
An ambush is a long-established military tactic in which a combatant uses an advantage of concealment or the element of surprise to attack unsuspecting enemy combatants from concealed positions, such as among dense underbrush or behind mountaintops. Ambushes have been used consistently throughout history, from ancient to modern warfare. In the 20th century, an ambush might involve thousands of soldiers on a large scale, such as over a choke point such as a mountain pass, or a small irregulars band or insurgent group attacking a regular armed force patrols. Theoretically, a single well-armed and concealed soldier could ambush other troops in a surprise attack. Sometimes an ambush can involve the exclusive or combined use of improvised explosive devices, that allow the attackers to hit enemy convoys or patrols while minimizing the risk of being exposed to return fire.

Fatah, formerly the Palestinian National Liberation Movement, is a Palestinian nationalist social democratic political party and the largest faction of the confederated multi-party Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) and second-largest party in the Palestinian Legislative Council (PLC). Mahmoud Abbas, the President of the Palestinian Authority, is a member of Fatah.

In military operations, reconnaissance or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, terrain, and other activities.

Technology during World War I (1914–1918) reflected a trend toward industrialism and the application of mass-production methods to weapons and to the technology of warfare in general. This trend began at least fifty years prior to World War I during the American Civil War of 1861–1865, and continued through many smaller conflicts in which soldiers and strategists tested new weapons.

A defensive fighting position (DFP) is a type of earthwork constructed in a military context, generally large enough to accommodate anything from one soldier to a fire team.

In military science, suppressive fire is "fire that degrades the performance of an enemy force below the level needed to fulfill its mission". When used to protect exposed friendly troops advancing on the battlefield, it is commonly called covering fire. Suppression is usually only effective for the duration of the fire. It is one of three types of fire support, which is defined by NATO as "the application of fire, coordinated with the maneuver of forces, to destroy, neutralise or suppress the enemy".
Mohammad Yusuf Dahlan born on September 29, 1961 in Khan Yunis Refugee Camp, Khan Yunis, Gaza Strip also known by the kunya Abu Fadi is a Palestinian politician, the former leader of Fatah in Gaza. Dahlan was born to a refugee family from Hamama, the youngest of six children.

Field artillery is a category of mobile artillery used to support armies in the field. These weapons are specialized for mobility, tactical proficiency, short range, long range, and extremely long range target engagement.

The Battle of Ong Thanh was fought at the stream of that name on the morning of 17 October 1967, in Chơn Thành District, at the time part of Bình Dương Province, South Vietnam, today in Bình Phước Province.

The 2007 Lebanon conflict began when fighting broke out between Fatah al-Islam, an Islamist militant organization, and the Lebanese Armed Forces (LAF) on May 20, 2007 in Nahr al-Bared, an UNRWA Palestinian refugee camp near Tripoli.

The Battle of Wanat took place on July 13, 2008, when around 200 Taliban insurgents attacked American troops stationed near Quam, in the Waygal district of Afghanistan's far eastern Nuristan province. The distant position was primarily defended by United States Army soldiers with 2nd Platoon, Chosen Company, 2nd Battalion, 503rd Infantry Regiment (Airborne), 173rd Airborne Brigade Combat Team.
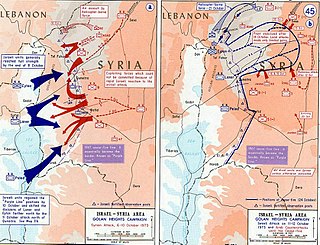
The First Battle of Mount Hermon was fought at the outset of the Yom Kippur War between the Syrian Army and the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). On Yom Kippur, October 6, 1973, Syrian commandos attacked and captured the IDF outpost on Mount Hermon. Two days later, the Syrians repelled an Israeli counterattack in the Second Battle of Mount Hermon. It was eventually recaptured by Israel on October 21 in the Third battle.

The Tactica is a military treatise written by or on behalf of Eastern Roman Emperor Leo VI the Wise in c. 895–908 and later edited by his son, Constantine VII. Drawing on earlier authors such as Aelian, Onasander and the Strategikon of emperor Maurice, it is one of the major works on Byzantine military tactics, written on the eve of Byzantium's "age of reconquest". The original Greek title is τῶν ἐν πολέμοις τακτικῶν σύντομος παράδοσις. The Tactica elaborates on a wide variety of issues, such as infantry and cavalry formations, drills, siege and naval warfare etc. It is written in a legislative form of language and comprises 20 Constitutions and an Epilogue and is concluded by 12 additional chapters, the latter mainly focusing on ancient tactics.

The Hannibal Directive is the code name for the procedure that Israel Defense Forces (IDF) are to follow to prevent the capture of Israeli soldiers by enemy forces.

The 2004 IDF outpost bombing attack was an integrated attack carried out on 12 December 2004 by a Palestinian militant squad of the Izz al-Din al-Qassam military wing of Hamas and the Fatah Hawks at an Israel Defense Forces outpost located on the border between the Gaza Strip and Egypt.

Legislative elections were held in the Palestinian territories on 25 January 2006 in order to elect the second Palestinian Legislative Council (PLC), the legislature of the Palestinian National Authority (PNA). The result was a victory for Hamas, contesting under the list name of Change and Reform, which received 44.45% of the vote and won 74 of the 132 seats, whilst the ruling Fatah received 41.43% of the vote and won just 45 seats.

The Palestinian Legislative Council (PLC) is the unicameral legislature of the Palestinian Authority, elected by the Palestinian residents of the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and Gaza Strip. It currently comprises 132 members, elected from 16 electoral districts of the Palestinian Authority. The PLC has a quorum requirement of two-thirds, and since 2006 Hamas and Hamas-affiliated members have held 74 of the 132 seats in the PLC. The PLC's activities were suspended in 2007 and remained so as of January 2021, while PLC committees continue working at a low rate and parliamentary panel discussions are still occurring.
The Battle of Gaza, also referred to as Hamas's takeover of Gaza, was a military conflict between Fatah and Hamas, that took place in the Gaza Strip between June 10 and 15, 2007. It was a prominent event in the Fatah–Hamas conflict, centered on the struggle for power, after Fatah lost the parliamentary elections of 2006. Hamas fighters took control of the Gaza Strip and removed Fatah officials. The battle resulted in the dissolution of the unity government and the de facto division of the Palestinian territories into two entities, the West Bank governed by the Palestinian National Authority, and Gaza governed by Hamas.

The Turkish military operation in Idlib Governorate, code-named Idlib De-escalation Control Force activities by Turkey, is an operation by the Turkish Armed Forces which started in October 2017, following the earlier Operation Euphrates Shield. It is the third cross-border operation by the Turkish military, following Operation Euphrates Shield and Operation Shah Euphrates.


















