Performance management (PM) is the process of ensuring that a set of activities and outputs meets an organization's goals in an effective and efficient manner. Performance management can focus on the performance of a whole organization, a department, an employee, or the processes in place to manage particular tasks. Performance management standards are generally organized and disseminated by senior leadership at an organization and by task owners, and may include specifying tasks and outcomes of a job, providing timely feedback and coaching, comparing employees' actual performance and behaviors with desired performance and behaviors, instituting rewards, etc. It is necessary to outline the role of each individual in the organization in terms of functions and responsibilities to ensure that performance management is successful.
Intellectual capital is the result of mental processes that form a set of intangible objects that can be used in economic activity and bring income to its owner (organization), covering the competencies of its people, the value relating to its relationships, and everything that is left when the employees go home, of which intellectual property (IP) is but one component. It is the sum of everything everybody in a company knows that gives it a competitive edge. The term is used in academia in an attempt to account for the value of intangible assets not listed explicitly on a company's balance sheets. On a national level, intellectual capital refers to national intangible capital (NIC).
Strategic planning is an organization's process of defining its strategy or direction, and making decisions on allocating its resources to attain strategic goals.
The reputation of a social entity is an opinion about that entity typically as a result of social evaluation on a set of criteria, such as behavior or performance.
Business performance management (BPM), also known as corporate performance management (CPM) and enterprise performance management (EPM),) is a set of performance management and analytic processes that enables the management of an organization's performance to achieve one or more pre-selected goals. Gartner retired the concept of "CPM" and reclassified it as "financial planning and analysis (FP&A)," and "financial close" to reflect two concepts: increased focus on planning and the emergence of a new category of solutions supporting the management of the financial close.
A balanced scorecard is a strategy performance management tool – a well structured report, that can be used by managers to keep track of the execution of activities by the staff within their control and to monitor the consequences arising from these actions.

A performance indicator or key performance indicator (KPI) is a type of performance measurement. KPIs evaluate the success of an organization or of a particular activity in which it engages. KPIs provide a focus for strategic and operational improvement, create an analytical basis for decision making and help focus attention on what matters most.
In management, business value is an informal term that includes all forms of value that determine the health and well-being of the firm in the long run. Business value expands concept of value of the firm beyond economic value to include other forms of value such as employee value, customer value, supplier value, channel partner value, alliance partner value, managerial value, and societal value. Many of these forms of value are not directly measured in monetary terms.
Social return on investment (SROI) is a principles-based method for measuring extra-financial value. It can be used by any entity to evaluate impact on stakeholders, identify ways to improve performance, and enhance the performance of investments.
Supplier relationship management (SRM) is the systematic, enterprise-wide assessment of suppliers’ strengths, performance and capabilities with respect to overall business strategy, determination of what activities to engage in with different suppliers, and planning and execution of all interactions with suppliers, in a coordinated fashion across the relationship life cycle, to maximize the value realized through those interactions. The focus of SRM is to develop two-way, mutually beneficial relationships with strategic supply partners to deliver greater levels of innovation and competitive advantage than could be achieved by operating independently or through a traditional, transaction purchasing arrangement. Underpinning disciplines which support effective SRM includes supplier information management, compliance, risk management and performance management.
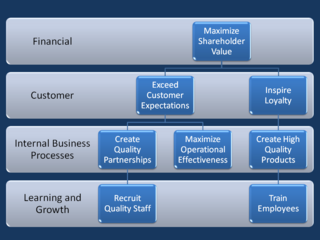
A strategy map is a diagram that documents the strategic goals being pursued by an organization or management team. It is an element of the documentation associated with the Balanced Scorecard, and in particular is characteristic of the second generation of Balanced Scorecard designs that first appeared during the mid-1990s. The first diagrams of this type appeared in the early 1990s, and the idea of using this type of diagram to help document Balanced Scorecard was discussed in a paper by Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton in 1996.
Organizational effectiveness is a concept organizations use to gauge how effective they are at reaching intended outcomes. Organizational effectiveness embodies the degree to which firms achieve the goals they have decided upon, a question that draws on several different factors. Among those are talent management, leadership development, organization design and structure, design of measurements and scorecards, implementation of change and transformation, deploying smart processes and smart technology to manage the firms' human capital and the formulation of the broader Human Resources agenda.

Performance measurement is the process of collecting, analyzing and/or reporting information regarding the performance of an individual, group, organization, system or component.

Internal auditing is an independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization's operations. It helps an organization accomplish its objectives by bringing a systematic, disciplined approach to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk management, control and governance processes. Internal auditing might achieve this goal by providing insight and recommendations based on analyses and assessments of data and business processes. With commitment to integrity and accountability, internal auditing provides value to governing bodies and senior management as an objective source of independent advice. Professionals called internal auditors are employed by organizations to perform the internal auditing activity.
IT portfolio management is the application of systematic management to the investments, projects and activities of enterprise Information Technology (IT) departments. Examples of IT portfolios would be planned initiatives, projects, and ongoing IT services. The promise of IT portfolio management is the quantification of previously informal IT efforts, enabling measurement and objective evaluation of investment scenarios.
Strategic planning software is a category of software that covers a wide range of strategic topics, methodologies, modeling and reporting.
In business performance management, a third-generation balanced scorecard is a version of the traditional balanced scorecard, a structured report, supported by proven design methods and automated tools, that can be used by managers to keep track of the execution of activities by the staff within their control, and to monitor the consequences arising from these actions.

Sustainability accounting was originated about 20 years ago and is considered a subcategory of financial accounting that focuses on the disclosure of non-financial information about a firm's performance to external stakeholders, such as capital holders, creditors, and other authorities. Sustainability accounting represents the activities that have a direct impact on society, environment, and economic performance of an organisation. Sustainability accounting in managerial accounting contrasts with financial accounting in that managerial accounting is used for internal decision making and the creation of new policies that will have an effect on the organisation's performance at economic, ecological, and social level. Sustainability accounting is often used to generate value creation within an organisation.
GQM+Strategies is a method that provides concepts and actionable steps for creating the link between goals and strategies across an organization and allows for measurement-based decision-making. It was developed by Victor Basili, Jens Heidrich, Mikael Lindvall, Jürgen Münch, Myrna Regardie, Carolyn B. Seaman, and Adam Trendowicz. The method was originally developed for organizations having a strong focus on IT and the development of software systems, but the method's popularity has grown to other domains and can be applied to any organization. The book Aligning Organizations through Measurement gives a comprehensive overview of the method, provides actionable guidance, case studies, and practical applications.
Management accounting in supply chains is part of the supply chain management concept. This necessitates planning, monitoring, management and information about logistics and manufacturing processes throughout the value chain. The goal of management accounting in supply chains is optimizing these processes. This strategy focuses on supporting management.





