
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is an additive manufacturing (AM) technique that uses a laser as the power and heat source to sinter powdered material, aiming the laser automatically at points in space defined by a 3D model, binding the material together to create a solid structure. It is similar to selective laser melting; the two are instantiations of the same concept but differ in technical details. SLS is a relatively new technology that so far has mainly been used for rapid prototyping and for low-volume production of component parts. Production roles are expanding as the commercialization of AM technology improves.

Stereolithography is a form of 3D printing technology used for creating models, prototypes, patterns, and production parts in a layer by layer fashion using photochemical processes by which light causes chemical monomers and oligomers to cross-link together to form polymers. Those polymers then make up the body of a three-dimensional solid. Research in the area had been conducted during the 1970s, but the term was coined by Chuck Hull in 1984 when he applied for a patent on the process, which was granted in 1986. Stereolithography can be used to create prototypes for products in development, medical models, and computer hardware, as well as in many other applications. While stereolithography is fast and can produce almost any design, it can be expensive.

3D printing or additive manufacturing is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer control, with the material being added together, typically layer by layer.
S. Scott Crump is the inventor of fused deposition modeling (FDM) and co-founder of Stratasys, Ltd. Crump invented and patented FDM technology in 1989 with his wife and Stratasys co-founder Lisa Crump. He is currently the chairman of the board of directors of Stratasys, which produces additive manufacturing machines for direct digital manufacturing ; these machines are popularly called “3D printers.” He took the manufacturing company public in 1994 (Nasdaq:SSYS). He also runs Fortus, RedEye on Demand, and Dimension Printing – business units of Stratasys.

3D Systems Corporation headquartered in Rock Hill, South Carolina, is a company that engineers, manufactures, and sells 3D printers, 3D printing materials, 3D Printed Parts, and application engineering services. The company creates product concept models, precision and functional prototypes, master patterns for tooling, as well as production parts for direct digital manufacturing. It uses proprietary processes to fabricate physical objects using input from computer-aided design and manufacturing software, or 3D scanning and 3D sculpting devices.

Rapid prototyping is a group of techniques used to quickly fabricate a scale model of a physical part or assembly using three-dimensional computer aided design (CAD) data. Construction of the part or assembly is usually done using 3D printing or "additive layer manufacturing" technology.
Chuck Hull is an American inventor who is the co-founder, executive vice president and chief technology officer of 3D Systems. He is one of the inventors of the SLA 3D printer, the first commercial rapid prototyping technology, and the widely used STL file format. He is named on more than 60 U.S. patents as well as other patents around the world in the fields of ion optics and rapid prototyping. He was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame in 2014 and in 2017 was one of the first inductees into the TCT Hall of Fame.

Stratasys, Ltd. is an American-Israeli manufacturer of 3D printers, software, and materials for polymer additive manufacturing as well as 3D-printed parts on-demand. The company is incorporated in Israel. Engineers use Stratasys systems to model complex geometries in a wide range of polymer materials, including: ABS, polyphenylsulfone (PPSF), polycarbonate (PC) and polyetherimide and Nylon 12.

MakerBot Industries, LLC was an American desktop 3D printer manufacturer company headquartered in New York City. It was founded in January 2009 by Bre Pettis, Adam Mayer, and Zach "Hoeken" Smith to build on the early progress of the RepRap Project. It was acquired by Stratasys in June 2013. As of April 2016, MakerBot had sold over 100,000 desktop 3D printers worldwide. Between 2009 and 2019, the company released 7 generations of 3D printers, ending with the METHOD and METHOD X. It was at one point the leader of the desktop market with an important presence in the media, but its market share declined over the late 2010s. MakerBot also founded and operated Thingiverse, the largest online 3D printing community and file repository. In August 2022, the company completed a merger with its long-time competitor Ultimaker. The combined company is known as UltiMaker, but retains the MakerBot name for its Sketch line of education-focused 3D printers.
Solidscape, Inc. is a company that designs, develops and manufactures 3D printers for rapid prototyping and rapid manufacturing, able to print solid models created in CAD.

Binder jet 3D printing, known variously as "Powder bed and inkjet" and "drop-on-powder" printing, is a rapid prototyping and additive manufacturing technology for making objects described by digital data such as a CAD file. Binder jetting is one of the seven categories of additive manufacturing processes according to ASTM and ISO.
Sculpteo is a French company specialized in 3D printing in the cloud. Sculpteo offers an online 3D printing service, for rapid prototyping and production using technologies such as laser sintering, stereo lithography, Multi Jet Fusion, FDM, Polyjet, DLS, DLP/LCD, SLM/DMLS or Binder Jetting. The company was founded in June 2009 by Eric Carreel, Clement Moreau and Jacques Lewiner. Sculpteo offers online 3D printing services, particularly in Europe and North America The company was acquired in 2019 by the German multinational chemical company BASF.
Solid Concepts, Inc. is a custom manufacturing company engaged in engineering, manufacturing, production, and prototyping. The company is headquartered in Valencia, California, in the Los Angeles County area, with six other facilities located around the United States. Solid Concepts is an additive manufacturing service provider as well as a major manufacturer of business products, aerospace, unmanned systems, medical equipment and devices, foundry cast patterns, industrial equipment and design, and transportation parts.
Solid ground curing (SGC) is a photo-polymer-based additive manufacturing technology used for producing models, prototypes, patterns, and production parts, in which the production of the layer geometry is carried out by means of a high-powered UV lamp through a mask. As the basis of solid ground curing is the exposure of each layer of the model by means of a lamp through a mask, the processing time for the generation of a layer is independent of the complexity of the layer. SGC was developed and commercialized by Cubital Ltd. of Israel in 1986 in the alternative name of Solider System. While the method offered good accuracy and a very high fabrication rate, it suffered from high acquisition and operating costs due to system complexity. This led to poor market acceptance. While the company still exists, systems are no longer being sold. Nevertheless, it's still an interesting example of the many technologies other than stereolithography, its predeceasing rapid prototyping process that also utilizes photo-polymer materials. Though Objet Geometries Ltd. of Israel retains intellectual property of the process after the closure of Cubital Ltd. in 2002, the technology is no longer being produced.
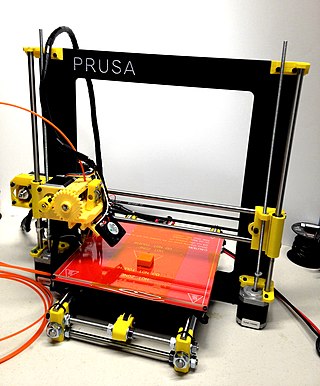
Fused filament fabrication (FFF), also known as fused deposition modeling, or filament freeform fabrication, is a 3D printing process that uses a continuous filament of a thermoplastic material. Filament is fed from a large spool through a moving, heated printer extruder head, and is deposited on the growing work. The print head is moved under computer control to define the printed shape. Usually the head moves in two dimensions to deposit one horizontal plane, or layer, at a time; the work or the print head is then moved vertically by a small amount to begin a new layer. The speed of the extruder head may also be controlled to stop and start deposition and form an interrupted plane without stringing or dribbling between sections. "Fused filament fabrication" was coined by the members of the RepRap project to give an acronym (FFF) that would be legally unconstrained in its use.

In recent years, 3D printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most common applications being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design, and can vary from fully functional to purely aesthetic applications.

A variety of processes, equipment, and materials are used in the production of a three-dimensional object via additive manufacturing. 3D printing is also known as additive manufacturing, because the numerous available 3D printing process tend to be additive in nature, with a few key differences in the technologies and the materials used in this process.
Desktop Metal, Inc. is a public American technology company that designs and markets 3D printing systems. Headquartered in Burlington, Massachusetts, the company has raised $438 million in venture funding since its founding from investors such as Google Ventures, BMW, and Ford Motor Company. Desktop Metal launched its first two products in April 2017: the Studio System, a metal 3D printing system catered to engineers and small production runs, and the Production System, intended for manufacturers and large-scale printing. In November 2019, the company launched two new printer systems: the Shop System for machine shops, and the Fiber industrial-grade composites printer for automated fiber placement. The World Economic Forum named Desktop Metal a Technology Pioneer in 2017.
Multi-material 3D printing is the additive manufacturing procedure of using multiple materials at the same time to fabricate an object. Similar to single material additive manufacturing it can be realised through methods such as FFF, SLA and Inkjet 3D printing. By expanding the design space to different materials, it establishes the possibilities of creating 3D printed objects of different color or with different material properties like elasticity or solubility. The first multi-material 3D printer Fab@Home became publicly available in 2006. The concept was quickly adopted by the industry followed by many consumer ready multi-material 3D printers.

Massivit 3D Printing Technologies Ltd. (Massivit3D) is an Israeli public company traded on the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange (TASE:MSVT) Its headquarters are in Lod. The company develops, constructs and sells Additive Manufacturing printers for production of large parts and develops printing materials for use in their printers.











