
An optical attenuator, or fiber optic attenuator, is a device used to reduce the power level of an optical signal, either in free space or in an optical fiber. The basic types of optical attenuators are fixed, step-wise variable, and continuously variable.

In fiber-optic communication, a single-mode optical fiber (SMF), also known as fundamental- or mono-mode, is an optical fiber designed to carry only a single mode of light - the transverse mode. Modes are the possible solutions of the Helmholtz equation for waves, which is obtained by combining Maxwell's equations and the boundary conditions. These modes define the way the wave travels through space, i.e. how the wave is distributed in space. Waves can have the same mode but have different frequencies. This is the case in single-mode fibers, where we can have waves with different frequencies, but of the same mode, which means that they are distributed in space in the same way, and that gives us a single ray of light. Although the ray travels parallel to the length of the fiber, it is often called transverse mode since its electromagnetic oscillations occur perpendicular (transverse) to the length of the fiber. The 2009 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Charles K. Kao for his theoretical work on the single-mode optical fiber. The standards G.652 and G.657 define the most widely used forms of single-mode optical fiber.
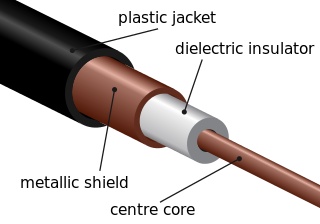
A transmission medium is a system or substance that can mediate the propagation of signals for the purposes of telecommunication. Signals are typically imposed on a wave of some kind suitable for the chosen medium. For example, data can modulate sound, and a transmission medium for sounds may be air, but solids and liquids may also act as the transmission medium. Vacuum or air constitutes a good transmission medium for electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves. While material substance is not required for electromagnetic waves to propagate, such waves are usually affected by the transmission media they pass through, for instance, by absorption or reflection or refraction at the interfaces between media. Technical devices can therefore be employed to transmit or guide waves. Thus, an optical fiber or a copper cable is used as transmission media.

Photonics is the physical science and application of light (photon) generation, detection, and manipulation through emission, transmission, modulation, signal processing, switching, amplification, and sensing. Though covering all light's technical applications over the whole spectrum, most photonic applications are in the range of visible and near-infrared light. The term photonics developed as an outgrowth of the first practical semiconductor light emitters invented in the early 1960s and optical fibers developed in the 1970s.

A ferrule is any of a number of types of objects, generally used for fastening, joining, sealing, or reinforcement. They are often narrow circular rings made from metal, or less commonly, plastic. Ferrules are also often referred to as eyelets or grommets within the manufacturing industry.
Liquid crystal on silicon is a miniaturized reflective active-matrix liquid-crystal display or "microdisplay" using a liquid crystal layer on top of a silicon backplane. It is also referred to as a spatial light modulator. LCoS was initially developed for projection televisions but is now used for wavelength selective switching, structured illumination, near-eye displays and optical pulse shaping. By way of comparison, some LCD projectors use transmissive LCD, allowing light to pass through the liquid crystal.

An optical table is a vibration control platform that is used to support systems used for laser- and optics-related experiments, engineering and manufacturing. The surfaces of these tables are designed to be very rigid with minimum deflection so that the alignment of optical elements remains stable over time. Many optical systems require that vibration of optical elements be kept small. As a result, optical tables are typically very heavy and incorporate vibration isolation and damping features in their structure. Many use pneumatic isolators that act as mechanical low-pass filters, reducing the ability of vibrations in the floor to cause vibrations in the tabletop.

A telescopic sight, commonly called a scope informally, is an optical sighting device based on a refracting telescope. It is equipped with some form of a referencing pattern – known as a reticle – mounted in a focally appropriate position in its optical system to provide an accurate point of aim. Telescopic sights are used with all types of systems that require magnification in addition to reliable visual aiming, as opposed to non-magnifying iron sights, reflector (reflex) sights, holographic sights or laser sights, and are most commonly found on long-barrel firearms, particularly rifles, usually via a scope mount. The optical components may be combined with optoelectronics to form a digital night scope or a "smart scope".

Cosina Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer of high-end optical glass, optical precision equipment, cameras, video and electronic related equipment, based in Nakano, Nagano Prefecture, Japan.

An optical fiber connector joins optical fibers, and enables quicker connection and disconnection than splicing. The connectors mechanically couple and align the cores of fibers so light can pass. Better connectors lose very little light due to reflection or misalignment of the fibers. In all, about 100 different types of fiber optic connectors have been introduced to the market.

An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber and find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths than electrical cables. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss; in addition, fibers are immune to electromagnetic interference, a problem from which metal wires suffer. Fibers are also used for illumination and imaging, and are often wrapped in bundles so they may be used to carry light into, or images out of confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope. Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety of other applications, some of them being fiber optic sensors and fiber lasers.

A mirror mount is a device that holds a mirror. In optics research, these can be quite sophisticated devices, due to the need to be able to tip and tilt the mirror by controlled amounts, while still holding it in a precise position when it is not being adjusted.

A fiber-optic cable, also known as an optical-fiber cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable, but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable is used. Different types of cable are used for different applications, for example, long distance telecommunication, or providing a high-speed data connection between different parts of a building.

The 5.45 mm subkarabinek wz. 1989 Onyks is a lightweight Polish carbine variant of the 5.45 mm wz. 1988 Tantal assault rifle, also based on the AKS-74U. Work on the weapon began in 1989 at the Ośrodek Badawczo-Rozwojowy state research institute in the city of Radom. The weapon’s technical specifications were confirmed that same year. It was not until 1990 that production approval was given for the first prototypes, evaluated the following year in a series of military qualification tests resulting in an order for an initial pre-production batch in 1993, to be manufactured at the Łucznik Arms Factory in Radom.
Optoform is an optical bench system or cage system that provides multiple opto-mechanical components that may be assembled in various configurations to construct a variety of optical instruments. Unlike traditional cubic optical systems, Optoform employs a concentric bore pattern that allows interconnection between mounts using rods along their optical axis, or at right angles via corner connectors. The circular patterns allow for easier assembly of optical components in a more natural fashion with other optical components, such as lenses. These bores could also utilize linear bearings, and micrometers for precise linear, and X-Y positioning of optical elements.

Translucent concrete is a concrete based building material with light-transmissive properties due to embedded light optical elements — usually optical fibers. Light is conducted through the stone from one end to the other. Therefore, the fibers have to go through the whole object. This results in a certain light pattern on the other surface, depending on the fiber structure. Shadows cast onto one side appear as silhouettes through the material.
In optical physics, laser detuning is the tuning of a laser to a frequency that is slightly off from a quantum system's resonant frequency. When used as a noun, the laser detuning is the difference between the resonance frequency of the system and the laser's optical frequency. Lasers tuned to a frequency below the resonant frequency are called red-detuned, and lasers tuned above resonance are called blue-detuned.

The term fine adjustment screw typically refers to screws with threads from 40 to 100 TPI and ultra fine adjustment screw has been used to refer to 100–508 TPI. Even though these are non-standard threads, both ISO metric screw thread designations and UNC designations have been used to call out thread dimensions and fit (class). A typical use for a fine adjustment screw is in an optical mirror mount as an adjuster. Typically 80 TPI screws are used in mirror mounts. Ultra fine adjuster screws are used in applications requiring extremely fine motion like laser alignment, fiber coupling.
Thorlabs, Inc. is an American privately held optical equipment company headquartered in Newton, New Jersey. The company was founded in 1989 by Alex Cable, who serves as its current president and CEO. As of 2018, Thorlabs has annual sales of approximately $500 million. Outside its multiple locations in the United States, the company has offices in Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, Japan, Sweden, and the United Kingdom. It sells approximately 20,000 different products.
In telecommunications, a line splice is a method of connecting electrical cables or optical fibers.
















