
Lae (German: Preußen-Reede, later Lehe) is the capital of Morobe Province and is the second-largest city in Papua New Guinea. It is located near the delta of the Markham River on the northern coast of Huon Gulf. It is at the start of the Highlands Highway, which is the main land transport corridor between the Highlands Region and the coast. Lae is the largest cargo port of the country and is the industrial hub of Papua New Guinea. The city is known as the Garden City and home of the Papua New Guinea University of Technology.

Kaiser-Wilhelmsland formed part of German New Guinea, the South Pacific protectorate of the German Empire. Named in honour of Wilhelm I, who reigned as German Emperor from 1871 to 1888, it included the northern part of present-day Papua New Guinea. From 1884 until 1920 the territory was a protectorate of the German Empire. Kaiser-Wilhelmsland, the Bismarck Archipelago, the northern Solomon Islands, the Caroline Islands, Palau, Nauru, the Northern Mariana Islands, and the Marshall Islands comprised German New Guinea.

Wewak is the capital of the East Sepik province of Papua New Guinea. It is on the northern coast of the island of New Guinea. It is the largest town between Madang and Jayapura. It is the see city (seat) of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Wewak.

Morobe Province is a province on the northern coast of Papua New Guinea. The provincial capital and largest city is Lae. The province covers 33,705 km2, with a population of 674,810, and since the division of Southern Highlands Province in May 2012 it is the most populous province. It includes the Huon Peninsula, the Markham River, and delta, and coastal territories along the Huon Gulf. The province has nine administrative districts. At least 101 languages are spoken, including Kâte and Yabem language. English and Tok Pisin are common languages in the urban areas, and in some areas pidgin forms of German are mixed with the native language.

The New Guinea campaign of the Pacific War lasted from January 1942 until the end of the war in August 1945. During the initial phase in early 1942, the Empire of Japan invaded the Territory of New Guinea on 23 January and Territory of Papua on 21 July and overran western New Guinea beginning on 29 March. During the second phase, lasting from late 1942 until the Japanese surrender, the Allies—consisting primarily of Australian forces—cleared the Japanese first from Papua, then New Guinea, and finally from the Dutch colony.

The New Britain campaign was a World War II campaign fought between Allied and Imperial Japanese forces. The campaign was initiated by the Allies in late 1943 as part of a major offensive which aimed to neutralise the important Japanese base at Rabaul, the capital of New Britain, and was conducted in two phases between December 1943 and the end of the war in August 1945.

Umboi is a volcanic island between the mainland of Papua New Guinea and the island of New Britain. It is separated from New Britain by the Dampier Strait, and Huon Peninsula and New Guinea by the Vitiaz Strait. It has an elevation of 1,335 metres.
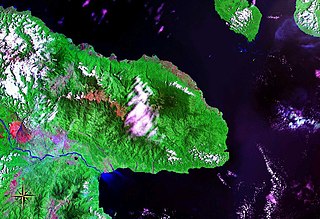
Huon Peninsula is a large rugged peninsula on the island of New Guinea in Morobe Province, eastern Papua New Guinea. It is named after French explorer Jean-Michel Huon de Kermadec. The peninsula is dominated by the steep Saruwaged and Finisterre and Cromwell Mountains. The nearest large town is the Morobe provincial capital Lae to the south, while settlements on the north coast include the former German town of Finschhafen, the district capital of Wasu, Malalamai and Saidor with its World War II era Saidor Airport.

The Huon Peninsula campaign was a series of battles fought in north-eastern Papua New Guinea in 1943–1944 during the Second World War. The campaign formed the initial part of an offensive that the Allies launched in the Pacific in late 1943 and resulted in the Japanese being pushed north from Lae to Sio on the northern coast of New Guinea over the course of a four-month period. For the Australians, a significant advantage was gained through the technological edge that Allied industry had achieved over the Japanese by this phase of the war, while the Japanese were hampered by a lack of supplies and reinforcements due to Allied interdiction efforts at sea and in the air.
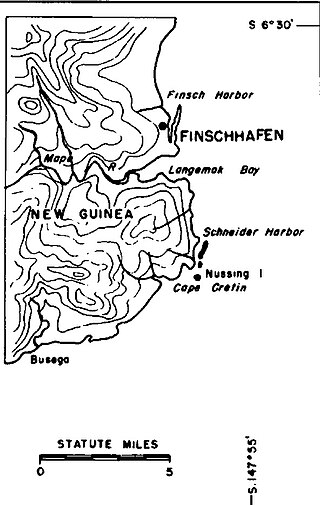
Finschhafen is a town 80 kilometers (50 mi) east of Lae on the Huon Peninsula in Morobe Province of Papua New Guinea. The town is commonly misspelt as Finschafen or Finschaven. During World War II, the town was also referred to as Fitch Haven in the logs of some U.S. Navy men.
Sio is a town on the north coast of Huon Peninsula, Papua New Guinea. It is located in Wasu Rural LLG, Morobe Province.

Malahang is a suburb of Lae, Morobe Province in Papua New Guinea.
Kelanoa is a town on the north coast of Huon Peninsula, Papua New Guinea.
Sattelberg, also spelt Satelberg, is a village on the Huon Peninsula, in Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea. The village is set on a peak about 900 metres (3,000 ft) above sea level, and dominates the area, with Finschhafen below. A Lutheran mission was founded by Johann Flierl in 1892, when the area was part of German New Guinea. As part of the settlement of World War I in 1919, responsibility for administering the territory was passed to Australia. In 1921, the Australian government gave permission for the German missionaries to remain, but placed the Lutheran Church of Australia in control of the mission. In the early 1930s, German influence was re-established as the Lutheran Church of Australia relinquished its control of the mission.

Shigeru Katagiri was a general in the Imperial Japanese Army, commanding Japanese ground forces on New Guinea until his death.
Sadahiko Miyake was a general in the Imperial Japanese Army, commanding Japanese ground forces on New Guinea during the closing months of the war.
Gusika is a village on the Huon Peninsula, in Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea. The village was liberated by the Australian Army during World War II in November 1943.

The 51st Division was an infantry division of the Imperial Japanese Army. Its call sign was the Base Division. It was formed on 10 July 1940 at Utsunomiya, Tochigi, simultaneously with 52nd, 54th, 55th, 56th, and 57th divisions. The 51st Division was initially assigned to the Eastern District Army and placed under command of Lieutenant General Kenichiro Ueno.
The Hopoi Mission Station is a Lutheran filial station situated in Morobe Province in Papua New Guinea now under the auspice of the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Papua New Guinea.

The Battle of Madang, fought between early February and late April 1944, was the break-out and pursuit phase of the Markham and Ramu Valley – Finisterre Range and Huon Peninsula campaigns, which were part of the wider New Guinea campaign of World War II. After overcoming the Japanese defences around Shaggy Ridge, the Australian forces descended the steep slopes of the Finisterre Range and pursued the withdrawing Japanese towards Bogadjim and then Madang on the north coast of New Guinea. There they linked up with US and Australian forces that had advanced along the coast from the Huon Peninsula, while the remnants of three Japanese divisions withdrew towards Wewak, where further fighting would take place throughout late 1944 and into 1945.














