
A dye laser is a laser that uses an organic dye as the lasing medium, usually as a liquid solution. Compared to gases and most solid state lasing media, a dye can usually be used for a much wider range of wavelengths, often spanning 50 to 100 nanometers or more. The wide bandwidth makes them particularly suitable for tunable lasers and pulsed lasers. The dye rhodamine 6G, for example, can be tuned from 635 nm (orangish-red) to 560 nm (greenish-yellow), and produce pulses as short as 16 femtoseconds. Moreover, the dye can be replaced by another type in order to generate an even broader range of wavelengths with the same laser, from the near-infrared to the near-ultraviolet, although this usually requires replacing other optical components in the laser as well, such as dielectric mirrors or pump lasers.

A tunable laser is a laser whose wavelength of operation can be altered in a controlled manner. While all laser gain media allow small shifts in output wavelength, only a few types of lasers allow continuous tuning over a significant wavelength range.

Theodor Wolfgang Hänsch is a German physicist. He received one-third of the 2005 Nobel Prize in Physics for "contributions to the development of laser-based precision spectroscopy, including the optical frequency comb technique", sharing the prize with John L. Hall and Roy J. Glauber.

A solid-state laser is a laser that uses a gain medium that is a solid, rather than a liquid as in dye lasers or a gas as in gas lasers. Semiconductor-based lasers are also in the solid state, but are generally considered as a separate class from solid-state lasers, called laser diodes.
Amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) or superluminescence is light, produced by spontaneous emission, that has been optically amplified by the process of stimulated emission in a gain medium. It is inherent in the field of random lasers.
A fiber laser is a laser in which the active gain medium is an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements such as erbium, ytterbium, neodymium, dysprosium, praseodymium, thulium and holmium. They are related to doped fiber amplifiers, which provide light amplification without lasing.
Ormosil is a shorthand phrase for organically modified silica or organically modified silicate. In general, ormosils are produced by adding silane to silica-derived gel during the sol-gel process. They are engineered materials that show great promise in a wide range of applications such as:

Francisco Javier "Frank" Duarte is a laser physicist and author/editor of several books on tunable lasers.
Beam expanders are optical devices that take a collimated beam of light and expand its width.

The first description of multiple-prism arrays, and multiple-prism dispersion, was given by Newton in his book Opticks. Prism pair expanders were introduced by Brewster in 1813. A modern mathematical description of the single-prism dispersion was given by Born and Wolf in 1959. The generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory was introduced by Duarte and Piper in 1982.

Laser medicine is the use of lasers in medical diagnosis, treatments, or therapies, such as laser photodynamic therapy, photorejuvenation, and laser surgery.
Fritz Peter Schäfer was a German physicist, born in Hersfeld, Hesse-Nassau. He is the co-inventor of the organic dye laser. His book, Dye Lasers, is considered a classic in the field of tunable lasers. In this book the chapter written by Schäfer gives an ample and insightful exposition on organic laser dye molecules in addition to a description on the physics of telescopic, and multiple-prism, tunable narrow-linewidth laser oscillators.
A solid-state dye laser (SSDL) is a solid-state lasers in which the gain medium is a laser dye-doped organic matrix such as poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), rather than a liquid solution of the dye. These lasers are also referred to as solid-state organic lasers and solid-state dye-doped polymer lasers.
Gas in scattering media absorption spectroscopy (GASMAS) is an optical technique for sensing and analysis of gas located within porous and highly scattering solids, e.g. powders, ceramics, wood, fruit, translucent packages, pharmaceutical tablets, foams, human paranasal sinuses etc. It was introduced in 2001 by Prof. Sune Svanberg and co-workers at Lund University (Sweden). The technique is related to conventional high-resolution laser spectroscopy for sensing and spectroscopy of gas, but the fact that the gas here is "hidden" inside solid materials give rise to important differences.

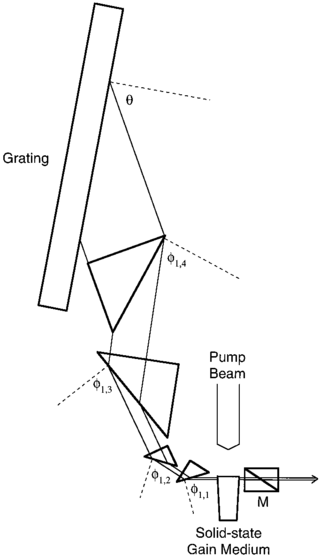
Multiple-prism grating laser oscillators, or MPG laser oscillators, use multiple-prism beam expansion to illuminate a diffraction grating mounted either in Littrow configuration or grazing-incidence configuration. Originally, these narrow-linewidth tunable dispersive oscillators were introduced as multiple-prism Littrow (MPL) grating oscillators, or hybrid multiple-prism near-grazing-incidence (HMPGI) grating cavities, in organic dye lasers. However, these designs were quickly adopted for other types of lasers such as gas lasers, diode lasers, and more recently fiber lasers.
Laser linewidth is the spectral linewidth of a laser beam.
A liquid-crystal laser is a laser that uses a liquid crystal as the resonator cavity, allowing selection of emission wavelength and polarization from the active laser medium. The lasing medium is usually a dye doped into the liquid crystal. Liquid-crystal lasers are comparable in size to diode lasers, but provide the continuous wide spectrum tunability of dye lasers while maintaining a large coherence area. The tuning range is typically several tens of nanometers. Self-organization at micrometer scales reduces manufacturing complexity compared to using layered photonic metamaterials. Operation may be either in continuous wave mode or in pulsed mode.
Organic photorefractive materials are materials that exhibit a temporary change in refractive index when exposed to light. The changing refractive index causes light to change speed throughout the material and produce light and dark regions in the crystal. The buildup can be controlled to produce holographic images for use in biomedical scans and optical computing. The ease with which the chemical composition can be changed in organic materials makes the photorefractive effect more controllable.

The International Conference on Lasers and Applications, Lasers 'XX was an annual conference organized by the former Society for Optical and Quantum Electronics. The conference, known in short by Lasers 'XX, was held at various locations in The United States from 1978 to 2000.

Organic photonics includes the generation, emission, transmission, modulation, signal processing, switching, amplification, and detection/sensing of light, using organic optical materials.









