1955–1956 at the Nevada Test Site. These tests followed the Operation Wigwam series and preceded the Operation Redwing series.
A nuclear detonation detection system (NDDS) is a device or a series of devices that are able to indicate, and pinpoint a nuclear explosion has occurred as well as the direction of the explosion. The main purpose of these devices or systems was to verify compliance of countries that signed nuclear treaties such as the Partial Test Ban treaty of 1963 (PTBT) and the Treaty of Tlatelolco.
Nuclear shaped charges refers to nuclear weapons that focus the energy of their explosion into certain directions, as opposed to a spherical explosion. Edward Teller referred to such concepts as third-generation weapons, the first generation being the atom bomb and the second the H-bomb.












