CollabNet VersionOne is a software firm headquartered in Alpharetta, Georgia, United States. It was Founded by Tim O’Reilly, Brian Behlendorf, and Bill Portelli. CollabNet VersionOne products and services belong to the industry categories of value stream management, DevOps, agile management, application lifecycle management (ALM), and enterprise version control.

Rogue Wave Software was an American software development company based in Louisville, Colorado. It provided cross-platform software development tools and embedded components for parallel, data-intensive, and other high-performance computing (HPC) applications.
Build automation is the practice of building software systems in an relatively unattended fashion. The build is configured to run with minimized or no software developer interaction and without using a developer's personal computer. Build automation encompasses the act of configuring the build system as well the resulting system itself.

Seapine Software was a privately held Mason, Ohio-based software and services company. The company developed a suite of software products that managed the full software development lifecycle. Seapine's tools included testing tools, configuration management, test-case management, and requirements management. The company was best known for its TestTrack line of application lifecycle management (ALM) software.
AnthillPro is a software tool originally developed and released as one of the first continuous integration servers. AnthillPro automates the process of building code into software projects and testing it to verify that project quality has been maintained. Software developers are able to identify bugs and errors earlier by using AnthillPro to track, collate, and test changes in real time to a collectively maintained body of computer code.
Parasoft SOAtest is a testing and analysis tool suite for testing and validating APIs and API-driven applications. Basic testing functionality include functional unit testing, integration testing, regression testing, system testing, security testing, simulation and mocking, runtime error detection, web UI testing, interoperability testing, WS-* compliance testing, and load testing.

Parasoft is an independent software vendor specializing in automated software testing and application security with headquarters in Monrovia, California. It was founded in 1987 by four graduates of the California Institute of Technology who planned to commercialize the parallel computing software tools they had been working on for the Caltech Cosmic Cube, which was the first working hypercube computer built.
With operations in 11 countries, Serena Software Inc. is an American software company that provides IT management products to enterprises. Serena solutions offer a process orchestration approach and span the areas of development, DevOps and IT management.
DevOps is a methodology in the software development and IT industry. Used as a set of practices and tools, DevOps integrates and automates the work of software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) as a means for improving and shortening the systems development life cycle. DevOps is complementary to agile software development; several DevOps aspects came from the agile way of working.
Continuous testing is the process of executing automated tests as part of the software delivery pipeline to obtain immediate feedback on the business risks associated with a software release candidate. Continuous testing was originally proposed as a way of reducing waiting time for feedback to developers by introducing development environment-triggered tests as well as more traditional developer/tester-triggered tests.
Continuous delivery (CD) is a software engineering approach in which teams produce software in short cycles, ensuring that the software can be reliably released at any time and following a pipeline through a "production-like environment", without doing so manually. It aims at building, testing, and releasing software with greater speed and frequency. The approach helps reduce the cost, time, and risk of delivering changes by allowing for more incremental updates to applications in production. A straightforward and repeatable deployment process is important for continuous delivery.
Application-release automation (ARA) refers to the process of packaging and deploying an application or update of an application from development, across various environments, and ultimately to production. ARA solutions must combine the capabilities of deployment automation, environment management and modeling, and release coordination.
Parasoft Virtualize is a service virtualization product that can create, deploy, and manage simulated test environments for software development and software testing purposes. These environments simulate the behavior of dependent resources that are unavailable, difficult to access, or difficult to configure for development or testing. It simulates the behavior of dependent resources such as mainframes, ERP systems, databases, web services, third-party information systems, or other systems that are out of direct developer/tester control. The product is used in conjunction with hardware/OS virtualization to provide developers and testers with the resources they need to execute their development and testing tasks earlier, faster, or more completely. Its technologies for automating continuous testing are used as part of continuous delivery, continuous integration, and continuous release.

BlazeMeter is a continuous testing platform that was acquired in 2021 by Perforce Software, which is based in Minneapolis, Minnesota. It provides enterprise-level GUI functional testing, performance testing, API functional testing, mock services, test data management, API monitoring, and reporting.

BuildMaster is an application release automation tool, designed by the software development team Inedo. It combines build management and ARA capabilities to manage and automate processes primarily related to continuous integration, database change scripts, and production deployments, overall releasing applications reliably. The tool is browser-based and able to be used "out-of-the-box". Its feature set and scope puts it in line with the DevOps movement, and is marketed as "more than a release automatigs together the people, processes, and practices that allow teams to deliver software rapidly, reliably, and responsibly.” It's a tool that embodies incremental DevOps adoption.
XebiaLabs is an independent software company specializing in DevOps and continuous delivery for large enterprise organizations. XebiaLabs offers a DevOps Platform for application-release automation (ARO). These components include release orchestration, deployment automation and DevOps intelligence.
Perforce Software, Inc. is an American developer of software used for developing and running applications, including version control software, web-based repository management, developer collaboration, application lifecycle management, web application servers, debugging tools, platform automation, and agile planning software.
DBmaestro is a computer software company with sales headquartered in Boston. It markets its services for DevOps collaboration between development and IT operations teams.
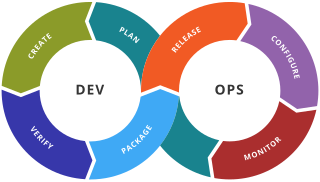
A DevOps toolchain is a set or combination of tools that aid in the delivery, development, and management of software applications throughout the systems development life cycle, as coordinated by an organisation that uses DevOps practices.

Tricentis is a software testing company founded in 2007 and headquartered in Austin, Texas. It provides software testing automation and software quality assurance products for enterprise software.






