An authenticator is a means used to confirm a user's identity, that is, to perform digital authentication. A person authenticates to a computer system or application by demonstrating that he or she has possession and control of an authenticator. In the simplest case, the authenticator is a common password.
RSA SecurID, formerly referred to as SecurID, is a mechanism developed by RSA for performing two-factor authentication for a user to a network resource.
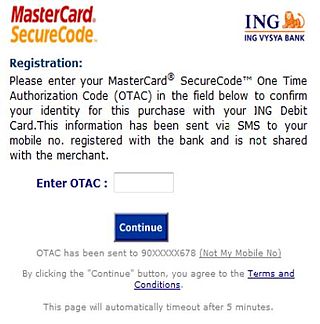
A one-time password (OTP), also known as a one-time PIN, one-time passcode, one-time authorization code (OTAC) or dynamic password, is a password that is valid for only one login session or transaction, on a computer system or other digital device. OTPs avoid several shortcomings that are associated with traditional (static) password-based authentication; a number of implementations also incorporate two-factor authentication by ensuring that the one-time password requires access to something a person has as well as something a person knows.

A security token is a peripheral device used to gain access to an electronically restricted resource. The token is used in addition to, or in place of, a password. Examples of security tokens include wireless key cards used to open locked doors, a banking token used as a digital authenticator for signing in to online banking, or signing transactions such as wire transfers.

A software token is a piece of a two-factor authentication security device that may be used to authorize the use of computer services. Software tokens are stored on a general-purpose electronic device such as a desktop computer, laptop, PDA, or mobile phone and can be duplicated.
Password fatigue is the feeling experienced by many people who are required to remember an excessive number of passwords as part of their daily routine, such as to log in to a computer at work, undo a bicycle lock or conduct banking from an automated teller machine. The concept is also known as password chaos, or more broadly as identity chaos.

Multi-factor authentication is an electronic authentication method in which a user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more pieces of evidence to an authentication mechanism. MFA protects personal data—which may include personal identification or financial assets—from being accessed by an unauthorized third party that may have been able to discover, for example, a single password.

Time-based one-time password (TOTP) is a computer algorithm that generates a one-time password (OTP) using the current time as a source of uniqueness. As an extension of the HMAC-based one-time password algorithm (HOTP), it has been adopted as Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard RFC 6238.

Google Authenticator is a software-based authenticator by Google. It implements multi-factor authentication services using the time-based one-time password and HMAC-based one-time password, for authenticating users of software applications.
LinOTP is Linux-based software to manage authentication devices for two-factor authentication with one time passwords. It is implemented as a web service based on the python framework Pylons. Thus it requires a web server to run in.

multiOTP is an open source PHP class, a command line tool, and a web interface that can be used to provide an operating-system-independent, strong authentication system. multiOTP is OATH-certified since version 4.1.0 and is developed under the LGPL license. Starting with version 4.3.2.5, multiOTP open source is also available as a virtual appliance—as a standard OVA file, a customized OVA file with open-vm-tools, and also as a virtual machine downloadable file that can run on Microsoft's Hyper-V, a common native hypervisor in Windows computers.
Rublon is a multi-factor authentication platform that offers an extra layer of security for users logging into networks, servers, endpoints, and desktop, cloud, web and mobile applications. Rublon MFA secures remote access and local logins using hardware and software authenticators, including the Rublon Authenticator mobile app, which holds the digital identity of the account owner. Numerous Rublon MFA connectors allow strong authentication to be implemented for all or selected users. Individually configurable security policies allow customizing Rublon MFA to suit the organization’s needs. Rublon's multi-factor authentication platform helps protect enterprise data and achieve regulatory compliance.

The YubiKey is a hardware authentication device manufactured by Yubico to protect access to computers, networks, and online services that supports one-time passwords (OTP), public-key cryptography, authentication, and the Universal 2nd Factor (U2F) and FIDO2 protocols developed by the FIDO Alliance. It allows users to securely log into their accounts by emitting one-time passwords or using a FIDO-based public/private key pair generated by the device. YubiKey also allows storing static passwords for use at sites that do not support one-time passwords. Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Twitter, and Facebook use YubiKey devices to secure employee accounts as well as end-user accounts. Some password managers support YubiKey. Yubico also manufactures the Security Key, a similar lower-cost device with only FIDO2/WebAuthn and FIDO/U2F support.
Universal 2nd Factor (U2F) is an open standard that strengthens and simplifies two-factor authentication (2FA) using specialized Universal Serial Bus (USB) or near-field communication (NFC) devices based on similar security technology found in smart cards. It is succeeded by the FIDO2 Project, which includes the W3C Web Authentication (WebAuthn) standard and the FIDO Alliance's Client to Authenticator Protocol 2 (CTAP2).

privacyIDEA is a two factor authentication system which is multi-tenency- and multi-instance-capable. It is open source, written in Python and hosted at GitHub. privacyIDEA is a LinOTP's fork from 2014.
Biometric tokenization is the process of substituting a stored biometric template with a non-sensitive equivalent, called a token, that lacks extrinsic or exploitable meaning or value. The process combines the biometrics with public-key cryptography to enable the use of a stored biometric template for secure or strong authentication to applications or other systems without presenting the template in its original, replicable form.
Credential Management, also referred to as a Credential Management System (CMS), is an established form of software that is used for issuing and managing credentials as part of public key infrastructure (PKI).

Bitwarden is a freemium open-source password management service that is used to store sensitive information, such as website credentials, in an encrypted vault. The platform hosts multiple client applications, including a web interface, desktop applications, browser extensions, mobile apps, and a command-line interface. The platform offers a free US or European cloud-hosted service as well as the ability to self-host.

Passwordless authentication is an authentication method in which a user can log in to a computer system without entering a password or any other knowledge-based secret. In most common implementations users are asked to enter their public identifier and then complete the authentication process by providing a secure proof of identity through a registered device or token.
The following is a general comparison of OTP applications that are used to generate one-time passwords for two-factor authentication (2FA) systems using the time-based one-time password (TOTP) or the HMAC-based one-time password (HOTP) algorithms.










