
A turboprop engine is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller.

An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years many small UAVs have used electric motors.

The bypass ratio (BPR) of a turbofan engine is the ratio between the mass flow rate of the bypass stream to the mass flow rate entering the core. A 10:1 bypass ratio, for example, means that 10 kg of air passes through the bypass duct for every 1 kg of air passing through the core.
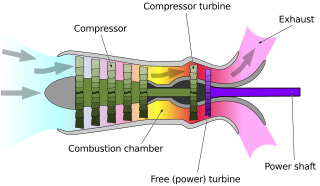
A turboshaft engine is a form of gas turbine that is optimized to produce shaftpower rather than jet thrust. In concept, turboshaft engines are very similar to turbojets, with additional turbine expansion to extract heat energy from the exhaust and convert it into output shaft power. They are even more similar to turboprops, with only minor differences, and a single engine is often sold in both forms.

UEC NPO Saturn, PJSC is a Russian aircraft engine manufacturer, formed from the mergers of Rybinsk Motors and Lyul'ka-Saturn in 2001. Saturn's engines power many former Eastern Bloc aircraft, such as the Tupolev Tu-154. Saturn holds a 50% stake in the PowerJet joint venture with Safran Aircraft Engines. The company, founded by Pavel Soloviev, has its headquarters in the town of Rybinsk.
The Kuznetsov Design Bureau was a Russian design bureau for aircraft engines, administrated in Soviet times by Nikolai Dmitriyevich Kuznetsov. It was also known as (G)NPO Trud and Kuybyshev Engine Design Bureau (KKBM).
The JSC Klimov presently manufactures internationally certified gas turbine engines, main gearboxes and accessory drive gearboxes for transport aircraft.

The Rolls-Royce Gnome is a British turboshaft engine originally developed by the de Havilland Engine Company as a licence-built General Electric T58, an American mid-1950s design. The Gnome came to Rolls-Royce after their takeover of Bristol Siddeley in 1968, Bristol having absorbed de Havilland Engines Limited in 1961.
Ivchenko-Progress ZMKB, formerly OKB-478 and Ivchenko Lotarev, is a state design bureau that creates drafts and plans for aircraft engines in Zaporizhzhia, Ukraine whose products are widely used in both civil and military aircraft, most notably by Antonov, Beriev, Ilyushin, Tupolev, Mil and Yakovlev. The design bureau works closely with Motor Sich, the turbine manufacturer located in Zaporizhzhia which produces those engines.
JSC Kuznetsov is one of the leading Russian producers of aircraft engines, liquid-propellant rocket engines as well as aeroderivative gas turbines and modular stations.
The Kamov Ka-126 is a Soviet light utility helicopter with co-axial rotors. Evolved from Ka-26 with engine pods removed from stub wings, fitted with one TVO-100 turboshaft engine positioned on top of fuselage, modified rotor blades, new fuel system.
This is a glossary of acronyms and initials used for aero-engines and aircraft equipment in the Russian federation and formerly the USSR. The Latin-alphabet names are phonetic representations of the Cyrillic originals, and variations are inevitable.

The Klimov TV7-117 is a Russian turboprop engine certified in 1997 to power the Ilyushin Il-114 regional commuter aircraft. The new engine features enhanced reliability, fuel economy and greater service life compared to its predecessors produced in the former Soviet Union. The engine has a modular design. The nine modules can be replaced in the field, which dramatically reduces costs and accelerates repair and maintenance. The engine has an electronic-hydromechanical control system.

The Klimov TV2-117 is a Soviet gas-turbine turboshaft engine intended for helicopter use. Designed in the early 1960s by the Isotov Design Bureau the engine became the first purpose built gas turbine engine for helicopter use by the Soviet Union with previous helicopter turbines being adapted aeroplane powerplants. It was later produced by Klimov, production ending in 1997.

The Klimov GTD-350 is a Soviet gas-turbine turboshaft engine intended for helicopter use. Designed in the early 1960s by the Isotov Design Bureau the engine was later produced by Klimov and PZL, production ending in the late 1990s.

The Ivchenko AI-24 turboprop aircraft engine was designed and developed in the late-1950s by the Ivchenko design bureau and manufactured thereafter by Motor Sich. It was designed to power Antonov's successful An-24, An-26 and An-30 aircraft series.

Atec, Inc. specializes in the design, manufacture, construction and maintenance of precision components, large fabrications, systems and facilities. Atec provides solutions for low to medium volume requirements involving engine test, aero support equipment, spaceflight components, and energy service products. Over 20,000 Atec products have been used by the United States Armed Forces and others, including the Federal Aviation Administration. Atec was named NASA Small Business Subcontractor of the Year for 2016, in recognition of contributions to NASA and Boeing Manned Spaceflight Programs.

JSC United Engine Corporation is a Russian state-owned company responsible for production of engines for military and civil aviation and space exploration programs. It manufactures power turbines for electricity and heat generation, gas compressor units and marine gas-turbine units.

Salyut Machine-Building Production Association is a company based in Moscow, Russia. NPC Saljut have three plants and office with further plants outside Moscow city. It is a subsidiary of United Engine Corporation.
Aeroprogress is a Russian aircraft design company based in Moscow. Aircraft are certified by subsidiary company the ROKS-AERO Aviation Design Bureau.













