The United States Navy, United States Coast Guard, and United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) use a hull classification symbol to identify their ships by type and by individual ship within a type. The system is analogous to the pennant number system that the Royal Navy and other European and Commonwealth navies use.

USS Biloxi (CL-80) was a United States Navy Cleveland-class light cruiser, the first ship named after the city of Biloxi, Mississippi.

USS Enterprise (CV-6) was a Yorktown-class carrier built for the United States Navy during the 1930s. She was the seventh U.S. Navy vessel of that name. Colloquially called "The Big E", she was the sixth aircraft carrier of the United States Navy. Launched in 1936, she was one of only three American carriers commissioned before World War II to survive the war. She participated in more major actions of the war against Japan than any other United States ship. These actions included the attack on Pearl Harbor — 18 Douglas SBD Dauntless dive bombers of her Air Group arrived over the harbor during the attack; seven were shot down with eight airmen killed and two wounded, making her the only American aircraft carrier with men at Pearl Harbor during the attack and the first to sustain casualties during the Pacific War — the Battle of Midway, the Battle of the Eastern Solomons, the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands, various other air-sea engagements during the Guadalcanal Campaign, the Battle of the Philippine Sea, and the Battle of Leyte Gulf. Enterprise earned 20 battle stars, the most for any U.S. warship in World War II, and was the most decorated U.S. ship of World War II. She was also the first American ship to sink a full-sized enemy warship after the Pacific War had been declared when her aircraft sank the Japanese submarine I-70 on 10 December 1941. On three occasions during the war, the Japanese announced that she had been sunk in battle, inspiring her nickname "The Grey Ghost". By the end of the war, her planes and guns had downed 911 enemy planes, sunk 71 ships, and damaged or destroyed 192 more.

The fourth USS Princeton (CVL-23) was a United States Navy Independence-class light aircraft carrier active in the Pacific Ocean during World War II. She was launched in 1942 and lost at the Battle of Leyte Gulf in 1944.

USS Langley (CVL-27) was an Independence-class light aircraft carrier that served the United States Navy from 1943 to 1947, and French Navy as La Fayette from 1951 to 1963.

USS Independence (CVL-22) was a United States Navy light aircraft carrier. The lead ship of her class, she served during World War II.

USS Belleau Wood was a United States Navy Independence-class light aircraft carrier active during World War II in the Pacific Theater from 1943 to 1945. The ship also served in the First Indochina War under French Navy temporary service as Bois Belleau.

USS Cowpens (CV-25/CVL-25/AVT-1), nicknamed The Mighty Moo, was an 11,000-ton Independence-class light aircraft carrier that served the United States Navy from 1943 to 1947.

USS Cabot (CVL-28/AVT-3) was an Independence-class light aircraft carrier in the United States Navy, the second ship to carry the name. Cabot was commissioned in 1943 and served until 1947. She was recommissioned as a training carrier from 1948 to 1955. From 1967 to 1989, she served in Spain as Dédalo. After attempts to preserve her failed, she was scrapped in 2002.

The New York Shipbuilding Corporation was an American shipbuilding company that operated from 1899 to 1968, ultimately completing more than 500 vessels for the U.S. Navy, the United States Merchant Marine, the United States Coast Guard, and other maritime concerns. At its peak during World War II, NYSB was the largest and most productive shipyard in the world. Its best-known vessels include the destroyer USS Reuben James (DD-245), the cruiser USS Indianapolis (CA-35), the aircraft carrier USS Kitty Hawk (CV-63), the nuclear-powered cargo ship NS Savannah, and a quartet of cargo-passenger liners nicknamed the Four Aces.

USS Skipjack (SS-184), a Salmon-class submarine, was the second ship of the United States Navy to be named after the fish. Her keel was laid down by the Electric Boat Company in Groton, Connecticut, on 22 July 1936. She was launched on 23 October 1937 sponsored by Miss Frances Cuthbert Van Keuren, daughter of Captain Alexander H. Van Keuren, Superintending Constructor, New York Navy Yard. The boat was commissioned on 30 June 1938 with Lieutenant Herman Sall in command. She earned multiple battle stars during World War II and then was sunk, remarkably, by an atomic bomb during post-war testing. Among the most "thoroughly sunk" ships, she was refloated and then sunk a second time as a target ship two years later.

USS Mugford (DD-389), a Bagley-class destroyer, was the 2nd ship of the United States Navy to be named for James Mugford, who commanded the schooner Franklin in the Continental Navy, serving through 1775.

Operation Hailstone, 17–18 February 1944, was a massive United States Navy air and surface attack on Truk Lagoon conducted as part of the American offensive drive against the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) through the Central Pacific Ocean during World War II.

USS Wedderburn (DD-684), was a Fletcher-class destroyer of the United States Navy.

USS Porterfield (DD-682) was a Fletcher-class destroyer of the United States Navy. She was laid down by the Bethlehem Shipbuilding, San Pedro, California 12 December 1942; launched 13 June 1943; sponsored by Mrs Louis B. Porterfield and commissioned 30 October 1943, with Commander J. C. Woefel in command.
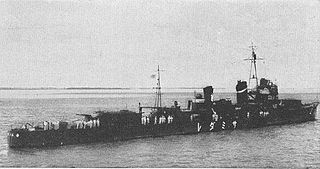
Samidare was the fifth of ten Shiratsuyu-class destroyers, built for the Imperial Japanese Navy under the Circle One Program.

Chitose (千歳) was a warship of the Imperial Japanese Navy that served from 1938 to 1944, seeing service as a seaplane carrier and later as a light aircraft carrier during World War II. In her initial guise as a seaplane carrier, she first saw service during the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1938, and subsequently played a key role in the Imperial Japanese Navy's development of a network of seaplane bases on the islands of the Pacific Ocean. After the outbreak of World War II in the Pacific, she took part in the Philippines campaign, the Dutch East Indies campaign, the Battle of Midway, and the Guadalcanal campaign, during which she was damaged in the Battle of the Eastern Solomons and also saw service related to the Battle of Cape Esperance.

Akashi was a Japanese repair ship, serving during World War II. She was the only specifically designed repair ship operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy. The navy based her design on the US Navy's USS Medusa.

Akitsushima (秋津洲) was a seaplane tender of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during World War II from 1942 until being sunk in September 1944.




















