The M25 or London Orbital Motorway is a major road encircling most of Greater London. The 117-mile-long (188 km) motorway is one of the most important roads in the UK and one of the busiest. Margaret Thatcher opened the final section in 1986, making the M25 the longest ring road in Europe upon opening. The Dartford Crossing completes the orbital route but is not classed as motorway; it is classed as a trunk road and designated as the A282. In some cases, including notable legal contexts such as the Communications Act 2003, the M25 is used as a de facto alternative boundary for Greater London.

The M6 motorway is the longest motorway in the United Kingdom. It is located entirely within England, running for just over 230 miles (370 km) from the Midlands to the border with Scotland. It begins at Junction 19 of the M1 and the western end of the A14 at the Catthorpe Interchange, near Rugby before heading north-west. It passes Coventry, Birmingham, Wolverhampton, Stoke-on-Trent, Preston, Lancaster and Carlisle before terminating at Junction 45 near Gretna. Here, just short of the Scottish border it becomes the A74(M) which continues to Glasgow as the M74. Its busiest sections are between junctions 4 and 10a in the West Midlands, and junctions 16 to 19 in Cheshire; these sections have now been converted to smart motorways.

The M1 motorway connects London to Leeds, where it joins the A1(M) near Aberford, to connect to Newcastle. It was the first inter-urban motorway to be completed in the UK; the first motorway in the country was the Preston Bypass, which later became part of the M6.
The A1, also known as the Great North Road, is the longest numbered road in the United Kingdom, at 410 miles (660 km). It connects London, the capital of England, with Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. The numbering system for A-roads, devised in the early 1920s, was based around patterns of roads radiating from two hubs at London and Edinburgh. The first number in the system, A1, was given to the most important part of that system: the road from London to Edinburgh, joining the two central points of the system and linking the UK's (then) two mainland capital cities. It passes through or near north London, Hatfield, Stevenage, Baldock, Biggleswade, Peterborough, Stamford, Grantham, Newark-on-Trent, Retford, Doncaster, Pontefract, York, Wetherby, Ripon, Darlington, Durham, Gateshead, Newcastle upon Tyne, Morpeth, Alnwick, Berwick-upon-Tweed, Dunbar, Haddington, Musselburgh, and east Edinburgh.
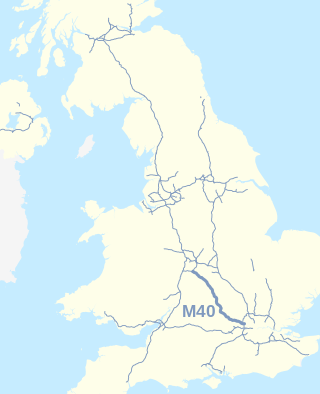
The M40 motorway links London, Oxford, and Birmingham in England, a distance of approximately 89 miles (143 km).

The M3 is a motorway in England, from Sunbury-on-Thames, Surrey, to Eastleigh, Hampshire; a distance of approximately 59 miles (95 km). The route includes the Aldershot Urban Area, Basingstoke, Winchester, and Southampton.

The A57 is a major road in England. It runs east from Liverpool to Lincoln via Warrington, Salford and Manchester, and then through the Pennines over the Snake Pass (between the high moorlands of Bleaklow and Kinder Scout), around the Ladybower Reservoir, through Sheffield and past Worksop. Between Liverpool and Glossop, the road has largely been superseded by the M62, M602 and M67 motorways. Within Manchester a short stretch becomes the Mancunian Way, designated A57(M).

The M18 is a motorway in Yorkshire, England. It runs from the east of Rotherham to Goole and is approximately 26 miles (42 km) long. A section of the road forms part of the unsigned Euroroute E13.

The A14 is a major trunk road in England, running 127 miles (204 km) from Catthorpe Interchange, a major intersection at the southern end of the M6 and junction 19 of the M1 in Leicestershire to the Port of Felixstowe, Suffolk. The road forms part of the unsigned Euroroutes E24 and E30. It is the busiest shipping lane in East Anglia carrying anything from cars to large amounts of cargo between the UK and Mainland Europe.

The island of Ireland, comprising Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland, has an extensive network of tens of thousands of kilometres of public roads, usually surfaced. These roads have been developed and modernised over centuries, from trackways suitable only for walkers and horses, to surfaced roads including modern motorways. Driving is on the left-hand side of the road. The major routes were established before Irish independence and consequently take little cognisance of the border other than a change of identification number and street furniture. Northern Ireland has had motorways since 1962, and has a well-developed network of primary, secondary and local routes. The Republic started work on its motorway network in the early 1980s; and historically, the road network there was once somewhat less well developed. However, the Celtic Tiger economic boom and an influx of European Union structural funding, saw national roads and regional roads in the Republic come up to international standard quite quickly. In the mid-1990s, for example, the Republic went from having only a few short sections of motorway to a network of motorways, dual carriageways and other improvements on most major routes as part of a National Development Plan. Road construction in Northern Ireland now tends to proceed at a slower pace than in the Republic, although a number of important bypasses and upgrades to dual carriageway have recently been completed or are about to begin.

A dual carriageway (BrE) or a divided highway (AmE) is a class of highway with carriageways for traffic travelling in opposite directions separated by a central reservation (BrE) or median (AmE). Roads with two or more carriageways which are designed to higher standards with controlled access are generally classed as motorways, freeways, etc., rather than dual carriageways.

A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway, and expressway. Other similar terms include throughway or thruway and parkway. Some of these may be limited-access highways, although this term can also refer to a class of highways with somewhat less isolation from other traffic.

Road signs in the United Kingdom and in its associated Crown dependencies and overseas territories conform broadly to European design norms, though a number of signs are unique: direction signs omit European route numbers, and road signs generally use the imperial system of units, unlike the rest of Europe. Signs in Wales (Welsh) and parts of Scotland are bilingual.

M1 Pacific Motorway is a 127-kilometre motorway linking Sydney to Newcastle via the Central Coast and Hunter regions of New South Wales. Formerly known but still commonly referred to by both the public and the government as the F3 Freeway, Sydney–Newcastle Freeway, and Sydney–Newcastle Expressway, it is part of the AusLink road corridor between Sydney and Brisbane.

The A453 road was formerly the main trunk road connecting the English cities of Nottingham and Birmingham. However, the middle section of this mainly single-carriageway road has largely been downgraded to B roads or unclassified roads following the construction of the parallel M42-A42 link around 1990. The M42 was originally meant to pass further north than it does, and to join the M1 at Sandiacre in Derbyshire. The M42/A42 does not enter Derbyshire, but instead joins the M1 closer to the A453 junction at Kegworth. The A42 shadows the former A453 from Appleby Magna to Castle Donington. The road historically connected the East Midlands with the West Midlands.

A roundabout interchange is a type of interchange between a controlled access highway, such as a motorway or freeway, and a minor road. The slip roads to and from the motorway carriageways converge at a single roundabout, which is grade-separated from the motorway lanes with bridges.

Driver location signs are signs placed every 500 metres (550 yd) along each side of English motorways, and some other major English roads, to provide information that will allow motorists to know their precise location. As of July 2009, roads in England, but not Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland, have these signs. This information might be useful in the event of an emergency or breakdown. They were first introduced in 2003, and they complement distance marker posts. Both types of sign display a unique location number. The number, although given without units, is the distance in kilometres from a designated datum location for the road, although signs meant for driver navigation are in miles.

A smart motorway, also known in Scotland as an intelligent transport system, is a section of motorway in the United Kingdom that employs active traffic management (ATM) techniques to increase capacity through the use of MIDAS technology including variable speed limits and occasionally hard shoulder running and ramp metering at busy times. They were developed at the turn of the 21st century as a cost-effective alternative to traditional carriageway widening, with intended benefits ranging from more reliable journey times to lower vehicle emissions. However, despite the risk of a collision occurring between two moving vehicles being found to be decreased, there has been an acknowledged rise in the incidence of collisions involving vehicles where at least one was stationary in the first few years following the widespread removal of the hard shoulder on the country's busiest sections of motorway. Smart motorways garnered intense criticism from politicians, police representatives and motoring organisations, particularly from 2020 onwards, after a surge in near miss incidents and dozens of fatalities were revealed, and as of April 2023, no new smart motorways will be built.

Road signs in New Zealand are similar to those set by the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals. While New Zealand is not a signatory to the convention, its road signs are generally close in shape and function. New Zealand uses yellow diamond-shaped signs for warnings in common with Australia, the Americas, Ireland, Japan and Thailand. Speed limit signs are a red circle with a white background and the limitation in black, and are in kilometres per hour. There are also some signs unique to New Zealand. Road signs in New Zealand are controlled by NZ Transport Agency Waka Kotahi and are prescribed in the Land Transport Rule: Traffic Control Devices 2004 and set out in the Traffic Control Devices (TCD) Manual.
A permanently signed detour route is a type of route which is used temporarily during special circumstances. Various areas have developed these systems as part of incident management. The purpose of these routes is to provide a detour in the event that the parent route is impassable, due to either a traffic jams, traffic collision, or road closure. Sometimes these routes are signed as a prefixed or suffixed numbered road, making them a type of special route.